Biomes handout - Newberry
advertisement

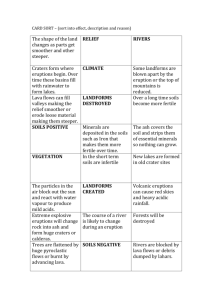
BIO 431: Ecology BIOMES OF THE WORLD BIOME = Area of planet with similar climate and vegetation TEMPERATE DECIDUOUS FOREST Dominant Vegetation: broad-leaved deciduous trees forming dense canopy, such as oak, beech, hickory, maple, tulip poplar Climate & Soils: distinct warm and cool seasons, most rainfall during summer 40-60"/yr; soils are podzols, high in organic matter Dominant Animals: small to moderate mammals, mostly herbivores such as rabbits, deer Location: eastern North America, including South Carolina; parts of France and Spain BOREAL FOREST Dominant Vegetation: narrow-leaved evergreen trees such as fir, spruce, pine Climate & Soils: distinct short warm and long cold seasons, most rainfall in spring 30-50"/yr; soils are podzols Dominant Animals: large herbivores such as moose, deer, porcupine plus their predators Location: eastern Canada, also northern Europe TUNDRA Two types, based on latitude and elevation: circumpolar (near poles, low elevation) montaine (equator to mid latitude, high elevation) Dominant Vegetation: mostly grasses and sedges, some small shrubs, many lichens and mosses Climate & Soils: growing season 100 days or less, possibility of frost any one day, precipitation of 4-5"/yr; soils characterized by permafrost (never thaws below a certain distance – gleization) Dominant Animals: a few small rodents and numerous predators Location: northern Canada, Rocky Mountains above 13,000 ft GRASSLAND Dominant Vegetation: grasses and other herbs; shrubs and trees only along streams Climate & Soils: variable rainfall, 10-40"/yr, most near end of cool/cold season (winter); soils by calcification, high in organic matter; fires important to keeping trees from becoming established Dominant Animals: large grazing mammals or small burrowers Location: Midwestern USA (prairie), central Russia (steppe), Argentina (pampas) TROPICAL EVERGREEN RAINFOREST Dominant Vegetation: many species of trees, no one dominant; many lianas and epiphytes also Climate & Soils: high rainfall amounts, 70-150"/yr; soils lateritic, most nutrients leached out Dominant Animals: high diversity of birds, insects, monkeys and other small animals; most animal life up in the trees Location: east coast of Central America, Amazon basin of South America, west central Africa, southeastern Asia TROPICAL SAVANNAH Dominant Vegetation: mixture of shrubs to small trees and grasslands, typically more of the latter; trees are typically of the legume family and possess thorns Climate & Soils: very seasonal rainfall, 70-100"/yr; soils lateritic Dominant Animals: diversity of grazing mammals and associated predators Location: central to southern Africa, north coast of Brazil SHRUB-SCRUB (included in savanna by some) Dominant Vegetation: shrubs with many thorns, many areas of bare ground Climate & Soils: dry, 10-20"/yr, usually all at once; soils sandy and high in minerals (calcification) Dominant Animals: small burrowing rodents and reptiles Location: scattered areas of western USA, west coast of Central America DESERT Two types, based on temperature: warm (extreme temperature changes in 24 hrs), cold (always cold, such as Antarctica or mountains); warm described below Dominant Vegetation: drought resistant such as cacti (New World) and euphorbes (Old World), also many fast growing annuals; many areas lack ground cover Climate & Soils: dry, less that 10"/yr; soils sandy and high in minerals (calcification); hardpan typically forming in B horizon; very little organic matter buildup Dominant Animals: small burrowing rodents and reptiles Location: basins within Rocky Mountains of USA and Mexico, northern Africa, western Australia OCEAN Dominant Vegetation: algae, no known vascular plants Climate & Soils: influx of freshwater due to rainfall minimal; water temperature relative to currents; no soils, nutrients only in coastal areas and areas of upwelling Dominant Animals: numerous invertebrates, fish, whales Location: 75% of planet covered by ocean