Word Document
advertisement

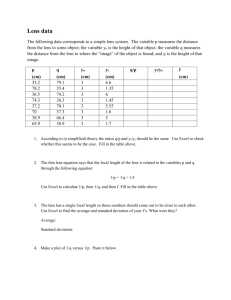
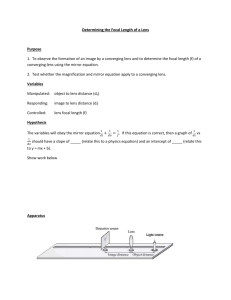
Laboratory Exercise 3 In the laboratory exercise students will observe image formation and determine the focal length of a thin lens using two different methods. They will also observe aberrations. Equipment: He-Ne laser Diffuse reflecting screen Converging lens Mirror Lamp Optical track Ruler Experiment 1: Determine the focal length of a converging lens! Procedure: Place the lens in its holder on the track. Turn on the laser and shine it onto the diffuse reflecting screen. You should see a red spot. Make sure the red spot and the center of the lens are at the same height, and as you look along the track, the spot is aligned with the middle for the lens. This red spot will be your object. If this object is located in the focal plane of the lens, then light from the object will leave the lens as a parallel beam. If a parallel beam is incident on the lens, it will come to a focus in the focal plane. This is called the principle of ray reversibility. Place the mirror approximately 25 cm away from the screen. Make sure the center of the mirror is at the same height as the red spot and the center of the lens. The mirror will reflect a parallel beam of the light and focus it back to a small spot. Move the lens until you obtain the smallest reflected spot possible. Adjust the mirror so that the reflected spot appears just above the object spot. Measure the distance from the center of the lens to the screen (in units of cm). That distance is your measured focal length of the lens. Record your measured focal length in the table below. Check if moving the mirror a small distance along the track changes anything. Rotate the lens approximately 20 degrees about the vertical axis in either direction. Describe what happens to the reflected spot. You should observe a lens aberration called “coma”. It is observed when the light rays make large angles with the optic axis. Experiment 2: Observe the formation of a real image using a converging lens! Procedure: Turn off the laser and place the lamp on the track as shown. Make sure the lamp and the lens are at the same height. Place the lens approximately 25 cm away from the lamp on the track. A black cross is painted onto the lamp. Move the screen along the track until you see the sharpest image of the cross on the screen. Measure the object distance xo from the cross on the lamp to the center of the lens and the image distance xi from the center of the lamp to the image on the index card and record these distances in the table below. Measure the height of the cross ho and the height of its image hi and record these heights in the table below. Note if the image is upright or inverted. Using the lens equation, 1/xo + 1/xi = 1/f, calculate the focal length and using the equation M = -xi/xo calculate the magnification. Repeat these measurements with the lens placed approximately 30 cm and 35 cm away from the lamp. Again rotate the lens approximately 20 degrees about the vertical axis in either direction. Describe what happens to the image. Are the vertical and horizontal lines still in focus at the same place? If not, move the screen to put either the vertical or the horizontal line of the cross in focus. You should observe a lens aberration called “astigmatism”. Experiment 3: Your lens is a plano-convex lens. One side is flat and one side is curved. With the lens approximately 25 cm away from the lamp, look into the lens from the lamp side. With the curved side facing you, you should see a virtual image of the cross produced by reflection from the front surfaces of the lens. Move the lens back and force and try to "touch" the images with your finger. Is it in front or behind the lens? With the plane side facing you, you should see a real image of the cross produced by reflection from the back surfaces of the lens. Move the lens back and force and try to "touch" the images with your finger. Is it in front or behind the lens? Observe! Experiment 1: measured focal length: Experiment 2: measured measured calculated measured measured measured calculated xo xi focal ho hi magnification: magnification: length: M = -hi/ho M = -xi/xo f= xoxi/(xo + xi) Laboratory 3 Report: Name: E-mail address: In a few words, describe the experiment. Comment on the procedure. Did you encounter difficulties or surprises? Present the table with your results. Comment on your results. For example: Do the measured and the calculated focal length agree within experimental uncertainties? Do the measured and the calculated magnification agree within experimental uncertainties? Did you observe an inverted or an upright image? Did you observe aberrations? What did you observe when you looked for the images produced by reflection?