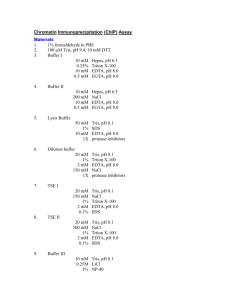
Biotin-Switch procedure

Biotin-Switch procedure
Outer or inner medullary tissue samples were homogenized in ice-cold homogenization buffer (25 mM HEPES, 0.1 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40,
0.5 mM PMSF, plus protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma), pH 7.4), using a Potter-
Elvehjem tissue grinder, followed by centrifugation (2000 g, 10 min). Aliquots
(
500 µl) of supernatants (1 mg/ml protein concentration) were blocked with 4 volumes of blocking buffer containing 225 mM HEPES (pH 7.7), 0.9 mM neocuproine, 2.5% SDS, and 60 mM methylmethanethiosulphonate for 30 min at
50°C. Subsequently, proteins were precipitated for 60 min at -20°C in 2 vol acetone, centrifuged for 10 min at 2,000 g at 4°C, washed with 10 ml cold acetone, dried, and resuspended in the dark in 100
μl HENS buffer containing
250 mM HEPES (pH 7.7), 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% neocuproine, and 1% SDS. Snitrosothiols were decomposed by adding ascorbic acid to a final concentration of
4 mM, followed by incubation with 1/3 vol 4 mM N-(6-(biotinamido)hexyl)3′-(2′pyridyldithio)-propionamide (biotin-HPDP; Thermo Scientific) for 1 h at room temperature. After another precipitation with 2 vol acetone at -
20°C for 1 h, pellets were resuspended in 100 μl HENS buffer. Two vol neutralization buffer, containing 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.7), 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.5% (v/v)
Triton X-100, were added and biotinylated proteins were recovered by incubation of the mixture with 15 µl neutravidin-agarose beads (Thermo Scientific) for 1 h at room temperature with gentle agitation. The beads were collected by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 30 s at 4°C and washed five times with washing buffer containing 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.7), 600 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.5%
Triton X-100. After the final wash, biotinylated proteins were eluted in buffer containing 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.7), 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 100 mM 2mercaptoethanol for 30 min at 37°C with agitation. Proteins in the supernatant were analyzed subsequently by SDS-PAGE and Western blot and probed with anti-TonEBP/NFAT5 antibody.
Detection of S-nitrosylated TonEBP/NFAT5 by immunoprecipitation
Outer or inner medullary tissue samples were homogenized in ice-cold homogenization buffer (25 mM HEPES, 0.1 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40,
0.5 mM PMSF, plus protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma), pH 7.4), using a Potter-
Elvehjem tissue grinder, followed by centrifugation (2000 g, 10 min). For detection of S-nitrosylated TonEBP/ NFAT5, 200 µl lysates (1 mg/ml) of renal medullary tissue homogenates were pre-cleared by the addition of 50 µl protein A sepharose (GE Healthcare Europe, Freiburg, Germany). Subsequently, 2.5 µg polyclonal antiS -nitrosothiol antibody (Sigma) or normal rabbit IgG (Santa Cruz
Biotechnology) was added to the supernatant, and the mixture incubated for 1 h at 4°C with agitation. Immunocomplexes were precipitated by the addition of 50
µl protein A sepharose, followed by incubation for 1 h at 4°C with agitation, and centrifugation at 200 g for 30 s. The pellets were subsequently washed twice with
1 ml chilled TBS containing 1% ( v / v ) NP-40 and 1 mg/ml BSA and once with 0.5
M Tris
–HCl. Following the final centrifugation step, the pellet was resuspended in
SDS sample buffer, subjected to Western blot analysis, and immunostained for
TonEBP/NFAT5 as described above.
Analytical TonEBP/NFAT5-DNA immunoprecipitation
Nuclear extracts from rat inner medullae were prepared using a comercially available nuclear protein extraction kit (Fermentas, St Leon-Rot, Germany), and purity of the extracts were verified by immunodetection of histones. For determination of TonEBP/NFAT5 D
NA binding activity, 10 µg nuclear proteins was incubated with a DNA fragment corresponding to bp –1085 to +49 of the human UT-A promoter and containing a TonE in the native context, for 15 min at room temperature in DNA binding buffer (20 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 1 μg poly(dIdC), 5% glycerol, 0.05% NP-40, 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl
2
, 1 mM EDTA, and
10
μg BSA). Subsequently, DNA-protein complexes were cross-linked with formaldehyde (1% final concentration) for 10 min at 37°C. Aliquots were diluted
10-fold in dilution buffer (0.01% SDS, 1.1% Triton X-100, 1.2 mM EDTA, 16.7 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.1, 167 mM NaCl) and pre-cleared for 2 h with protein Aagarose at 4°C. Protein-DNA complexes were immunoprecipitated using 5 µg
TonEBP/NFAT5 antibody or rabbit-IgG (as negative control). The respective antibody, bound to protein A-agarose, was added to pre-cleared supernatants and incubated overnight at 4°C with constant rotation. Immuncomplexes were consecutively washed with low-salt wash buffer (0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 2 mM EDTA, 20 mM TRIS-HCl, pH 8.1, 150 mM NaCl), high-salt wash buffer (0.1%
SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 2 mM EDTA, 20 mM TRIS-HCl, pH 8.1, 500 mM NaCl),
LiCl wash buffer (0.25 M LiCl, 1% IGEPAL CA630, 1% deoxycholic acid, 1 mM
EDTA, 10 mM TRIS, pH 8.1) and TE buffer. Subsequently, protein A-
immunocomplexes were dissoluted in complete lysis buffer (20 mM Tris
–HCl, pH
7.5, 5 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaCl, 1% (wt/vol) SDS, 50 μg ml −1
proteinase K) for 2 h at 68°C. DNA fragments were recovered (PCR purification kit, Qiagen, Hilden,
Germany) and quantified by semiquantitative PCR, using oligonucleotides “UT-A promoter qPCR” (see Supplemental Table 1, Supplemental Digital Content 2, http://links.lww.com/CCM/A448
) and the “MESA blue 2x PCR Master Mix”
(Eurogentec, Cologne, Germany). Specificity of PCR product formation (~350 bp) was confirmed by melting point analysis and by agarose gel electrophoresis.
Determination of nitrite/nitrate excretion
Urine samples (100 µl) were incubated with 0.1 U/ml nitrate reductase, 50 μM
NADPH, and 5 μM FAD in a final volume of 160 μl for 15 min at 37°C.
Subsequently, lactate dehydrogenase (10 U/ml final concentration) and sodium pyruvate (10 mM final concentration) were added to a final volume of 170 μl and the mixture incubated for 5 min at 37°C. After addition of an equal volume of
Griess reagent and incubation for 15 min at room temperature, the absorbance was measured at 540 nm. Nitrite/nitrate concentration was determined by comparison with a standard curve. Urinary nitrite/nitrate levels were normalized to urinary creatinine concentrations.
Statistical planning
The sample sizes were originally determined to detect relative differences in gene expression values and TonEBP/NFAT5 S-nitrosylation of 25% between the
groups with a power of 0.80 based on the experience from former experiments and on an underlying standard deviation of 15%. Based on this assumption, a calculated number of 6 rats per group were specified in the application of the animal experiment. Since the actually measured relative differences were significantly higher, statistical significant differences between the groups could be detected with n=4 per group. Tissue samples not used for determination of gene expression or TonEBP/NFAT5 S-nitrosylation were then used to determine
TonEBP/NFAT5 DNA-binding activity.
Legend to Supplemental data Fig. 1: Effect of LPS on mRNA levels of V2R
R ats were injected with LPS (■; 5 mg/kg i.p.) or vehicle PBS ( ■
; as control). After
24 h, the animals were sacrificed and kidney samples from the cortex (Cx), outer
(OM) and inner medulla (IM) were processed for further analysis of mRNA abundance of V2R by qRT-PCR. Expression in the IM of PBS-treated animals was defined as 1. Relative mRNA abundance was determined by the
CTmethod, using
-actin as housekeeping gene. Data are means
SEM for n =4;
* P <0.05. Supplemental Figure 1 can be accessed through this link: Supplemental
Digital Content 3, http://links.lww.com/CCM/A449.