Outline - Chondrichthyes lectures:

Outline - Chondrichthyes lectures:
PP SLIDE 1: Geologic time line. Shark ancestors (380-450 million years ago)
PP SLIDE 2: Patterns of vertebrate diversification through time: http://www.devoniantimes.org/who/pages/sharks.html
PP SLIDE 3: Chondrichthyes diversity: http://www.mesa.edu.au/seaweek2005/images/sharks_montage.jpg
PP SLIDE 4: Phylogeny: http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://wwwpersonal.umich.edu/~pwebb/NRE422-BIO440/elasclad.gif&imgrefurl=http://wwwpersonal.umich.edu/~pwebb/NRE422-
BIO440/lec05.html&h=317&w=536&sz=4&hl=en&start=1&tbnid=TSa2-Eh-
T8n9aM:&tbnh=78&tbnw=132&prev=/images%3Fq%3Delasmobranch%2Bphylogeny%
26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DG
PP SLIDE 5: Lateral view of shark skull: red = jaws (upper jaw: palatoquadrate; lower jaw: Meckelian cartilage), green = gill arches; blue = olfactory bulbs. http://www.usm.maine.edu/bio/courses/bio205/gnathostome_skull.gif
PP SLIDE 6: Phylogeny: http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://wwwpersonal.umich.edu/~pwebb/NRE422-BIO440/elasclad.gif&imgrefurl=http://wwwpersonal.umich.edu/~pwebb/NRE422-
BIO440/lec05.html&h=317&w=536&sz=4&hl=en&start=1&tbnid=TSa2-Eh-
T8n9aM:&tbnh=78&tbnw=132&prev=/images%3Fq%3Delasmobranch%2Bphylogeny%
26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DG
PP SLIDE 7: Elasmobranch phylogeny: http://www.elasmoresearch.org/education/classification/class_images/galea_squalea.gif
PP SLIDE 8: Phylogeny we will use for Chondrichthyes (Holocephalii)((Galea,
Squalea)Batoidea)). The Holocephali are primitive, the batoids are monophyletic, and sharks are placed into two groups Galea and Squalea which are presumed to be close relatives. Draw this tree so you have it for your notes
PP SLIDE 9: Mating sharks: http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Mating_in_sharks.jpg
PP SLIDE 10: Claspers in male sharks: http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fish/education/questions/claspers.jpg
PP SLIDE 11: Egg cases and embryos: http://www.mlssa.asn.au/nletters/Image256.gif; http://www.elasmodiver.com/Sharkive%20images/Big%20Skate%20Egg%20Case%2000
2.jpg; http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.seaworld.org/infobooks/Sharks%26
Rays/images/viviparous.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.seaworld.org/infobooks/Sharks%26R
ays/reproduction.html&h=202&w=300&sz=19&hl=en&start=4&um=1&tbnid=u8vFYG
QPSL5RGM:&tbnh=78&tbnw=116&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dviviparous%2Bshark%2Be mbryos%26svnum%3D10%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DG
PP SLIDE 12: Phylogeny we will use for Chondrichthyes (Holocephalii)((Galea,
Squalea)Batoidea)). The Holocephali are primitive, the batoids are monophyletic, and sharks are placed into two groups Galea and Squalea which are presumed to be close relatives. Draw this tree so you have it for your notes
PP SLIDE 13: Chimeras: http://www.glaucus.org.uk/Rabbit.JPG; http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a5/Elephant_shark_melb_aqua rium.jpg/800px-Elephant_shark_melb_aquarium.jpg; http://www.elasmoresearch.org/artists/fleetham/ratfish.jpg
PP SLIDE 14: Holocephali: Gills covered by an operculum; one opening on each side of the head; lack spiracle; Palatoquadrate (upper jaw) fused to cranium; Branchial basket ventral to neurocranium; Teeth are mineralized grinding plates (4 upper and 2 lower teeth); replaced slowly; Skin lacks denticles; Ribs absent; Stomach absent; Males with pelvic & cephalic claspers; eggs in cases
PP SLIDE 15: Phylogeny we will use for Chondrichthyes (Holocephalii)((Galea,
Squalea)Batoidea)). The Holocephali are primitive, the batoids are monophyletic, and sharks are placed into two groups Galea and Squalea which are presumed to be close relatives. Draw this tree so you have it for your notes
PP SLIDE 16: Elasmobranchs: http://biology.unm.edu/ccouncil/Biology_203/Summaries/Deuterostomes.htm
PP SLIDE 17: Porbeagle shark skeleton: http://www.marinebiodiversity.ca/shark/english/images/porbeagle%20skeleton%20for%2
0web.jpg
PP SLIDE 18: Cartilagnious skeletons; fortified in jaws & vertebrae by tesserae - hexagonal plates of calcium salts; Teeth are problematic; most abundant elasmobranch fossils’ Denticles in skin form a type of exoskeleton; muscles attach to skin; Gill slits (5-
7) lateral in galeans & squaleans, ventral in batoids; spiracle behind eye or on upper body surface; Osmoregulation accomplished through concentration of urea and trimethylamine oxide in the tissues
PP SLIDE 19: Dogfish internal anatomy: www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Chondrichthyes.htm
PP SLIDE 20: Skate internal anatomy: http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.elasmoresearch.org/education/topics/topic_images/manta_feeding_struct.gif&imgrefurl=http://w ww.elasmo-
research.org/education/topics/lh_manta_faq.htm&h=331&w=483&sz=25&hl=en&start=
33&tbnid=wXeSqgVqM7hmDM:&tbnh=88&tbnw=129&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dshark
%2Bclaspers%26start%3D20%26gbv%3D2%26ndsp%3D20%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3
Den%26sa%3DN
PP SLIDE 21: Male and female internal anatomy: http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.daviddarling.info/images/shark_an atomy.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/F/fish.html&h=448&w
=385&sz=69&hl=en&start=151&tbnid=816aeg9f65iO4M:&tbnh=127&tbnw=109&prev
=/images%3Fq%3Dshark%2Bskull%26start%3D140%26gbv%3D2%26ndsp%3D20%26 svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DN
PP SLIDE 22: Brains: http://cache.eb.com/eb/image?id=63581&rendTypeId=4
PP SLIDE 23: Lateral view of shark head showing neuromasts and Ampullae of
Lorenzini: www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Chondrichthyes.htm
PP SLIDE 24: Lateral view of head showing Ampullae of Lorenzini: www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Chondrichthyes.htm
PP SLIDE 25: Shark catching seal: http://img.dailymail.co.uk/i/pix/2006/11/shark191106_468x397.jpg
PP SLIDE 26: Basking shark: http://www.gla.ac.uk/centres/marinestation/graphics/basking_shark_feeding_425.jpg
PP SLIDE 27: Great White Shark & Prey: http://www.untamed.com/images/large/002826-SB1.jpg
PP SLIDE 28: Filter feeders: Whale Shark: http://www.travelyucatan.com/whale_shark_holbox/whale_shark_isla_holbox_food.php
Rays: http://mozmarinescience.googlepages.com/mantarayresearch
PP SLIDE 29: Filter feeding in elasmobranchs:
Evolved during early-mid Tertiary in 4 lineages
Whale sharks (carpet shark lineage - Orectolobiformes)
Megamouth Shark (mackerel shark - Lamiformes)
Basking Shark (mackerel shark - Lamiformes)
Devil Rays and Manta Rays (stingrays - Myliobatiformes)
Enormous animals with terminal mouths, reduced dentition, gill rakers (plankton sieves);
Baleen whales evolved during same time period; Two elasmobranch mechanisms: gill raker method (Basking Shark & Megamouth) & spongy horizontal plates (whale shark, rays)
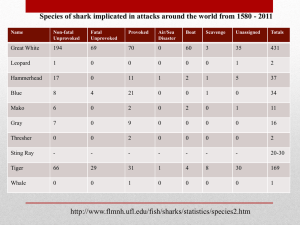
PP SLIDE 30: Shark Attacks http://www.pelagic.org/research/pics/shark_bite.jpg; http://users.aber.ac.uk/sac5/images/rodneyfox.jpg; http://www.calnaturalist.com/images/shark_1.jpg; http://aussie_news_views.typepad.com/aussie_news_views/images/shark_attack.jpg
PP SLIDE 31: Feeding frenzy:
Whale Sharks: http://www.mcss.sc/images/Newsletter/feeding_frenzy_2.jpg
Gray Reef Sharks: http://www.ecoscene.com/graphics/ec_im257.jpg
PP SLIDE 32: Geologic time line: First Major Radiation of sharks in Carboniferous
PP SLIDE 33: Early sharks:
Ctenacanthus - Late Devonian/Early Carboniferous: http://www.devoniantimes.org/who/pages/sharks.html
Stenacanthus - Carboniferous shark: http://www.hmnh.org/archives/category/chordates/sharks
PP SLIDE 34: Fossil Sharks: Akmonistion and Falcatus http://www.hmnh.org/archives/category/chordates/sharks
PP SLIDE 35: Time Line - Shark diversity high during Carboniferous (45 families compared to 40 families today).
PP SLIDE 36: Time line: Major extinction event at end of Permian (250 mya); 99% of all marine species, including Stentharcid sharks went extinct.
PP SLIDE 37: Time Line: Second radiation of sharks during Jurassic (208-144 mya); ancestors of modern sharks evolved during Jurassic
PP SLIDE 38: Hybodus was an early Jurassic shark; may be ancestor of living sharks: http://www.devoniantimes.org/who/pages/sharks.html
PP SLIDE 39: Early fossil sharks: Mcmurdodus and Paleospinax : http://www.elasmo-research.org/education/evolution/origin_modern.htm
PP SLIDE 40: Time Line: Rapid radiation and by mid-Cretaceous (100 mya), modern sharks were extant; opportunistic feeders on bony fish
PP SLIDE 41: Time Line: Cretaceous extinction event; wiped out hybodonts.
PP SLIDE 42: Phylogeny we will use for Chondrichthyes (Holocephalii)((Galea,
Squalea)Batoidea)). The Holocephali are primitive, the batoids are monophyletic, and sharks are placed into two groups Galea and Squalea which are presumed to be close relatives. Draw this tree so you have it for your notes
PP SLIDE 43: Elasmobranch teeth: tooth growth direction: www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Chondrichthyes.htm; http://www.sharkking.com/files/Tawney_Teeth.JPG
PP SLIDE 44: Shark Tail shapes: http://www.nhm.ac.uk/nature-online/life/reptilesamphibians-fish/fathomseminar-jaws/session1/no-fish-fathomseminar-jaws-session1.html
PP SLIDE 45: Pilot fish & shark: http://www.oonasdivers.com/diary_mikeward_liveaboard.shtml
Remora & shark: http://www.ryanphotographic.com/gcuvier.htm
PP SLIDE 46: Galea:
Variety of sharks; Nocturnally active predators; ontogenetic feeding shifts; Eggs laid in cases; 5-12 months pre-hatching; Apex predators; many dangerous to humans; Two families have species that retain metabolic heat; Shortfin Mako fastest shark (56 km/hr)
PP SLIDE 47: Carpet Shark (Orectolobiformes) examples: http://www.treasuresofthesea.org.nz/uploads/images/138_image_main.jpg http://www.sharkattackphotos.com/Wobbegong-shark.jpg
PP SLIDE 48: Examples of Carpet Sharks: Whale shark: http://scienceblogs.com/deepseanews/2007/04/whale_sharks_do_it_deeper.php
Zebra Shark: http://animalworld.com/encyclo/marine/sharks_rays/images/ZebraSharkWMS_C920.jpg
Nurse Shark: http://www.elasmodiver.com/Sharkive%20images/Nurse-shark013.jpg
Epaulette Shark: http://www.reefed.edu.au/__data/assets/image/0005/17159/epaulette.jpg
PP SLIDE 49: Frillshark: http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2007/01/photogalleries/frilledshark/images/primary/frillshark-big-2.jpg
PP SLIDE 50: Sawshark: http://www.discoverychannel.co.uk/sharks/detail/sixgill/index.shtml
PP SLIDE 51: Squaliform sharks (member of the Squaliformes) = Dogfish sharks; high species richness; Dwarf Lanternshark ( Etmopterus perryi ): http://www.elasmoresearch.org/education/shark_profiles/profile-images/squal/e_perryi.gif; Greenland
Shark: http://shopping.requins.free.fr/img/squ_lat.jpg; Spined Pygmy Shark, Squaliolus laticaudus : http://shopping.requins.free.fr/img/squ_lat.jpg
Spiny Dogfish: Squalus acanthias : http://www.sharkinfo.ch/images/fs/squalusa.jpg
PP SLIDE 52: Cookie Cutter Shark http://vivaldi.zool.gu.se/Fiskfysiologi_2001/Course_material/Introduction_fish_evolution
/Images/Cookie_cutters.GIF
PP SLIDE 53: Cookie Cutter Shark Bites: http://farm1.static.flickr.com/45/120509885_16121edb91.jpg
PP SLIDE 54: Phylogeny we will use for Chondrichthyes (Holocephalii)((Galea,
Squalea)Batoidea)). The Holocephali are primitive, the batoids are monophyletic, and sharks are placed into two groups Galea and Squalea which are presumed to be close relatives. Draw this tree so you have it for your notes
PP SLIDE 55: Batoids:
Dorsoventrally flattened bodies with expanded pectoral fins; Evolved during the Jurassic radiation of elasmobranchs; Mostly benthic, but some (e.g., eagle ray, manta ray) are powerful swimmers; Stingrays appeared during late Cretaceous and became widespread during the Tertiary; invaded freshwater systems
PP SLIDE 56: Batoid fossil: http://www.orecart.com/images/Stinger.gif
PP SLIDE 57: Swimming in batoids: Rajiform swimming: http://releeps.tripod.com/cgibin/stingray.jpg
Tail propulsion (guitarfish): http://www.deepseaimages.com/dsilibrary/showphoto.php?photo=10157
PP SLIDE 58: Barndoor skate: http://www.dkimages.com/discover/previews/1545/11719724.JPG
PP SLIDE 59: Stingray: http://swimatyourownrisk.com/wordpress/wpcontent/uploads/2007/01/stingray.jpg
PP SLIDE 60: Skate & ray example: www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Chondrichthyes.htm
PP SLIDE 61: River Stingray: http://www.elasmodiver.com/Sharkive%20images/Potamotrygon%20schroederi%20004.j
pg
PP SLIDE 62: Electric organ in Torpedo (from Hickman et al. 1994): www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Chondrichthyes.htm
PP SLIDE 63 - Torpedo rays: http://www.hms.harvard.edu/bss/neuro/cohen/torpedo.jpg http://www.gulfspecimen.org/images/disected-ray-2.jpg
PP SLIDE 64: Sawfish: http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fish/education/questions/sawfish1.jpg
PP SLIDE 65: Batoids: http://infolab.stanford.edu/~widom/photos/stingray.jpg http://www.malbertphoto.com/mobula_images/mobula2b.jpg
PP SLIDE 66: Manta Ray: http://library.thinkquest.org/5512/MantaRay.gif
PP SLIDE 67: shark finning: http://www.sharktrust.org/Uploads/1018/SHARKFI8crop.jpg