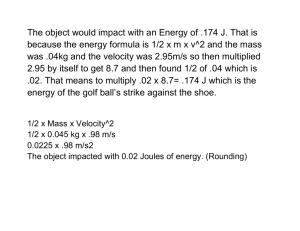Chapter 9 Motion Kathy Briggs

Chapter 9 Motion
Kathy Briggs
Describing Motion (pp. 309-310)
Complete the following sentences:
1. An object is in ______________________ when the distance from another object is changing.
2. An object is in motion if it changes position relative to a _______________________ .
Read this article from the NASA website, Ask an
Astrophysicist:
Suppose you are in a car traveling down the road. How can you tell how fast you are going? The speedometer tells you how fast your wheels are turning, but you could be standing dead still, spinning your wheels trying to get off a patch of ice, so put black tape over the speedometer. The car vibrates because it's working so hard, not necessarily because it's moving, so get a solidly built car that doesn't vibrate, and use a vibration absorbing seat cushion so you can't feel anything. The air whips noisily past your window as you drive through it, or maybe you're sitting still in a windstorm (was that a cow flying by?), use earplugs so that doesn't distract you. Outside you can see the scenery whizzing by, but it's actually a rear-projection screen that 'they' are showing moving images on to confuse you. Don't believe it--paint the windows black.
OK, now, how fast are you going? You have no way to tell. You don't feel like you're moving. You feel just as you would if you were standing still!
Now scrape off the paint off your windows before you run into a tree (or a tree runs into you).
David Palmer for Ask an Astrophysicist
3. The earth is going around the sun at 107,000 km/h or about 67,000 mph, or 300 km per second. Can you feel that motion? How do you know we are actually traveling through space?
4. The Earth is spinning on its axis at just over 1000 mph.
Can you feel it turning? List 3 ways you can tell it is turning:
1.
2.
3.
5. What would you call the things you just listed?
_____________________________
Speed and Velocity
(pp. 312-317)
6. What is the formula used to calculate the speed of an object?
7. How would you find the average speed of a cyclist throughout an entire race?
Graphing Motion (pp. 316-317)
8. The slant of a line on a graph is called its
_________________________.
9. True or False? The steepness of a graph’s slope for distance versus time depends on how quickly or slowly the object is moving.
10. The distance-versus-time graph above shows the motion of a jogger. How far did the jogger run in:
2 minutes? __________ 6 minutes? __________ 15 minutes? ____________
What is the definition of velocity?
An approaching storm is moving at 15 km/hr. What else do you need to know to know its velocity?