4th Grade Informative Instructional Writing Rubric
advertisement

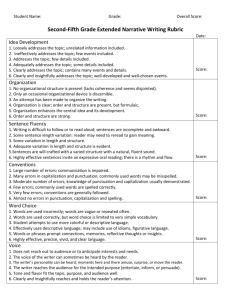
Grade 4 Informative Writing Rubric Aligned to Next Generation Standards and Objectives Focus Content: Topic Development and Support Organization and Flow Smarter Balanced Claim 2: Students can produce effective and well- grounded writing for a range of purposes and audiences. 4 Exemplary 3 Adequate 2 Partial The writer examines a topic and conveys ideas and information clearly by providing a clear introduction, by grouping related information logically; by including formatting, relevant illustrations and multimedia; by linking to ideas within categories or information using words, phrases and clauses (e.g., another, for example, etc.), by using precise language and domainspecific vocabulary and by providing a concluding statement or section. The writer examines a topic and conveys ideas and information clearly by providing a clear introduction, by grouping related information, including formatting, relevant illustrations and multimedia; by linking to ideas within categories or information using words and phrases (e.g., another, for example, etc.), by using precise language and domain-specific vocabulary and by providing a concluding statement. The writer examines a topic and conveys ideas and information clearly by providing an introduction, grouping related information, including illustrations and multimedia; by linking to ideas or information using words and phrases (e.g., another, for example, etc.), by using domain-specific vocabulary, and by providing a concluding statement. The writer examines a topic and conveys information by providing an introduction, related information and illustrations; by linking information using words and phrases (e.g., another, for example, etc.) and by providing a conclusion. The writer develops the topic in an interesting manner by including relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations or other information and examples; the development is to the point and appropriate to task, purpose and audience. The writer develops the topic with facts, definitions, details, quotations or other information and examples related to the topic; the development is to the point and appropriate to task, purpose and audience. The writer develops the topic by including facts, definitions, details, quotations or other information and examples related to the topic; the development is appropriate to task, purpose and audience. The writer develops the topic by including few facts, examples or other information related to the topic; the development is appropriate to task. The writer’s focus is clear and coherent; there are no unnecessary words or information; above grade level words and phrases are used to convey ideas precisely; figurative language and punctuation are used effectively. The writer’s focus is clear and coherent, no unnecessary information is included; grade appropriate words and phrases convey ideas precisely; figurative language and punctuation are used effectively. The writer’s focus is clear and appropriate for the assignment; words and phrases convey ideas precisely; some figurative language is used. The writer attempts to focus on the assignment by using appropriate words and phrases. West Virginia Department of Education Grade 4 Informative 1 Minimal Next Generation Standards Conventions Language Use The writer demonstrates command of the conventions of Standard English grammar and usage by effectively using relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, why); The writer demonstrates partial command of the conventions of Standard English grammar and usage when using relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, why); The writer demonstrates knowledge of the conventions of Standard English grammar and usage by using relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, why); The writer demonstrates some knowledge of the conventions of Standard English grammar and usage when using relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, why); forming and using the progressive verb tenses; forming and using the progressive verb tenses; forming and using the progressive verb tenses; forming and using the progressive verb tenses; using modal auxiliaries (e.g., can, may, must) to convey various conditions; using modal auxiliaries (e.g., can, may, must) to convey various conditions; using modal auxiliaries (e.g., can, may, must) to convey various conditions; using modal auxiliaries (e.g., can, may, must) to convey various conditions; ordering adjectives according to conventional patterns; ordering adjectives according to conventional patterns; ordering adjectives according to conventional patterns; ordering adjectives according to conventional patterns; forming and using prepositional phrases; forming and using prepositional phrases; forming and using prepositional phrases; forming and using prepositional phrases; producing complete sentences and avoiding inappropriate fragments and run-ons; producing complete sentences and avoiding inappropriate fragments and run-ons; producing complete sentences and avoiding inappropriate fragments and run-ons; producing complete sentences and avoiding inappropriate fragments and run-ons; correctly using frequently confused words (e.g., to, too, two). correctly using frequently confused words (e.g., to, too, two). correctly using frequently confused words (e.g., to, too, two). correctly using frequently confused words (e.g., to, too, two). The writer uses correct capitalization and punctuation, including commas and quotation marks to identify direct speech and quotations from a text, a comma before the coordinating conjunction in compound sentences, and spells grade-appropriate words with insignificant errors that need little or no editing. The writer uses correct capitalization and punctuation, including commas and quotation marks to identify direct speech and quotations from a text, a comma before the coordinating conjunction in compound sentences, and spells grade-appropriate words with few errors that need editing but do not distract from the message. West Virginia Department of Education The writer uses capitalization and punctuation, including commas and quotation marks to identify direct speech and quotations from a text and a comma before a coordinating conjunction in compound sentences, and spells grade-appropriate words with errors that need editing. Grade 4 Informative The writer uses capitalization and punctuation, including commas and quotation marks to identify direct speech and quotations from a text and a comma before a coordinating conjunction in compound sentences and spells grade-appropriate words with frequent and repeated errors that distract from the message. Next Generation Standards