Med Guide 2014 - Unity Health System
advertisement

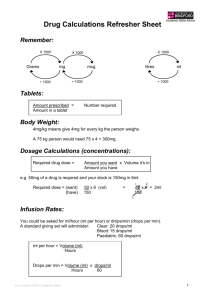
Rochester Regional Health System Nursing Education/Staff Development Medication Review Packet 2014 The Medication Administration Examination for all new hire nurses consists of fifty multiplechoice questions. The test questions consist of twenty dosage calculations for oral and parenteral medications and thirty questions on principles of medication administration and therapeutic effects/side effects of medications. On the day of your exam please bring a calculator. You may also bring a current dug reference book. Part I of this study guide provides information on dosage calculations and IV flow rate calculations. The answers for the sample practice questions have been provided to assist in your review. A calculator may be used for the calculation portion of the exam. Part II of this packet provides the name of the drugs that you will need to know for the drug portion of the exam. Please use a current nursing drug reference book to review the drug’s action, side effects and important nursing administration implications for each of the drugs listed. The Joint Commission and Unity Health System’s prohibited abbreviations are to be reviewed as part of the medication exam expectation. See attached page to this guide. If you have any questions in regards to the test or the review packet please contact Clinical Education at 723-7115. Part I: Dosage and IV drip rate Calculations To calculate the correct oral and parenteral medication dosage ordered follow 3 steps: 1) Be sure all measures are in the same system of measurement and all units are in the same size. Do not forget to convert whenever necessary. Remember: Always convert unit measures to be the same. gram= g = 1 gram microgram =mcg (ug) = 0.001 milligram milligram = mg = 0.001 gram 1000 mcg = 1 milligram 1000 mg =1 gram liter = L = 1 millilitre = ml = 0.001L 1000 ml =1L 1kg = 2.2 lbs When converting grams to milligrams: move the decimal point to the right 3 places (larger to smaller) 1 When converting milligrams to grams: move the decimal point 3 places to the left (smaller to larger). 3) Calculate the drug dosage using one of the suggested formula: Formula Example One: Amount to be Given = Desired Dose Dose Available X Quantity Available Example 1: Ordered: Lasix 60 mg IV Available: Lasix 10 mg/ml Amount to be Given= Desired Dose Dose Available X Quantity Available 60 mg X 1 ml = 6 ml Dose to be given = 6 ml 10 mg Example 2: A patient who weighs 60 kgs is to receive 5mg/kg/day of a medication intravenously in divided doses q 8 hrs. How many mg should the patient receive of the medication with each dose: Dose= 5 mg X 60 kg/day= 300 mg/day 3 doses Dose to be given: 100 mg Formula Example Two: Ratio proportion (fraction method) Dose on hand Vehicle = Dose desired Amount desired The know quantities are on the left side of the equation. A “vehicle” is the quantity available. The one known and one unknown (x) is on the right side. Example One: The order reads 200mg and you have on hand a bag of 400mg in 500cc. Theophylline 400 mg = 200 mg 500cc x cc 400 x = 500 X 200 400 x = 100000 x = 100000 400 x = 250 cc 2 Practice Problems for Oral and Parenteral Medications 1. Ordered: Hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg PO Give: ______tab(s) Available in 25mg tablets 2. Ordered: Lasix 20 mg IV Give: ______ml(s) Available: Lasix 100mg in 10 ml 3. Ordered: Lanoxin 0.125 mg PO daily Give: ______tab(s) Available: Lanoxin 0.25mg tablets 4. Ordered: Inderal 15 mg PO Give: ______tab(s) Available: Inderal 10 mg tablets 5. Ordered: Penicillin 250,000 units IM Give: ______ml(s) Available: Penicillin 500,000 units per 10 ml 6. Ordered: Ampicillin 250 mg IV q 6 hrs Give: ______ Available: Ampicillin 1 Gm in 500 ml 7. Ordered: Demerol 50 mg IM q 4 hrs prn Give: ______ml(s) Available: Demerol 100 mg in 2 ml 8. Ordered: Amoxicillin 100 mg PO qid Give: ______ml(s) Available: 80 ml suspension 125mg per 5 ml 9. Ordered; Duricef 1 Gm PO qid ac Give ______tab(s) Available: Duricef 250 mg tablets 10. How many milligrams are equal to 0.50 grams? __________ 11. Ordered: Dopamine 4 mcg/kg/min. The patient weights 50 kg. Available: Dopamine 400 mg mixed in 500 ml of IV solution. The infusion pump should be set at how many ml per hour? Remember: Always convert unit measures to be the same. gram= g = 1 gram milligram = mg = 0.001 gram microgram =mcg (ug) = 0.001 milligram 1000 mcg = 1 milligram 1000 mg =1 gram liter = L = 1 millilitre = ml = 0.001L 1000 ml =1L 1kg = 2.2 lbs When converting grams to milligrams: move the decimal point to the right 3 places (larger to 3 smaller) When converting milligrams to grams: move the decimal point 3 places to the left (small to large) Answer Key Oral and Parenteral Medications: Amount to be Given = 1. 50 mg 25 mg X 1 tablet = 2 tablets 2. 20 mg X 10 ml = 2 ml 100 mg 3. 0.125 mg 0.25 mg X 1 tablet = 0.5 tablet 4. 15 mg 10 mg X 1 tablet = 1.5 tablets 5. 250,000 units 500,000 units X 10 ml = 5 ml Desired Dose X Quantity Available Dose Available 6. Ordered dose is in mg. Available dose is in gm. You first need to convert grams to milligrams to ensure the dosage units your are comparing are the same.1 gram = 1000mg. Next: 250 mg 1000mg X 500 ml = 125 ml 7. 50 mg 100mg X 2ml = 1 ml 8. 100 mg 125 mg X 5 ml = 0.8 X 5 ml = 4 ml 9. Convert grams to milligrams to have like units. 1000 mg 250 mg X 1 tablet = 4 tablets 10. 0.5. gram = how many mg? 1 gm = 1000 mg 0.50 gram X 1000mg = 500 mg 11. Calculate Dose: Desired Dose Dose= 4 mcg X 50 kg Dose= 200 mcg per min. Convert 200 mcg to mg (1mcg =.001 mg) 200 mcg = 0.2 mg then Dose on hand 4 Dopamine 400 mg in 500 ml or 400 mg = 4 mg 500 ml 5 ml Desired Dose = 0.2 mg/min X 5 ml = 1 mg/min = 0.25ml/min X 60 min = 15 ml Dose on hand 4 mg 1 4 I.V. flow rate calculations To calculate the correct and accurate flow rate ordered, be sure to follow three simple steps: Step 1: Be sure all measures are in the same system, and all units are in the same size. Convert when necessary. Step 2: Carefully consider what is a reasonable amount of the drug that should be administered. Step 3: Calculate the intravenous drip rate using the formula: Drip Rate = Volume to be infused X drip factor (gtt/ml) Total time in minutes Example: Ordered: Infuse 1200 ml of normal saline over 6 hrs Drip rate factor of the infusion is 15 gtt/ml What will be the drip rate in gtts/minute: Step 1: Calculate total time in minutes: 6 hours X 60 minutes = 360 minutes Step 3: Calculate drip rate Drip rate = Volume to be infused X drip factor Total time in minutes Drip Rate = 1200 ml X 15 gtts/ml = 50 gtts/min 360 min When rounding numbers: round to the nearest whole number. If tenths > 5, round up; if the tenths is < 5, round down. If the tenths is = 5, then look at the hundredths and utilize the >, < principle. Example: Round 24.82 to the nearest whole number = 25 Round 36.6 to the nearest number = 37 Round 35.8 to the nearest number = 36 5 Practice Problems for Intravenous Drug Calculations: 1. Ordered: Ampicillin 500 mg dissolved in 200 ml D5W to infuse within 2 hours Drip rate: ________gtts/min Drip factor: 10 gtts/ml 2. Ordered; Normal Saline 1200 ml to infuse over 10 hrs Drip rate: ________gtts/min Drip factor: 15gtts/ml 3. Ordered: 1000 ml Lactated Ringers IV in 24 hrs Drip rate: ________gtts/min Drip factor: 60 gtts/ml 4. Ordered: 1500 ml D5NS IV to run for 12 hrs Drip rate: ______gtts/min Drip factor: 20gtts/ml 5. Ordered: 1 L D5W to run from 0900 to 1800 Drip rate: ________gtts/min Drip factor: 10gtts/ml 6. Ordered: 2.5 L NS IV to infuse at 125ml/hr Drip rate: ______gtts/min Drip factor: 20 gtts/ml 7. Ordered: 1000 ml D5W IV for 6 hrs Drip rate: ________gtts/min Drip factor: 15gtts/ml 8. Ordered: Ancef 1Gm in 100cc D5W IVPB to infuse > 45 min. Drip rate: _________gtts/min Drip factor: 60gtts/ml 9. Ordered: Ampicillin 500 mg in 50 ml of NS to infuse > 30 min. Drip rate: ______gtts/min. Drip factor: 15gtts/ml Ordered: 500 ml D5LR to infuse >3 hrs Drip factor: 60gtts/ml 10. 6 Answers to IV drug calculations 1. 200 ml X 10 gtts/ml 120 min = 16.66 or 17 gtts/min 2. 1200 ml X 15 gtts/ml 600 min = 30 gtts/min 3. 1000 ml X 60 gtts/ml 1440 min = 41.66 or 42 gtts/min 4. 1500 X 20 gtt/ml 720 = 41.66 or 42 gtt/min 5. 1000 ml X 10 gtt/ml 540 min = 18.52 or 19 gtts/min 6. 125 ml X 20 gtts/ml 60 min = 41.66 or 42 gtts/min 7. 1000 X 15 gtts/ml 360 min = 41.66 or 42 gtts/min 8. 100 X 60 gtts/ml 45 min = 133.33 or 133gtts/min 9. 50 X 15 gtts/ml 30 min 10. = 25 gtts/min 500 X 60 gtts/ml 180 min = 166.6 or 167 gtts/min 7 Part II: Drug List It is important for the nurse administering medications to know how the drug he/she is administering will affect the patient. The nurse must be aware of the drug’s actions, contraindications, side effects and nursing implications to facilitate the delivery of safe quality patient care. Please refer to a current nursing drug reference book to review the following medications for the exam. Activated charcoal Ativan Atropine Adrenalin Beta-blockers- i.e. Metoprolol Cardizem XL Corticosteriods Cafergot Demerol Digoxin Dilantin Dimercaprol Dopamine Epinephrine Estrogen Preperations Flu Vaccine Flumazenil Heparin Insulin-NPH, Lantus, Regular, Humalog Lasix Lithium Lovenox Morphine Sulfate Narcan Nitroglycerin NSAIDS Opioids Protamine Sulfate Premarin Tricyclic antidepressants- i.e. Elavil Unasyn Vancomycin Ventolin 8 Attachment A Prohibited Acceptable ug Use mcg for microgram T.I.W. Write out three times weekly, 3 X weekly qd or q.d. Use q day, q 24 hours, every day or daily q hs Write out q hour of sleep or at bedtime q.o.d. or qod Write out every other day, q other day u or U Write out units X 3 d, X 2 d Write out 3 days, 2 days IU Write out international unit MS or MSO4 Write out Morphine Sulfate MgSO4 Write out Magnesium Sulfate Never use a zero by itself after a decimal point. Correct: 1 mg Incorrect: 1.0 mg Always use a zero before a decimal point. Correct: 0.5 mg Incorrect: .5 mg Trailing zeros after decimal point A decimal point without a zero Caution: Always use a space between drug name, dose and units of measure 9 Clinical Education revised 1/11 10