Similarity - WordPress.com
advertisement

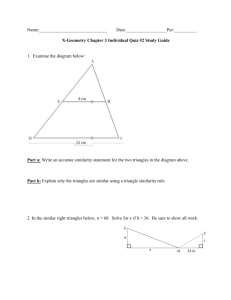
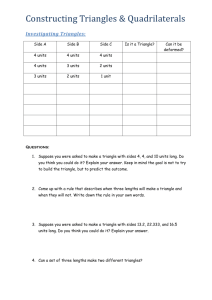
Length Ratio a b Surface Area Ratio 2 a b2 Volume Ratio a3 b3 Similarity Context: This unit is designed for a high school Geometry classroom. Our school is on a block schedule, so I see my students for roughly100 minutes two times a week and 60 minutes on Friday. This will be the second to the last unit of the year. We will have just finished units on area and volume, and earlier in the year the students have already learned properties of triangles and how to prove triangles are congruent. This unit will lead into the next unit on basic trigonometric ratios. For the creation of this unit, I looked at the state and district standards first to help develop the enduring understandings and essential questions for the unit. In the curriculum map, the state standard designated by a G (G.3.A, G.3.B, etc.) and the district standards are designated by a PS (PS3, PS10, etc). The primary method of assessment in this unit is from observations of the students work during investigations and guided practice and on homework. There are additional formal assessments listed in the curriculum map. Standards: G.3 Core Content: Two- and three-dimensional figures PS3 Students are able to determine, prove, and apply triangle congruence, triangle similarity, and the sum of angles property for triangles. G.3.A Know, explain, and apply basic postulates and theorems about triangles and the special lines, line segments, and rays associated with a triangle. G.3.B Determine and prove triangle congruence, triangle similarity, and other properties of triangles G.6 Additional Key Content PS10 Students are able to solve problems by applying formulas for surface area and volume of three-dimensional figures (prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres) and are able to predict and verify the effect of changing one or more linear dimensions on the surface area and volume of a figure. G.6.C Apply formulas for surface area and volume of three-dimensional figures to solve problems. G.6.D Predict and verify the effect that changing one, two, or three linear dimensions has on perimeter, area, volume, or surface area of two- and three- dimensional figures. G.7 Core Processes: Reasoning, problem solving, and communication PS11 Students are able analyze and represent problem situations mathematically; select and apply appropriate strategies to solve the problem, verify their solutions, and communicate their methods and solutions efficiently using appropriate mathematical representations, symbols, and language. G.7.A Analyze a problem situation and represent it mathematically G.7.B Select and apply strategies to solve problems. G.7.C Evaluate a solution for reasonableness, verify its accuracy, and interpret the solution in the context of the original problem. G.7.F Summarize mathematical ideas with precision and efficiency for a given audience and purpose. Essential Questions Concepts Skills Assessments Methods 1. Proportions 1. Solve a proportion regardless of the location of the missing information Formative Assessments: 1. Unit PreAssessment given after last test. 2. Homework 3. Classroom observations Anticipatory Set – The students will work on a percentage problem which they have had experience with in past years. Model – Show the students the steps for solving 2 different proportions where the missing part is in a different location for each Guided Practice – Students solve 4 proportion problems while working with their partner. Independent Practice – Students will work on problem from the book P.561 #1-18 Investigation – Students will measure the side lengths and angles of two similar shapes in order to form a definition of similarity Group Discussion – Students will propose their definitions of similarity Modeling – Show students how proportions can be used to solve for missing side lengths Guided Practice – Have students find missing side lengths and angles of similar shapes. Independent Practice – Students will work on problem from the book P.568 #3, 6-14 Day 1 Enduring Understandings Day 2 Week 1 The students will understand a constant ratio exists between the corresponding lengths of similar figures. 1. What is the difference between similarity and congruence? 2. What is the relationship between similar figures and proportions? 2. Similar Polygons 2. Solve for missing lengths of similar shapes by applying the properties of proportional segments Materials 1. Proportions ActivBoard Flipchart 2. Proportions worksheet 3. Book 1. Similarity ActivBoard Flipchart 2. Handout with pairs of similar shapes for investigation 3. Patty Paper 4. Rulers 5. Book 3. Similar Triangles 3. Determine if two triangle are similar and then solve for missing sides and angles 3. Similar Triangles 3. Determine if two triangles are similar and then solve for missing lengths of altitudes, medians, and angle bisectors 4. Area and Volume of similar shapes 4. Find the ratio of area and volume for similar shapes when given the ratio of the side lengths and vice versa. Day 1 Day 3 3. How is similarity of geometric figures applied and verified? Day 3 Day 2 Week 2 The students will understand the change in lengths between similar figures has a predictable change on the area and/or volume of those figures. 4. How does the change of lengths between similar figures affect the area and volume of the figures? Formative Assessments: 1. Homework 2. Classroom observations 3. Review Quiz over content covered during the first five days of the unit Investigation – Jigsaw activity. Students divide into groups of 3. Each student gets a similarity shortcut to investigate. Students with similar shortcuts get together compare results, and then go back to share with original group. Group Discussion – Have students share findings and write on the board so students have common notes. Model – Use the shortcuts that were just discovered to show students how to determine if two triangles are similar Guided Practice – Students work in pairs to determine if pairs of triangles are similar Independent Practice – Students will work on problem from the book P. 574 #2-7, 9, 10, 11 Investigation – Students will construct two similar triangles and measure the corresponding altitudes, medians, and angle bisectors. Group Discussion - Have students share findings and the class will decide on a common theorem for their findings. Guided Practice – Students missing altitudes, medians, and angle bisectors between similar triangle pairs Independent Practice – Students will work on problem from the book P. 588 #1-10 Investigation – Students will double and triple the dimensions of a square and compare the ratio of side lengths to the ratio of areas. Then they will do the same for a cube and compare the ratio of side lengths to the ratio of volume. Group Discussion - Have students share findings and the class will decide on a common theorem for their findings. Guided Practice – Students will find the area and volume ratios of a cube and cylinder when given the length ratios. Independent Practice – Students will work on problem from the book P. 595 #1-8, 10 Today will be a review day. The students will take a review quiz over proportions, similar polygons, similar triangles, and volume and area of similar shapes. 1. Similar Triangle ActivBoard Flipchart 2. Jigsaw activity worksheet 3.Compasses 4. Straightedges 5. Protractors 6. Book 1. Similar Triangle ActivBoard Flipchart 2. Compasses 3. Rulers 4. Book 1. Area and Volume ActivBoard Flipchart 2. Square Tiles 3. Stacking Blocks 4. Book 1. Review Quiz 5. Indirect Measurement Day 1 5. When can you use proportions to solve problems? Formative Assessments: 1. Homework 2. Classroom observations Summative Assessments: 1. Similarity Station Lab 2. Unit Test Station Lab – The students will spend the entire class working on different labs that are set up around the room and in the hall. Each lab deals with a from of indirect measure or other similarity idea. Day 3 Day 2 Week 3 The students will understand the properties of similarity can be used to solve applied problems. 5. Find a height or distance without measuring by using the properties of similar triangles. Anticipatory Set – The students will try to determine the height of a boy standing next to my friend, who is 6’5”, in a photograph. Guided Practice – Students will break into groups and work on a problem from the book that uses shadow lengths and the height of a pole to determine the height of a building. Independent Practice – Students will work on problem from the book P.582 #1-3, 5, 11-13 Unit Test – The students will take a unit test on proportions, similar polygons, similar triangles, area and volume ratios, and indirect measurement. Reference: Washington State 6-12 Mathematics Standards http://www.k12.wa.us/mathematics/Standards.aspx Lake Washington School District Geometry Power Standard http://www.lwsd.org/PARENTS/TEACHING-CURRICULUM/Pages/Power-Standards.aspx Greenwich Public Schools Math Standards http://www.greenwichschools.org/uploaded/district/curriculum/math/High_Objectives/MathGeometry.pdf 1. Indirect measurement ActivBoard Flipchart 2. Book 1.Tape Measures 2.Meter Sticks 3. Rulers 4. String 5. Circle Templates 6. Projector with slide of smiley face and tripod with cardboard sheet to move in front of screen 7. Plastic Mirrors 8. Stacking Blocks 1. Similarity Unit Test