Family relations - CareerVarsity.com
advertisement

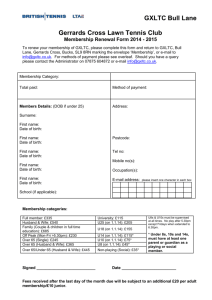
Family relations Father: a male parent Mother: a female parent Dad (informal): one's father Mum, mummy, mom (informal): one's mother Parent: father or mother Child (Plural Children): a son or daughter of any age Son: a male child Daughter: a female child Brother: a man or boy in relation to other children of his parents Sister: a woman or girl in relation to other children of her parents Grandfather (Informal grandpa): the father of one's father or mother Paternal grandfather: the father of one's father Maternal grandfather: the father of one's mother Grandmother (Informal grandma): the mother of one's father or mother Paternal grandmother: the mother of one's father Maternal grandmother: the mother of one's mother Grandson: a boy child of one's son or daughter Granddaughter: a girl child of one's son or daughter Uncle: the brother of one's father or mother or the husband of one's aunt Aunt: the sister of one's father or mother or the wife of one's uncle Cousin: any child of one's uncle or aunt Nephew: a son of one's brother or sister or of one's brother-in-law or sister-in-law Niece: a daughter of one's brother or sister or of one's brother-in-law or sister-in-law Fiancée: a woman to whom a man is engaged to be married Fiance: a man to whom a woman is engaged to be married Bride: a woman on her wedding day or just before and after the event Bridegroom: a man on his wedding day or just before and after the event Wife: the woman to whom a particular man is married Husband: the man to whom a particular woman is married Spouse: one's husband or wife Father-in-law: the father of one's husband or wife Mother-in-law: the mother of one's husband or wife Sister-in-law: the sister of one's husband or wife or the wife of one's brother or brother-in-law Brother-in-law: the brother of one's husband or wife or the husband of one's sister or sister-inlaw Son-in-law: the husband of one's daughter Daughter-in-law: the wife of one's son Godparent: A person who presents a child at baptism and promises to be responsible for their religious education Words denoting groups and collections To talk about a limited quantity of something we use a word like piece or bit, together with of, before an uncountable noun. Bit is informal, and usually suggests a small quantity. A piece/bit of cake/bread Some pieces/bits of paper/wood A piece/bit of news/information There are other words too. Some common examples are given below. A bar of soap/chocolate A blade of grass A block of ice A drop of water/oil/vinegar A grain of sand/salt/rice An item of clothing/furniture A loaf of bread A slice of bread/cake/meat A sheet of paper/metal/plastic/stamps A stick of chalk/celery A suit of clothes/armour A bale of cotton Pairs Pair is used for many things that come in pairs. A pair of shoes/socks/ear-rings A pair of glasses/binoculars A pair of trousers/jeans/pyjamas A pair of scissors/pliers Collections Special words are used before certain nouns to talk about groups or collections. An army/a regiment/a battalion of soldiers A band of musicians A basket of fruits A bench of judges A bevy of girls/women A board of trustees/directors/examiners A brood of chickens A bunch of flowers/grapes A bundle of sticks A caravan of merchants/pilgrims/travelers A chain of mountains A congress of representatives/delegates A consignment of goods A crew of sailors A constellation of stars A fleet of ships A flight of birds A flock of sheep/geese A galaxy of stars A gang of prisoners/robbers/thieves/labourers A group of islands A heap of junk/stones/sand A herd of cattle/deer/goats A hive of bees A horde of pirates/robbers/savages A league of nations A litter of pigs/puppies A pack of hounds A pride of lions/peacocks A swarm of bees/ants A volley of shots/bullets Words denoting different sounds Beat of a drum Blaring of bands, trumpets Blowing of a bugle Booming of a gun Buzz of a telephone Call of a bugle Chattering of teeth Clanging of chains, hammers, arms Clatter of hoofs, plates Clinking of glasses, metal, keys Crackling of fire Crack of a whip Creaking of doors or shoes Hissing of steam Howling of wind Jingling of coins Lapping of water Patter of rain Pealing or ringing of bells Rattling of windows Roaring of guns Rustle of silk, leaves Shriek of a whistle Thundering or rumbling of clouds Sizzling of sausages Slam of a door Tick of a clock Toot of a horn Twang of a bow Whistling, roaring or howling of wind Names of young ones of a few animals Cub The young of a fox, bear, lion, wolf or other carnivorous mammal. Fawn A young deer in its first year. Cygnet A young swan Lamb A young sheep Leveret A young hare in its first year. Foal A young horse or related animal. Colt The young of a horse Gosling A young goose Kid A child or young person, a young goat Eaglet A young eagle Duckling A young duck Puppy A young dog Calf A young cow or bull. Also, the young of some other large mammals Kitten A young cat. Also, the young of certain other animals, such as the rabbit and beaver People of different trades and professions We have got different names for persons following different trades and professions. A few are listed below. People who drive our motorcars - Chauffeurs or drivers People who make law for us - Legislators People who keep our streets and drains clean - Scavengers People who sell us vegetables - Green grocers People who cell us spices, sugar, dried fruits etc. - Grocers People who sell us cloth/garments - Drapers/ clothiers/ outfitters People who sell us sweets - Confectioners People who sell us tobacco - Tobacconists People who mend shoes - Cobblers People who deal in and prescribe glasses - Opticians People who sell us writing materials, pens, pencils, notebooks etc. - Stationers People who dig up coal and iron - Miners People who take us across a stream or river in a boat - Ferrymen Financial/business vocabulary Absolute monopoly It refers to a condition of the market where only one seller has total command or control over the sale of a given article. In normal circumstances such a condition does not exist. Ad Valorem Duty It refers to the duty or tax imposed on a commodity depending upon its value. Authorised capital It refers to the maximum capital a public limited company can raise through public subscription by sale of shares. Balance sheet Statement of account over a specified period of time showing assets and liabilities under specific heads from which the soundness or otherwise of an institution or organization is determined. Bank credit Purchasing power provided by banks in excess of their cash balances, by reason of public confidence in their stability. Bank note A promissory note issued by a bank payable to bearer on demand without interest and acceptable as money Barter Trade by exchanging one commodity for another Bear A stock exchange term denoting a falling market when speculators sell stock in the hope of buying again at lower prices Bearer cheque A cheque that is encashable by bearer (person holding cheque) Black market Profiteering (usually illegal) by hoarding and selling at exorbitant prices, without accounting or false accounting Black money Money accumulated by way of illegal transactions without declaring it for tax purposes Bonus Payment in addition to wages and salaries for employees, and in addition to dividend for shareholders Budget A statement of anticipated revenue and expenditure of a sovereign body for a given period of time Budgetary deficit The difference between all the receipts and the total expenditure Bull It refers to that sort of a speculator, who stands to gain with a rise in the price of shares and stocks Buyer's market A market where goods and services are available in plenty and the prices are relatively low Capitalism A system under which private entrepreneurs have complete freedom to devise and control production and distribution for their own profits, competition being the only limiting factor Cash ratio It refers to the ratio of aggregate bank holdings of cash against its aggregate liabilities above a particular time Central bank The apex bank which controls, supervises and guides the functioning of commercial banks in the country Closed economy An economy which neither exports nor imports anything Letter of Credit A letter from a bank, firm or from one person to another, authorizing payment of a specified sum to third person for which the sender assumes responsibility Crossed Cheque A cheque crossed with two parallel lines and "&Co" written in between them. This is done as a safety measure. A crossed cheque is not to be paid on the counter. The amount is normally to be credited to the payee in his own account Current account Bank account from which withdrawals are allowed without any restriction on frequency or amount, so long as there is a credit balance Customs duty Tax on goods imported into and exported from a country Death duty Also called estate duty. Tax payable on property, after death of the owner, by his heirs Debenture Bond issued by an organization or undertaking to repay the amount with a specified interest after a specified period. Debenture holders are only creditors and not shareholders. Deficit financing When expenditure exceeds revenue, paper currency is printed to fill the gap. It is beneficial when it creates greater productivity. If there is no adequate increase in productivity it will generate serious inflation. Deflation It is the fall in prices, increase in unemployment, etc., as a result of less circulation of currency in the market Demonetization It is the government act of depriving metallic coins or paper money of specified denomination or its status as money. This is resorted to unearth hidden wealth. Depreciation In accounting, this is a percentage reduced from the value of machinery or fixed assets for wear and tear every year. Devaluation It is the deliberate reduction in the value of home currency in relation to foreign currency Dividend Share of the profits allotted to each share in a joint stock company Equity shares They are ordinary shares with no guarantee of dividend. Equity shares gain maximum returns when there are high profits. Exchange rate It refers to the rate at which the currency of one country exchanges with the currency of another country. Excise duty Tax levied on certain goods produced and consumed in the country Gift tax Gift on tax to prevent tax evasion by genuine or fictitious gifts Gross National Product It is the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced in a country during one year Hard currency Foreign exchange which is difficult to get. Inflation Undue increase in quantity of money in proportion to purchasing power Mixed economy An economic system where public and private sectors exist side by side Nationalisation Government take-over of business, industrial or public utility services Net National Product It is the gross national product minus allowance for depreciation of capital goods. Octroi It is a tax charged by municipality or local body on the goods and commodities brought into town. Open economy Economy that has trade relationships with other countries Per Capita Income It is the average income of an individual wage earner in a country in one year Primary sector It is the sector of the national economy which deals with the production of primary or raw materials, i.e., agriculture, mining etc. Public sector Undertakings financed and operated by a government Secondary sector It is the sector of the national economy which comprises manufacturing and processing industries Security A guarantee in the form of cash, bonds, property etc., kept as pledge for repayment of debt or protection against financial loss Soft loan It is a form of loan given either at a low rate of interest or without any interest. Turnover The total value of the sales made by a company or firm in one accounting year is called the turnover. Wealth Tax A tax imposed on the wealth possessed by individuals in a country Computer vocabulary Analog computer A computer that uses moving parts to show changing information Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) The component of a Central Processing Unit (CPU) responsible for the performance of arithmetic and logical operations Artificial intelligence The ability of a computer to perform tasks that usually requires human intelligence Assembler A translating program used to convert assembly language to machine language BASIC A simple programming language, BASIC stands for Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code. Binary system The number representation system, used in computers, with only two digits, 0 and 1 Browser A computer program used to move around the Internet Byte A unit of information in a computer that stands for a letter, number, or symbol. A byte usually consists of eight bits. CD-ROM Short for Compact Disc Read Only Memory. CD-ROM stores data for computers. Character A single letter, number or symbol. In computers, a character is the same as a byte. Chip A tiny, flat piece of silicon with a complete electric circuit on it. A chip stores and processes data in a computer. COBOL A high level commercial programming language Compact disc A flat, round, plastic disk that is often called a CD. A compact disc records sounds in a spiral track containing millions of tiny pits. Compiler A program which translates a source program written in a high level language into a low-level language Computer A high speed machine for calculating and handling information CPU Short for Central Processing Unit. CPU is the heart of a computer. It receives instructions from the user and then guides the computer's operations Cursor A symbol that moves on a computer screen to mark a position Cyberspace Everything that can be seen or heard through a computer Debug To correct a problem in a computer's hardware or software Delete To remove a character, data, or a file from a computer's memory or disk Digital computer A computer that uses numbers to present information or measurements Document A file of data or text that is stored in the computer's memory DOS Short for Disk Operating System. A program that directs a computer Download To move a computer file from one computer to another or to a disk E-mail Short for electronic mail. A message sent from one computer to another File A document or complete unit of data stored in a computer's memory or on a disk. Floppy disk A flat magnetic disk that stores information for computers Font A complete set of type. Each font contains letters, numbers and symbols of one style. FORTRAN Formula Translating System. FORTRAN is a high level programming language Hard copy Output from a computer that is printed on a page Hard disk The main memory or storage medium within a computer Hybrid computer A type of computer that combines the best features of analog and digital computer Hypertext A computer link between related bits of information. Hypertext makes it possible to quickly jump from one topic to another Input Data that are entered into a computer Interface Connection between two parts of a computer Internet A worldwide computer network made up of many smaller networks Local Area Network (LAN) A relatively inexpensive, simple communication system linking a number of computers within a defined small locality Megabyte The term used to represent 1 million bytes of storage Menu A list of possible operations and functions Monitor The display screen that shows the output of a computer Motherboard The main circuit board in a computer. The motherboard contains the CPU. Mouse A handheld device that moves the cursor on the monitor Personal computer A small computer used by one person at a time. Personal computer is often shortened to PC. Also called microcomputer. Random Access Memory (RAM) Main memory of a computer. Information can be read from and written to RAM by the user and therefore it is called read/write memory Read Only Memory (ROM) ROM is part of a computer's memory that contains data and instructions that cannot be changed. Software The instructions that direct a computer to perform many tasks Job seeker's vocabulary This glossary is designed to give a quick definition of the words you should know as a job seeker. Accomplishments These are achievements you have had in your career. These key points will help you sell you to an employer. Background check This is used by employers to verify the accuracy of the information you provide in your resume or job application and beyond. Career Objective/ Job Objective This is an optional part of your resume. Job objective can sharpen your resume and should be as specific as possible, and written in a way that shows how you can benefit your employer. Cold call The call a job seeker makes to an employer (usually through an uninvited cover letter) who has not publicly announced any job openings. Compensation package The combination of salary and fringe benefits an employer provides to an employee. When evaluating job offers, a job seeker should consider the total package and not just salary. Contract employee An employee who works for an organization that sells his or her services to another company on a project or time basis. Counter offer/ Counter Proposal This is a salary negotiation technique used by job seekers when a job offer is not at an acceptable level. Almost all elements of a job offer are negotiable, including the salary, non-salary compensation, moving expenses, benefits and job specific issues. Cover letter A letter that should always accompany your resume when you contract a potential employer. A good cover letter opens a window to your personality and describes specific strengths and skills you offer the employer. It should entice the employer to read your resume. Curriculum Vitae (CV) Another name for Resume Declining letter A letter sent to an employer to turn down a job offer. The writer should keep the door open in case he or she would like to approach the employer again someday. Employment gaps/ breaks Are those periods of time between jobs when job seekers are unemployed, either by choice or by circumstances. Freelancer/Consultant/Independent Contractor A person who works for himself/ herself and bid for temporary jobs and projects with one or more employers. Hidden job market Only about 5-20 % of all job openings are ever publicly known, which results in about four-fifths of the job market being 'closed', meaning you can't find out about any new job openings unless you do some digging. Strategies for uncovering the hidden job market include networking and cold calling. Internships Types of work experiences for entry-level job seekers. Internships involve working in your expected career field, either during a semester or over the summer. Screening interviews They are usually conducted by a member of the human resources department. The screening interview is designed to weed out unqualified candidates. Traditional Interviews The kind of interview that asks broad based questions such as, 'why do you want to work for this company,' and 'tell me about your strengths and weaknesses.' Behavioural interviews They are based on the premise that past performance is the best indicator of future behaviour and uses questions that probe specific past behaviours, such as, 'tell me about a time when you confronted an unexpected problem' and 'tell me about an experience when you failed to achieve a goal.' Situational interviews Also referred to as problem solving interview. A job seeker is placed in a hypothetical situation such as dealing with an irate customer, and is judged by how well she/he reacts to complex information and arrives at solutions. Stress interviews They are a deliberate attempt to see how you handle yourself under pressure. The interviewer may be sarcastic or argumentative, or may keep you waiting. Expect these things to happen and when they happen don't take them personally. Calmly answer each question as it comes. Also called intimidation interviews. The sciences Acoustics: The study of sound Aerodynamics: The branch of mechanics that deals with the motion of air and other gases. Also, the study of motion and control of solid bodies like aircraft, missiles, etc., in air Aeronautics: The science or art of flight Aeronomy: The study of the earth's atmosphere, including its composition, density, temperature and chemical reactions as recorded by sounding rockets and earth satellites Aerostatics: The branch of statics that deals with gases in equilibrium and with gases and bodies in them Aetiology: The science of causation Agrobiology: The science of plant life and plant nutrition Agronomy: The science of soil management and the production of field crops Agrostology: The study of grasses Alchemy: Chemistry in ancient times Anatomy: The science dealing with the structure of animals, plants or human body. Anthropology: The science that deals with the origin, physical and cultural development of mankind Arboriculture: Cultivation of trees and vegetables Archaeology: The study of antiquities Astrochemistry: The study of interstellar matter with a view to knowing the origin of universe Astrology: The ancient art of predicting the course of human destinies with the help of indications deduced from the position and movement of heavenly bodies Astronautics: The science of space travel Astronomy: The study of heavenly bodies Astrophysics: The branch of astronomy concerned with the physical nature of heavenly bodies Bacteriology: The study of bacteria Biochemistry: The study of chemical processes of living things Biology: The study of living things Biometry: The application of mathematics to the study of living things Biomechanics: The study of the mechanical laws relating to the movement or structure of living organisms Bionics: The study of functions, characteristics and phenomena observed in the living world and the application of this knowledge to the world of machines Bionomics: The study of the relation of an organism to its environments Bionomy: The science of the laws of life Biophysics: The physics of vital processes Botany: The study of plants Ceramics: The art and technology of making objects from clay Chemistry: The study of elements and their laws of combination and behaviour Chemotherapy: The treatment of disease by using chemical substances Chronobiology: The study of the duration of life Chronology: The science of arranging time in periods and ascertaining the dates and historical order of past events Conchology: The branch of zoology dealing with the shells of mollusks Cosmogony: The science of the nature of heavenly bodies Cosmography: The science that describes and maps the main features of the universe Cosmology: The science of the nature, origin and history of the universe Cryobiology: The science that deals with the study of organisms, especially warm-blooded animals, at low temperature Cryptography: The study of ciphers (secret writing) Crystallography: The study of the structure, forms and properties of crystals Cryogenics: The science dealing with the production, control and application of very low temperatures Cryotherapy: Use of cold, but not freezing cold, as a form of treatment Cytochemistry: The branch of cytology dealing with the chemistry of cells Cytogenetics: The branch of biology dealing with the study of heredity from the point of view of cytology and genetics Cytology: The study of cells, especially their formation, structure and functions Dactylography: The study of fingerprints for the purpose of identification Ecology: The study of the relation of animals and plants to their surroundings, animate and inanimate Embryology: The study of development of embryos Entomology: The study of insects Epidemiology: The branch of medicine dealing with epidemic diseases Epigraphy: The study of inscriptions Ethnography: A branch of anthropology dealing with the scientific description of individual cultures Ethology: The study of animal behaviour Eugenics: The study of the production of better offspring by the careful selection of parents Genealogy: The study of family origins and history. It includes the compilation of lists of ancestors and arranging them in pedigree charts Genecology: The study of genetical composition of plant population in relation to their habitats Genetics: The branch of biology dealing with the phenomena of heredity and the laws governing it Geobiology: The biology of terrestrial life Geobotany: The branch of botany dealing with all aspects of relations between plants and the earth's surface Geochemistry: The study of the chemical composition of the earth's crust and the changes which take place within it Geography: The development of science of the earth's surface, physical features, climate, population etc. Geology: The science that deals with the physical history of the earth Geomedicine: The branch of medicine dealing with the influence of climate and environmental conditions on health Geomorphology: The study of the characteristics, origin and development of land forms Geophysics: The physics of the earth Gerontology: The study of old age, its phenomena, diseases etc Glaciology: The study of ice and the action of ice in all its forms Histology: The study of tissues Horticulture: The cultivation of flowers, fruits, vegetables and ornamental plants Hydrology: The study of water with reference to its occurrence and properties in the hydrosphere and atmosphere Hydropathy: The treatment of disease by the internal and external use of water Hydroponics: The cultivation of plants by placing the roots in liquid nutrient solutions rather than oil Hydrostatics: The mathematical study of forces and pressures in liquids Hygiene: The science of health and its preservation Mammography: Radiography of the mammary glands Metallography: The study of the crystalline structures of metals and alloys Mettallurgy: The process of extracting metals from their ores Meteorology: The science of the atmosphere and its phenomena Metrology: The scientific study of weights and measures Microbiology: The study of minute living organisms, including bacteria, molds and pathogenic protozoa Molecular biology: The study of the structure of the molecules which are of importance in biology Morphology: The science of organic forms and structures Mycology: The study of fungi and fungus diseases Neurology: The study of the nervous system, its functions and its disorders Neuropathology: The study of diseases of the nervous system Numerology: The study of numbers. The study of the date and year of one's birth and to determine the influence on one's future life Odontology: The scientific study of the teeth Optics: The study of nature and properties of light Ornithology: The study of birds Orthopedics: The science of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases and abnormalities of musculoskeletal system Osteology: The study of the bones Paleobotany: The study of fossil plants Paleontology: The study of fossils Pathology: The study of diseases Philology: The study of written records, their authenticity etc Phonetics: The study of speech sounds and the production, transmission, reception etc Photobiology: The branch of biology dealing with the effect of light on organisms Phrenology: The study of the faculties and qualities of minds from the shape of the skull Phycology: The sudy of algae Physics: The study of the properties of matter Physiography: The science of physical geography Physiology: The study of the functioning of the various organs of living beings Phytogeny: The science dealing with origin and growth of plants Pomology: The science that deals with fruits and fruit growing Psychology: The study of human and animal behaviour Radiobiology: The branch of biology which deals with the effects of radiations on living organisms Radiology: The study of X-rays and radioactivity Seismology: The study of earthquakes and the phenomena associated with it Selenology: The scientific study of moon, its nature, origin, movement etc Sericulture: The raising of silkworms for the production of silk Sociology: The study of human society Telepathy: Communication between minds by some means other than sensory perception Therapeutics: The science and art of healing Toxicology: The study of poisons Virology: The study of viruses Zoology: The study of animal life The curious world of words English is the richest of the world’s 3,000 languages. The new Oxford Dictionary in 2 volumes lists 75,00,000 words. This dictionary was first published in 1933. Nearly about 2,00,000 words are in current use. The longest words in English Honorificabilitudinitatibus This word found in the Chambers Dictionary has 27 letters. It occurs in Shakespeare’s play Love’s Labour’s Lost and means ‘with honourableness.’ Antidisestablishmentarianism This word has 28 letters. It means ‘the act of opposing the separation of church and state.’ Floccinaucinihilipilification This word found in the Chambers and Oxford English Dictionaries has 29 letters. It means ‘the action or habit of estimating something as worthless.’ Pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis Found in Webster’s New Collegiate Dictionary, 8th edition and in Chambers Dictionary this word has 45 letters. It is a pneumoconiosis caused by the inhalation of very fine silicate or quartz dust. The most frequently used words in Written English 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. The Of And A To In Is You That It He For (Source: American Heritage Word Frequency Book) A reasonably common word which contains all five vowels each used once, and in their alphabetical order --Facetious A seven-letter word which doesn’t use any of the five vowels--Rhythms A word with more than 15 letters in which the only vowel is ‘e’--Strengthlessness Palindrome A palindrome is a word or a sentence that reads the same backward as forward. Palindrome is said to have been invented by the Greek Poet Sotades (3rd century BC). They are sometimes called Sotadics in his honour. Examples are given below. Deed Nun Noon Level Solos Peep Shahs Sagas Malayalam 'Madam I'm Adam' 'Able was I ere I saw Elba' 'A man, a plan a canal-Panama' 'Live not on evil' 'Was it a car or a cat I saw?' 'Pull up if I pull up' 'Some men interpret nine memos' 'Not New York, Roy went on' 'Niagara o roar again' 'Yawn a more Roman way' Tongue Twisters Peter piper picked a peck of pickled, pepper. Peter Piper's practical principles of plain and perfect pronunciation The sixth sick sheik's sixth sheep's sick A bloke's back brake-block broke A dozen double dam ask dinner napkins Rubber baby buggy bumpers Rain in Spain mainly stays in plains She sells seashells by the seashore The skunk sat on a stump; the skunk thump the stump stunk, but the stump thump the skunk stunk. A truly rural frugal ruler's mural Blake bug's blood They threw three quick things Still the sinking steamer sank Snow light, no swipe Betsy Bunder bought some butter, but the butter was bitter. So she bought some better butter to make the bitter butter better. Time periods Bicentennial: A period of 200 years Biennial: A period of 2 years Century: A period of 100 years Decade: A period of 10 years Centennial: Every 100 years Decennial: Every 10 years Leap year: A period of 366 days Millennium: A period of 1,000 years Month: A period of 28-31 days Olympiad: Every 4 years Quadrennial: Every 4 years Quadricentennial: Every 400 years Quincentennial: Every 500 years Septennial: Every 7 years Sexcentenary: A period of 600 years Sexennial: Every 6 years Tercentenary: A period of 300 years Triennial: Every 3 years Vicennial: Every 20 years Week: 7 days Year: 365 days Time intervals Annual: occurring every year Biannual: occurring twice a year Bimonthly: occurring every two months or twice a month Biweekly: every two weeks or twice a week Diurnal: daily, of each day Perennial: lasting through a year or several years Semi-annual: occurring twice a year Semi-diurnal: twice a day Semi-weekly: twice a week Trimonthly: every three months Triweekly: every three weeks or three times a week Thrice weekly: three times a week