Rock and Mineral Study Guide
advertisement

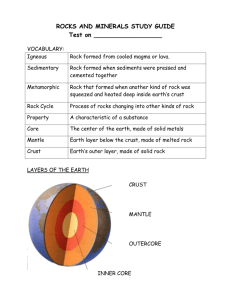
Rock and Mineral Study Guide Vocabulary Mineral Streak Metal Sediment Clastic rock Inorganic Density Nonmetal Metamorphic Organic rock Crystal Cleavage Gemstone Rock cycle Chemical rock Luster Fracture Rock igneous Extrusive rock Metamorphism Hardness Ore Sedimentary Intrusive rock Know these aspects of Minerals Characteristics of Minerals: More details in text. Inorganic Solid Naturally Occurring Have a definite composition (pureelement or compound) Have a crystal structure Properties of Minerals: More details in text Color Luster Hardness Streak Specific Gravity Cleavage Fracture Special Properties Magnetism, Taste Effervescence FluoresceOdor Taste Density Uses of Minerals Ores—minerals that metals or nonmetals can be extracted from Metals- shiny, conduct electricity and heat, malleable, ductile Must be smelted to extract – heat then cool Iron from limonite and hematite Aluminum from bauxite Lead from galena Copper used in wire and pipes Silver and gold in coins, jewelry, dental fillings May combine metals to make alloys stainless steel, brass Nonmetals- dull, poor conductors not easily shaped Sulphur matches, medicines fertilizer, steel production Fluorite fluorine in toothpastes Corundum Emery boards Halite table salt Gypsum drywall Gemstones- durable, hard, beautiful minerals that can be cut and polished Precious Gems most rare and valuable include ruby, emerald, diamond, sapphires Semi-precious tourmaline, amethyst, zircon, garnet turquoise, Pearls are gems but not minerals oysters Amber is a gem but not a mineral tree sap Know these aspects of Rocks Rocks are made from one or more minerals Igneous Rock Classified by texture and composition May be fine-grained or coarse grained May look glassy if cool quickly May see crystals if cool slowly Intrusive- form inside the Earth Extrusive- form at the Earth’s surface Look at Igneous worksheet for additional details. Sedimentary Rock Made from sediments Clastic cemented together by pressure or water Organic made from once living organisms Chemical made from evaporation Look at Sedimentary worksheet for additional details. Metamorphic Made from pressure and heat changing igneous or sedimentary rock Foliated- layers Unfoliated- no layers Shale slate Granite Gneis Chalk marble Please check metamorphic worksheets for additional details.