Writing
advertisement

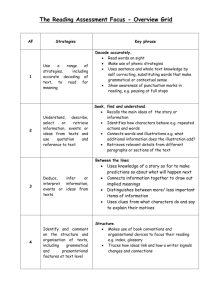
Curriculum Planning Guidelines – Progression Points – Familiarisation tools English – Writing (Level 5) Students write a variety of text types, both print and electronic form, including narratives, reports, persuasive texts and procedures. They write for a range of purposes including speculating, explaining and persuading. They write texts that develop a topic in a coherent way around their intended purpose and make some adjustments for audience knowledge and background. They use a variety of sentence forms, prioritise ideas through the use of headings, graphics, photographs or artwork to achieve their purpose. They draw on visual and morphemic knowledge to spell unfamiliar words and represent every sound with a logical letter combination. They display an awareness of grammatical conventions including tense and subject-verb agreement through appropriate use. Correct punctuation is usually used, including the use of colons and semi-colons. They use a range of strategies including the computer and graphic organisers in planning and collating knowledge for writing different text types. They use editing and proof-reading strategies for clarity in communicating the intended message. Students write a variety of text types, both print and electronic form, including narratives, reports, explanations, persuasive texts and procedures. They write for a range of purposes including speculating, explaining, persuading and reflecting. They write persuasive texts about contemporary issues and justify a personal viewpoint providing one or two arguments. They write texts that develop themes in coherent ways around their intended purpose and have an explicit, clearly stated viewpoint usually using suitable headings and subheadings to organise the information, graphics, photographs and artwork. They experiment with different techniques depending on the purpose, to influence the audience. They use a variety of sentence forms, appropriate grammatical conventions including tense, subject-verb agreement and noun-pronoun agreement. They mostly have correct spelling, having difficulty only with unusual spelling patterns. They use familiar base words to spell new words. They use strategies including planning of paragraphs and integrating ideas across sentences within a paragraph for different text types. They use editing and proof-reading skills for clarity and for cohesiveness of ideas. Students write a variety of text types, both print and electronic form, including narratives, reports, explanations, persuasive texts, procedures and transactions. They write persuasive texts and justify a personal viewpoint, using three or more pieces of supporting information. They write explanations or reports that target challenging themes and issues about topics that are less familiar with and personal reflections or evaluations of texts. They write expressively in their development of characters and development of a resolution. They strategically use headings and subheadings, graphics, photographs and artwork to directly support their text. They use morphemic knowledge to spell words when adding suffixes and prefixes and usually recognise when a word is spelt incorrectly. They use a variety of sentence forms including more complex sentences with embedded clauses or phrases, display appropriate grammatical conventions and punctuation. Computers are used to organise, format, revise and present texts. They proof read and redraft for clarity, cohesiveness and consistency of style. At Level 5, students produce, in print and electronic forms, texts for a variety of purposes, including speculating, hypothesising, persuading and reflecting. They write extended narratives or scripts with attention to characterisation, consistency of viewpoint and development of a resolution. They write arguments that state and justify a personal viewpoint; reports incorporating challenging themes and issues; personal reflections on, or evaluations of, texts presenting challenging themes and issues. Students improve the accuracy and readability of their writing, developing confidence in the identification and use of grammatical conventions and features of language and in their use of figurative language. They use a range of punctuation accurately to support meaning, including the use of ellipses, dashes, colons and semi-colons. They control tenses, and subject-verb and noun-pronoun agreement. They accurately identify and use different parts of speech. They edit their writing for clarity, coherence and consistency of style, and proofread and correct spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors. Office of Learning and Teaching DE&T