U - Waterford Public Schools
advertisement

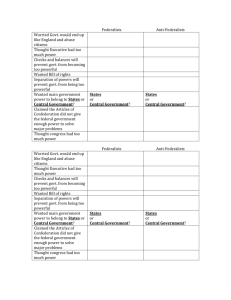
U.S. History The Road to Ratification: The Battle Between Federalists & Anti-Federalists After many long debates over how to structure the new government, the delegates completed a final draft of the U.S. Constitution on September 15, 1787. The completed U.S. Constitution was an outline for how the American government would operate. The document was a list of rules that the government would have to follow. On that day the delegates voted to support the Constitution in its final form. The next day it was written on four large pieces of parchment paper and all but three of the delegates signed the document. Copies of the document were then sent to all 13 states for ratification (official approval). Small conventions were held in each state where delegates could debate whether or not to ratify the new Constitution. Samuel Huntington said of the state conventions, This is a new event in the history of mankind. Heretofore, most governments have been formed by tyrants and imposed on mankind by force. Never before did a people…meet together by their representatives and…frame themselves a system of government. The Roots of America’s First Political Parties… The Constitution had been printed in pamphlets and newspapers distributed throughout the country. Citizens from all 13 states had been debating whether or not the Constitution would be a good replacement for the old Articles of Confederation. The Founding Fathers were aware that the Constitution was going to cause some controversy. They began using different tactics to persuade Americans to ratify the document. The Founding Fathers suspected that people would be afraid that the Constitution took away too much power from the state governments. To calm people’s nerves, the Founding Fathers explained that the Constitution was based on federalism. Federalism is a system of government in which power is shared between the central (sometimes called the federal or national) government and the states. Linking themselves to the idea of federalism, the people who supported the ratification of the Constitution became known as Federalists. Some historians view the Federalists as the first political party in the United States. The Federalists were a group of people who shared the same beliefs about government (i.e. that power should be shared between the states and the national government). Their main goal was to convince other Americans to ratify the Constitution. People who opposed the ratification of the Constitution were known as AntiFederalists. Some historians view the Anti-Federalists as one of the country’s first political parties because they also had shared beliefs about government. They thought that the Constitution took too much power away from the state governments. They feared that the powerful federal government established by the Constitution could take away people’s individual rights (much in the same way that the British Monarchy had done to the colonists). Anti-Federalists did not like that the Constitution created the office of the presidency. They feared that a powerful president might simply declare himself king. AntiFederalists wrote articles in newspapers saying that they could not believe that the same men who fought against the powerful British tyranny would try to establish a new tyranny like the Constitution. They feared that Americans would lose the liberties (freedoms) that they’d won after the Revolutionary War. The table below highlights some of the different beliefs that the Federalists and Anti-Federalists held. Federalists Anti-Federalists Supported removing some powers from the states and giving more power to the national government Wanted most of the important political powers to remain with the states Favored dividing powers among different branches of the government (legislative, executive, judicial) Proposed a single person (the president) to be the head of the executive branch Wanted the legislative branch (Congress) to have much more power than the executive branch (the president) Feared that a strong executive (president) might become a tyrannical king This map illustrates how a majority of people in each sate felt about the ratification of the Constitution. States that opposed the ratification had large populations of Anti-Federalists. States that supported the ratification had large populations of Federalists. Believed that a Bill of Rights needed to be included in the Constitution to protect people’s rights (i.e. the freedom of speech, right to privacy, right to own guns) Name: Date: Core: U.S. History The Road to Ratification: Reflection Questions Directions: Use your class notes (today’s Do At Bell: Vocabulary Builder) and the Road to Ratification: The Battle Between Federalists & Anti-Federalists handout to answer the following questions. Fact Check… 1. What is a political party? _________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the U.S. Constitution? ____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Define the verb “rratify”: __________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Define the word “ffederalism”: _____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Identify some ways that the two parties attempted to persuade other Americans to vote for or against the ratification of the Constitution. _________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Identify the two groups that some historians view as the United States’ first political parties. Be sure to write the name of the political party next to the beliefs about government that members of that political party held. Political Party Beliefs About Government This party felt that the Constitution gave too much power to the national government and did not give enough power to the states. This party believed that the Constitution was better than the Articles of Confederation because it balanced the powers of the national and state government. 7. Map Skills. Study the map key and use it to answer the following questions. a. Were most people in Connecticut Federalists or Anti-Federalists? _______________________ b. Were most people in Virginia Federalists or AntiFederalists? _______________________ c. Were most people in Masschusetts Federalists or Anti-Federalists? _______________________ Reader Response… 1. Based on your understanding of the reading, do you think a Federalist or an Anti-Federalist would support giving only state governments the power to tax people? Support your answer using evidence from the text. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 4 Exemplary Insightful, well organized, and fluent Deep understanding of text is demonstrated Specific references to text are used to support ideas Text references are well interpreted and clearly connected to response 3 Proficient Thoughtful, organized, and fluent Clear understanding of the text is demonstrated Relevant references to text are used to support ideas Text references are explained and connected to response 2 Progressing Organized and somewhat fluent Basic understanding of text is displayed At least one relevant example from text is used to support ideas Text references are somewhat connected to response 1 Beginning Disorganized or confusing Limited or no understanding of text is displayed Limited or no examples from text are used to support ideas Text reference seems irrelevant to response