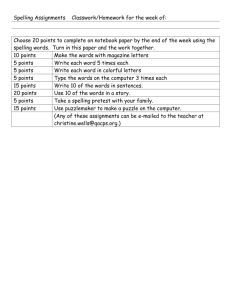
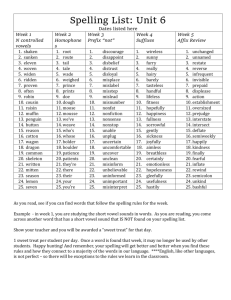
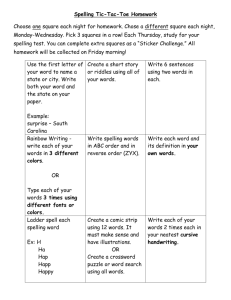
Stages of Developmental Spelling Reference Sheet
advertisement

Stages of Developmental Spelling Reference Sheet Adapted from Cox (2002) and Zarillo (2002) Precommunicative •Scribbling can be representational •Understands speech can be written •Lacks concept of a word •Makes letterlike shapes •May write name Semiphonetic •Spells few words correctly but knows letters make words •Still invents symbols for letters and words •Makes 1-3 letter representations of words, usually consonants •Has more control over beginnings and endings of words •Predicts words auditorially in frequently occurring patterns Phonetic •Spellings include all sound features of words as heard. •Invents system of phonetic spelling that is consistent •Understands relationship of sounds in speech to symbols in writing • Spelling can be read by others Example: I lik two fli a kit [I like to fly a kite] Transitional •Begin to spell conventionally and knows it is necessary for others to read their writing •Uses knowledge of how words look as well as sounds and applies to other words •Includes vowels in every syllable •Uses familiar spelling patterns. •Intersperses conventional spelling with invented spelling Example: He is on a spaceship sershing for a krater. Conventional •Begins to spell correctly •Has mastered root words, past tense, and short vowels •Still struggles with consonant doubling, letter position, and work affixes •Has growing knowledge of word meanings and complicated vowel patterns. (For RICA Reference) Methods of assessing spelling development: In Isolation- Spelling test In Context – writing samples How to teach spelling: Spelling lists and tests Small group and individualized spelling instruction “Invented Spelling” - phonetic spelling Orthographic patterns: RICA Content specifications use the phrase orthographic patterns, which are the frequently occurring letter combinations of English spelling (i.e., the rime –ight, the suffix –tion)