POLA_26060_sm_SuppInfo
advertisement

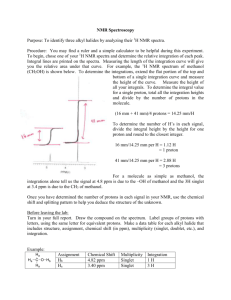
Supporting Information Synthesis and Poly[poly(ethylene Self-assembly of Amphiphilic glycol) Brush-Dendritic-Linear-like methyl ether methacrylate]-b-Polyamidoamine-b-Poly(ε-caprolactone) Copolymers Xiaohua He1, Liang Zhong1, Xiaomeng Wu1, Xin Cai1, Meiran Xie1, Shaoliang Lin2*, Deyue Yan3 1) Department of Chemistry, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China 2) The Key Laboratory of Advanced Polymer Materials of Shanghai, School of Materials Science and Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai 200237, China 3) School of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China Synthesis of the propargyl focal point polyamidoamine (PAMAM) type dendrons with 2m primary amine groups [denoted as Dm (m=1, 2, and 3: generation of dendron) The propargyl focal point PAMAM type dendrons (Dm) were synthesized according to the similar procedure reported by Lee et al.1 Under nitrogen atmosphere, methyl acrylate (MA, 40 mL, 0.44 mol) and methanol (50 mL) were added into a 150-mL round bottom flask equipped with magnetic stirrer bar. The flask was then immersed into an ice-water bath. A solution of progargylamine (denoted as D0, 3.0 mL, 43.8 mmol) in methanol (25 mL) was introduced dropwise to the flask through a dropping funnel over 30 min. The mixed solution was stirred vigorously for another 1 h at 0 oC, and then for an additional 48 h at room temperature under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction solution was evaporated on a rotary evaporator. The residues were further purified by a silica column chromatograph using ethyl acetate/petroleum ether (1:2 v/v) as eluent to afford 9.5 g of the methyl ester-terminated D0.5 as a colorless oil (yield: 96%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 3.66 (s, 6H, -OCH3), 3.47 (s, 2H, CHCCH2N-), 2.81 (t, 4H, -N(CH2CH2COO)2-), 2.49 (t, 4H, -N(CH2CH2COO)2-), 2.20 (s, 1H, CHCCH2N-). Under nitrogen atmosphere and stirring, a solution of D0.5 (6 g, 26.40 mmol) in methanol (30 mL) was added dropwise to another solution of ethylenediamine (EDA, 28 mL, 0.12mol) in methanol (40 mL) over 30 min at 0 oC. The reaction mixture was stirred vigorously for 1 h 1 at 0 oC and then for another 48 h at room temperature under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction solution was concentrated by a rotary evaporator at 35 oC, and the excess EDA was removed using azeotropic mixture of toluene and methanol (9:1 v:v). The remaining toluene was removed using an azeotropic distillation using methanol under nitrogen atmosphere, and the residue was dried in vacuo at 35 oC for 24 h to afford 6.88 g of the propargyl focal point polyamidoamine (PAMAM) type dendron D1 with 2 primary amine groups as a pale yellowish oil (yield: 92%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 7.32 (s, 2H, -CONH-), 3.42 (s, 2H, CHCCH2N-), 3.30 (t, 4H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2), 2.84 (q, 4H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2; 4H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.39 (t, 4H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.23 (s, 1H, CHCCH2N-), 1.45 (s, 4H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2). D2 and D3 was synthesized from D1 and D2, respectively, using the same method as successive Michael addition of primary amines with MA and amidation of methyl ester groups with a large excess of EDA. D1.5, ethyl acetate/methanol (9:1 v/v) as eluent, a pale yellowish oil, yield: 93%. 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 7.09 (s, 2H, -CONH-), 3.67 (s, 12H, -OCH3), 3.47 (s, 2H, CHCCH2-), 3.30 (q, 4H, -CONHCH2CH2N-), 2.85 (t, 4H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.76 (t, 8H, -NCH2CH2COO-), 2.55 (t, 4H, -CONHCH2CH2N-), 2.44 (t, 8H, -NCH2CH2COO-), 2.39 (t, 4H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.19 (s, 1H, CHCCH2-). D2, a pale yellowish oil, yield: 96%. 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 7.87 (s, 2H, -CONH-), 7.62 (s, 4H, -CONH-), 3.41 (s, 2H, CHCCH2N-), 3.26 (m, 8 H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2; 4H, -CONHCH2CH2N-), 2.81 (m, 12H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.72 (t, 8H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2), 2.52 (t, 4H, -CONHCH2CH2N-), 2.35 (t, 12H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.21 (s, 1H, CHCCH2N-), 1.49 (s, 8H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2). D2.5, ethyl acetate/methanol (1:1 v/v) as eluent, a pale yellowish viscous oil, yield: 88%. 1 H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 7.79 (s, 2H, -CONH-), 7.12 (s, 4H, -CONH-), 3.66 (s, 24H, -OCH3), 3.47 (s, 2H, CHCCH2-), 3.32-3.27 (m, 12H, -CONHCH2CH2N-), 2.82 (t, 12H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.76 (t, 16H, -NCH2CH2COO-), 2.55 (t, 12H, -CONHCH2CH2N-), 2.44 (t, 16H, -NCH2CH2COO-), 2.39 (t, 12H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.22 (s, 1H, CHCCH2-). D3, a pale yellowish viscous oil, yield: 95%. 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 7.96-7.54 (m, 14H, -CONH-), 3.45 (s, 2H, CHCCH2N-), 3.27 (m, 28H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.81 (m, 12H, 2 -CONHCH2CH2N-; 16H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2), 2.75 (t, 16H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2), 2.52 (m, 12H, -CONHCH2CH2N-), 2.37 (t, 28H, -NCH2CH2CONH-), 2.24 (s, 1H, CHCCH2N-), 1.65 (s, 16H, -CONHCH2CH2NH2). Synthesis of 2-Azidoethanol 2-azideoethanol was synthesized according to the similar procedure reported by Li et al. 2 The procedure was as follows: 2-chloroethanol (6.0 g, 75 mmol), sodium azide (9.7g, 150 mmol), tetrabutylammoniumiodide (3.0 g, 8 mmol) and 2-butanone (40 mL) were added into a 250 mL round-bottom flask equipped with a condenser, nitrogen inlet/outlet and a magnetic stirrer bar. The reaction mixture was stirred at 80 oC for 24 h. After removing the insoluble solid by a filter and evaporating the solvent by rotary evaporation, the obtained yellow oil residues were distilled under reduced pressure to afford 4.8 g of 2-azidoethanol as a colorless oil (yield: 74%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 4.79 (2H, CH2OH), 1.97 (1H, CH2OH), 3.48 (2H, CH2N3). Synthesis of 2-Azidoethyl-2-bromoisobutyrate (AEBIB) 2-Azidoethyl-2-bromoisobutyrate (AEBIB) was synthesized according to the similar procedure reported by Gao et al.3 2-Azidoethanol (2.0 g, 23 mmol), anhydrous Et3N (3.9 mL, 27.8 mmol) and anhydrous methylene chloride (30 mL) were added into a 100 mL two-neck round-bottom flask equipped with a 20-mL dropping funnel. Under nitrogen atmosphere and magnetic stirring, a mixture of 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide (5.8 g, 25 mmol) in anhydrous methylene chloride (15 mL) was added dropwise into the previous solution by the dropping funnel at 0 oC. The reaction mixture was stirred for 24 h. After removal of the insoluble solid, the solution was washed successively with distilled water (3×70 mL). The combined organic phase was dried over anhydrous MgSO4 overnight, filtered and evaporated methylene chloride on a rotary evaporator, and the residues were further purified by a silica column chromatograph using CH2Cl2/petroleum ether (1:1 v/v) as eluent to afford 4.9 g of AEBIB as a colorless oil (yield: 91%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, δ/ppm): 4.34 (t, 2H, -COOCH2CH2N3), 3.52 (t, 2H,-COOCH2CH2N3), 1.96 (s, 6H, -C(CH3)2-Br). 3 Figure S1. The micelles size distribution profiles of PPEGMEMA27-b-D2-b-(PCL90)4, determined by DLS. Reference 1 Lee, J. W.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, H. J.; Han, S. C.; Shin, W. S.; Jin, S.-H. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2418-2422. 2 Li, J.; He, W.-D.; Han, S.-c.; Sun, X.-l.; Li, L.-y.; Zhang, B.-y. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 786-796. 3 Gao, C.; He, H.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 360-370. 4