G10_Revision_HandOut
advertisement

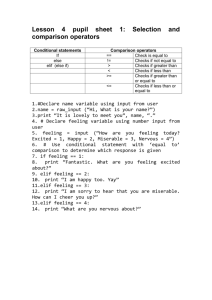
Port Said International Schools – National Section Better education for future generations Revision Handout Grade: 10 Loops & condition statements 1. For …Next: Used to repeat some commands for a specific number of times Example: Dim x As Integer = 1960 For x = 1970 To 2013 Step 2 ListBox1.Items.Add(x) Next x variable is declared in the public section, and we’ve set an initial value of 1960 for it. We’ve set another initial value for it in the For… Next loop. Step is used to determine the incrementing value (in this case it’s 2), so we’ll have these items in the ListBox1 (1970 – 1972 – 1974 – 1976 – 1978 - …………2010 – 2012) Notice that 2013 is NOT included because we add 2 each time until we reach 2013 or less. ================================================================= 2. If … Then … Else. If txt_UserName.Text = "Ahmed" And txt_password.Text = "123456" Then Form1.Show() Else MsgBox("The username or password is not valid", vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "Invalid User name or Password") End If I used compound condition here (Username = Ahmed And Password = 123456), both of them must be evaluated to True. I used the MsgBox( ) Function in the else statement to display a message error for the user Functions in VB Visual Basic functions are: 1) MsgBox( ): used to display message box to the user, it takes 4 parameters(The message that will appear in the dialog box – buttons – Icon - Title), only the message is required. Example: Dim answer As Byte answer = MsgBox("Are you sure ?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "Confirm") answer is used to declare a variable to save the msgbox result in it. The message is “Are you sure?”. The buttons are “vbYesNo”. The Icon is “vbQuestion”. The title is “Confirm”. 2) Rnd: Used to create random numbers between 0 and 1. Example: Randomize() MsgBox(Rnd()) Randomize( ) is used to randomize the random numbers, so each time you run the program you’ll get different numbers, if you don’t use it, each time you run the program you’ll get the same sequence of numbers. I used the Msgbox( ) function to show the result of the Rnd function. Port Said International Schools – National Section Revision Handout Better education for future generations Grade: 10 Size Mode property of the pictureBox has four options: 1. Zoom: is used to fit the image inside the border of the picture box while maintaining the aspect ratio “The ratio of the width to the height”. 2. Stretch image: is used to fit the image inside the border of the picture box without maintaining the aspect ratio “The ratio of the width to the height”. 3. Auto size: is used to enlarge or shrink the picture box control to the image size. 4. Normal: is used for put the image with its actual size in the control and hide part of it or display a part of the picture box background according to the image size – the image upper left corner will be aligned to the control upper left corner. 5. Center image: just like normal put it will center the image in the picture box control. image size and image bit depth properties of the image list: 1. Image size: is used to change the sizes of the images that are imported to this image list. Maximum value is (256, 256). 2. Bit depth: is used to change the sizes of the images that are imported to this image list. Maximum value is (Depth32Bit). Please pay much attention to the controls names, you’ve to follow the naming conventions, you can see examples of that in the accompanied code. Please check the programs you've taken with this revision handout, and read the comments very carefully. Port Said International Schools – National Section Revision Handout Better education for future generations Grade: 10 Multiplication Table: Public Class Form1 Dim fnum, maxnum As Integer Private Sub btn_ShowTable_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_ShowTable.Click fnum = Val(txt_FirstNumber.Text) 'getting the value of the first text box and assign it to the fnum variable maxnum = Val(txt_MaxNumber.Text) 'getting the value of the second text box and assign it to the max variable Dim result As Integer For index As Integer = 1 To maxnum result = fnum * index 'getting the multiplication results lb_Table.Items.Add(fnum & " * " & index & " = " & result) 'I'm displaying here the multiplication table 'lb_Table.Items.Add("Ramy") 'we can display my name as many times as the number of the iterations Next End Sub Private Sub btn_Clear_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_Clear.Click lb_Table.Items.Clear() 'clearing the content of the list box txt_FirstNumber.Clear() 'clearing the content of the first text box "txt_FirstNumber" txt_MaxNumber.Text = "" 'another way to clear a text box End Sub Private Sub btn_Exit_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_Exit.Click End 'Exit the project End Sub End Class Picture Random Position: Public Class Form1 Private Sub Timer1_Tick(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Timer1.Tick Randomize() picB_kodu.Top = Rnd() * 180 'used to get random number between 0 and 180 picB_kodu.Left = Rnd() * 175 End Sub Private Sub btn_hide_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_hide.Click picB_image.Visible = False 'this button is used to hide the picture box End Sub Private Sub btn_show_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click If picB_image.Visible = True Then 'if the image is displayed picB_image.Visible = False 'hide it Else 'if the image is hidden picB_image.Visible = True 'show it End If 'For more details about the size mode of the picture box, please check to the handout. 'For more details about the image size and image bit depth properties of the image list, 'please check the handout. End Sub Private Sub Button2_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_show.Click picB_image.Visible = True 'this button is used to show the picture box End Sub End Class Port Said International Schools – National Section Revision Handout Better education for future generations Grade: 10 Flags: Public Class Form1 Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click PictureBox1.Image = ImageList1.Images(1) 'getting the image from the image list by its index PictureBox2.Image = Nothing 'put nothing in the image property of the picture box. PictureBox3.Image = Nothing 'put nothing in the image property of the picture box. 'PictureBox1.Visible picture by using the visible 'PictureBox2.Visible picture by using the visible 'PictureBox3.Visible picture by using the visible = True property = False property = False property 'another way to show and hide the 'another way to show and hide the 'another way to show and hide the End Sub Private Sub Button2_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click PictureBox1.Image = Nothing PictureBox2.Image = ImageList1.Images(0) PictureBox3.Image = Nothing 'PictureBox1.Visible = False 'PictureBox2.Visible = True 'PictureBox3.Visible = False End Sub Private Sub Button3_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click PictureBox1.Image = Nothing PictureBox2.Image = Nothing PictureBox3.Image = ImageList1.Images(2) 'PictureBox1.Visible = False 'PictureBox2.Visible = False 'PictureBox3.Visible = True End Sub Private Sub ComboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged_1(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles ComboBox1.SelectedIndexChanged picB_big.Image = ImageList1.Images(ComboBox1.SelectedIndex) 'getting the image from the image list by its index and we get the image index 'by getting the selected item index fro the combo box. 'For more details about the image size and image bit depth properties of the image list, 'please check the handout. End Sub End Class Port Said International Schools – National Section Revision Handout Better education for future generations Grade: 10 Simple Calculator: Public Class Form1 Dim num1, num2, total As Integer 'the variables are public which means that we can use them in any place in the code Private Sub btn_factorial_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_factorial.Click num1 = txt_num1.Text total = 1 'initialize the total variable with 1 because we're multiplying numbers ' we can't initialize it to 0, because the result will always be zero For index = 1 To num1 - 1 'don't forget the start value and the end value total = num1 * total num1 = num1 - 1 'num1 -= 1 'another way to decrease the value of num 'num-'another way to decrease the value of num Next ' next keyword is required lbl_result.Text = total the text property 'displaaying the final result in the label by using End Sub Private Sub btn_add_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_add.Click num1 = txt_num1.Text num2 = txt_num2.Text total = num1 + num2 lbl_result.Text = total End Sub Private Sub btn_sub_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_sub.Click num1 = txt_num1.Text num2 = txt_num2.Text total = num1 - num2 lbl_result.Text = total End Sub Private Sub btn_multi_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_multi.Click num1 = txt_num1.Text num2 = txt_num2.Text total = num1 * num2 lbl_result.Text = total End Sub Private Sub btn_divide_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btn_divide.Click num1 = txt_num1.Text num2 = txt_num2.Text If num2 <> 0 Then 'if statement to make sure that we don't divide a number by zero total = num1 / num2 lbl_result.Text = total Else MsgBox("Can't divide by zero") 'message box to show a friendly error message txt_num2.Text = 1 End If End Sub End Class