LCS-SR-0090 System Safety Hazards Analysis for non
advertisement

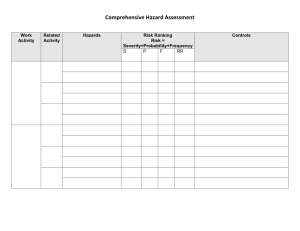
SUBCONTRACTOR DATA REQUIREMENT DESCRIPTION 1. SDRL NO: LCS-SR-0090 2. SDRL TITLE: SYSTEM SAFETY HAZARDS ANALYSIS for NON-COTS ITEMS 3. FREQUENCY: N/A 4. 1ST SUBMITTAL: SYSTEM SAFETY APPROACH TO BE PROVIDED WITH VENDOR’S PROPOSAL 5. SUB. SUBMITTALS: A HAZARD ANALYSIS REPORT 30 DAPO 30 DARC 30 DAYS AFTER A DESIGN CHANGE IS MADE TO THE ITEM 6. DISTRIBUTION TOTAL: N/A 7. REMARKS: This SDRL applies to equipment systems built for LCS that contain major components (such as pumps, valves, limit switches, motor, cut-outs). 8. REFERENCES: MIL-STD-882D System Safety Analysis Handbook. Unionville, VA: System Safety Society. 9. SYSTEM SAFETY APPROACH: A description of the Offeror's system safety approach and methods to accomplish a system safety program IAW Mil-Std-882D shall be included in the Offeror's technical proposal. The description shall include the information contained in the following instructions. INSTRUCTIONS: Include a description of your proposed methods of assessment of system safety. Describe your approach to integrating system safety into the design of the product. Identify the area within the Offeror's organization that will implement the system safety program. Describe its functional interrelationship within the Offeror's overall organization. 10. HAZARD ANALYSIS REPORT: A Hazard Analysis Report must be submitted which includes the following: 10.1.1 System Description. This will consist of detailed descriptions of the physical and functional characteristics of applicable system components. The capabilities, limitations and interdependence of these components shall be expressed in terms relevant to safety. The system and components shall be addressed in relation to its mission and its operational environment. System block diagrams and/or functional flow diagrams may be used to clarify system descriptions. 10.1.2 Data. This will consist of summaries of data used to determine the safety aspects of design features. 10.1.3 Hazard Analysis Results. This will consist of a summary and/or a total listing of the results of hazard analysis. Contents and formats may vary according to the individual requirements of this program. 10.2 Following are the minimum content and format requirements for Hazard Analysis Results: 10.2.1 PRELIMINARY HAZARD ANALYSIS (PHA) REPORT. The PHA is used to identify hazards based on system concepts, inherent known hazards, and is usually qualitative in nature. A PHA report shall include: a. A summary of the results. b. A listing of identified hazards by system/subsystem/unit to include the following information: (1) System/Subsystem/Unit. Enter the particular part of the system that this phase of analysis is concerned with. For example, if this item (or items) applies to a radar system modulator, enter “modulator”. If there are several modulators in the system, be sure and clearly specify which one the analysis pertains to. (2) System Event(s) Phase. The configuration, or phase of the mission of the system, when the hazard is encountered; for example, during maintenance, during flight, during pre-flight, full-power applied, etc. or is it encountered in all system events. (3) Hazard Description. A brief description of the hazard; for example, “Radiation leakage from radar set wave guide.” (4) Effect on System. The detrimental results an uncontrolled hazard source could inflict on the system or personnel. (5) Risk Assessment. An assigned risk assessment for each hazard as defined in MIL-STD-882D. (6) Recommended Action. A technical description of the recommended action to eliminate or control the hazard, for example, detailed design criteria, possible protective devices or special procedures. Include alternative designs and cost impact where appropriate. (7) Effect of Recommended Action. The effect of the recommended action on the assigned risk assessment. (8) Remarks. Any information relating to the hazard not covered in the other blocks; for example, applicable documents, previous failure data on similar systems or administrative directions. (9) Status. The status of actions to implement the recommended, or other, hazard controls. 10.2.2 SUBSYSTEM HAZARD ANALYSIS (SSHA) REPORT. The SSHA is used to determine the functional relationships of components and equipment comprising each subsystem and identifies all components whose performance degradation or functional failure could result in hazardous conditions. The SSHA report shall include: a. A summary of the results. b. A listing of identified hazards to include the following information: c. (1) Component failure modes which can result in a hazard. Failure modes which can result in a hazard. Failure modes generally answer the question of “how” it fails. (2) System Event(s) Phase. The configuration or phase of the mission the system is in when the hazard is encountered. (3) Hazard Description. A complete description of the hazard. (4) Effect on Subsystem. The detrimental results an uncontrolled hazard source could inflict. Possible upstream and downstream effects shall also be considered. (5) Risk Assessment. An assigned risk assessment for each hazard as defined in MIL-STD-882D, for severity and probability of occurrence. (6) Recommended Action. The recommended action required to eliminate or control the hazard. Include alternatives where appropriate. Sufficient technical detail is required in order to permit the design engineers and the customer to adequately develop and assess design criteria resulting from the analysis. (7) Effect of Recommended Action. The effect of the recommended action on the assigned risk assessment. (8) Remarks. Any information relating to the hazard not covered in the other blocks; for example, applicable documents, previous failure data in similar systems, or administrative directions. (9) Status. The status of actions to implement the recommended, or other, hazard controls. Specific analysis techniques which may be used in the course of performing a SSHA are listed below. Reports for these techniques will follow format and content requirements as contractually defined. (1) Fault Hazard Analysis. (2) Fault-Tree Analysis. (3) Sneak Circuit Analysis. (4) Other 10.2.3 SYSTEM HAZARD ANALYSIS (SHA) REPORT. The SHA defines the safety interfaces between subsystems to identify safety problem areas for the combined system. The SHA report shall include: a. A summary of the results. b. A listing of identified hazards to include the following information: c. (1) Subsystem Failure Mode(s). The subsystem failure mode description from SHA are similar to the component descriptions provided in the SSHA. However, emphasis is not placed on failures affecting interfacing subsystem operations. (2) System Event(s) Phase. The configuration or phase of the mission the system is in when the hazard is encountered. (3) Hazard Description. A complete description of the hazard. (4) Effect of System. The detrimental results an uncontrolled hazard source could inflict. Possible upstream and downstream effects shall also be considered. (5) Risk Assessment. An assigned risk assessment for each hazard as defined in MIL-STD-882D classification for severity and probability of occurrence. (6) Recommended Action. The recommended action required to eliminate or control the hazard. Include alternatives where appropriate. Sufficient technical detail is required in order to permit the design engineers and the customer to adequately develop and assess design criteria resulting from the analysis. (7) Effect of Recommended Action. The effect of the recommended action on the assigned risk assessment. (8) Remarks. Any information relating to the hazard not covered in the other blocks; for example, applicable documents, previous failure data in similar systems, or administrative directions. (9) Status. The status of actions to implement the recommended, or other, hazard controls. Specific analysis techniques which may be used in the course of performing a SHA are listed below. Reports for these techniques will follow format and content requirements as contractually defined. (1) Fault Hazard Analysis. (2) Fault-Tree Analysis. (3) Sneak Circuit Analysis. (4) Other 10.2.4 OPERATING AND SUPPORT HAZARD ANALYSIS (O&S)HA REPORT. An (O&S)HA is performed to identify and control hazards and determine safety requirements for personnel, procedures and equipment used in all phases of intended use. The (O&S)HA Report shall include: a. A summary of the results. b. A listing of identified hazards to include the following information: (1) System Component/Phase. The particular phase/component that analysis is concerned with. This could be a system, subsystem component, operating/maintenance procedure or environmental condition. (2) System Description. A description of what is normally expected to occur as the result of operating the component/subsystem or performing the operating/maintenance action. (3) Hazard Description. A complete description of the potential/actual hazards resulting from the normal actions or equipment failures. (4) Hazard Identification/Indication. A description of crew indications which include all means of identifying the hazard to operational/maintenance personnel. (5) Effect on System. The detrimental results an uncontrolled hazard could inflict on the system. (6) Risk Assessment. An assigned risk assessment for each hazard as defined in MIL-STD-882D, for a classification of severity and probability of occurrence. (7) Recommended Action. The recommended action required to eliminate or control the hazard. Include alternatives where appropriate. Sufficient technical detail is required in order to permit the design engineers and the customer to adequately develop and assess design criteria resulting from the analysis. (8) Effect of Recommended Action. The effect of the recommended action on the assigned risk assessment. If the recommended action will result in cost/schedule/performance penalties to the extent that the Supplier requires Buyer approval prior to incorporation, then these considerations shall be addressed. (9) Remarks. Any information relating to the hazard not covered in the other blocks; for example, applicable documents, previous failure data in similar systems, or administrative directions. (10) Status. The status of actions to implement the recommended, or other, hazard controls. (11) Caution and Warning Notes. A complete list of specific warnings, cautions and procedures required in operating and maintenance manuals and for training courses.