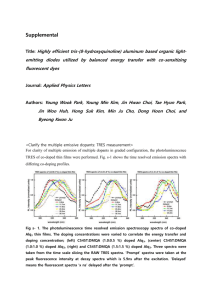
Development, characterization and electrochemical silver speciation
advertisement

Electrochemical characterization and metal speciation of silver LLDPE nanocomposite films Irene Domínguez*a, Antonio Doménech-Carbó*b, Josep P. Cerisueloa, Gracia LópezCarballoa, Pilar Hernández-Muñoza, Rafael Gavaraa a Packaging Lab., Instituto de Agroquímica y Tecnología de los Alimentos, IATA- CSIC, Av. Agustín Escardino 7, 46980 Paterna, Spain b Departament de Química Analítica, Universitat de València, Dr. Moliner 50, 46100 Burjassot, València, Spain. Supporting information Figure S.1. UV-Vis absorption spectra of the silver solutions used in the preparation of silver doped LLDPE films: AgCL (blue), AgYL (green) and AgBW (red). Coloured solutions were diluted with water before spectra recorded -AgYL (1:4) and AgBW (1:7). Figure S.2. Oxidative induction time curves of LLPE control sample and silver doped LLDPE films. Figure S.3. DSC analysis of LLDPE control sample and silver doped LLDPE films: AgCL (blue), AgYL (green) and AgBW (red). Figure S.4. Experimental Nyquist diagrams (black circles) for EIS at OCP of: a) PECL@Ag (black) and b) PEYL@Ag films immersed into in 0.25 M HAc/NaAc buffer at pH 4.75. Red lines/circles represent the theoretical impedance spectra obtained from equivalent circuit fitting to experimental data using the equivalent circuits represented as inset (a) and the inset in Fig. 7b (b). Figure S.1. 1.6 1.4 1.2 Absorbance 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 300 400 500 600 Wavelenght (nm) 700 800 Figure S.2. 1.0 Heat Flow (W/g) 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 -0.2 0 2 4 6 Time (min) 8 10 12 Figure S.3. Figure S.4. CPE1 a) Rs Rct b) Table S.1. Values for the elements of the equivalent circuit in Fig. 8b for EIS spectra of PEYL@Ag and PEBW@Ag films. Experimental conditions in caption for Figs. 7 and 8. Element PEYL@Ag PEBW@Ag Element PEYL@Ag PEBW@Ag Rs () 234 181 W (SI) 3,1x10-5 1,0x10-12 R1 () 1,2x103 5,2x104 C (F) 2,9x10-7 9,0x10-5 R2 () 526 260 Q1 (SI) 3,4x10-6 (0,42) 7,7x10-6 (0,62) Q2 (SI) 4,5x10-7 (0,84) 1,6x10-9 (0,95)