pmic7551-sup-0001-Supmat
advertisement

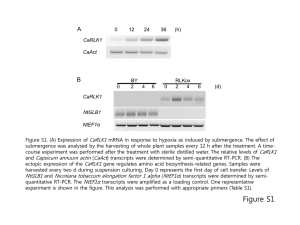
Supporting Information High Throughput Screening of Disulfide-Containing Proteins in a Complex Mixture Dong S. Zhao, 1,† Zachery R. Gregorich, 1,2 and Ying Ge1,2,3,4* 1 The Human Proteomics Program, 2 3 Department of Cell and Regenerative Biology, School of Medicine and Public Health, 4 Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, 53706. Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology Training Program, *Corresponding author: Ying Ge, PhD, 1300 University Ave., SMI 130, Madison, WI 53706, Tel: 608-263-9212, Fax: 608-2655512, E-mail: ge2@wisc.edu. † Current address: Irvine Pharmaceutical Services, Inc., 6 Vanderbilt, Irvine, CA 92618 EXPERIMENTAL Materials: All materials were obtained commercially and were used without further purification. Bovine insulin (5.7 kDa), bovine serum albumin (BSA, 66.4 kDa), bovine cytochrome C (Cyt C, 12.2 kDa), -lactoglobulin (BLG, 18.3 kDa), chicken egg lysozyme (Lyso, 14.3 kDa), glycosylated ribonuclease B (RNase B, 14.9 kDa), ubiquitin (Ubi, 8.6 kDa), formic acid (FA), citric acid, guanidineHCl, and tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) hydrochloride were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), used as received. Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) was obtained from Pierce (Rockford, IL, USA). Ultrapure water (specific conductivity, 18.2 M/cm) was produced by a MilliQ device (Millipore, Eschborn, Germany). HPLC grade acetonitrile (ACN) was purchased from EMD (Billerica, MA, USA). Solutions of 100 mM and 10 mM TCEP were freshly prepared for each use in distilled water. Disulfide Bonds Reduction with TCEP: Protein mixtures containing BSA, Cyt C, BLG, Lyso, RNase B, and Ubi were mixed with equal volume of TCEP in 0.1 M citric buffer (total protein:TCEP 1:5000, pH = 3) and incubated at 65 C for 30 min. There is no detectable protein precipitation in the acidic buffer during our experiments. This method produces a full reduction of disulfide bonds. Reversed-Phase Chromatography: The reversed-phase HPLC separation was carried out using a Waters 2695 HPLC system (Waters, Milford, MA) for on-line separation/desalting. An ACE C18 reversed-phase column (250 x 4.6 mm, 90 Å, ACE, Aberdeen, Scotland) was chosen for separation of the protein mixture at 40 C column temperature, monitoring at 214 nm. The separation was carried out with a linear gradient from 73% solvent A (0.025% TFA and 0.1% FA in H2O) and 27% solvent B (0.1% FA in ACN) to 50% solvent B in 40 minutes. Flow rate was 0.6 mL/min. Q-TOF MS and Data Processing: LC/MS spectra were collected on a Waters quadrupole time-offlight (Q-TOF) mass spectrometer equipped with a z-spray electrospray ionization source (Waters, Milford, MA). Data were acquired and analyzed by the Waters MassLynx software package. The instrument was calibrated over an m/z range of 100 to 2000 using multiply charged ions of sodium formate. Intact protein mass spectra were deconvoluted using Waters MassLynx Max-Ent 1 software to obtain the deconvoluted MWs. Supplemental Table 1. Determination of molecular weights of the non-reduced and reduced RNase B and assignment of their glycosylation state. Peaks Non-reduced Reduced Assignment of glycosylation state MW. Cal. MW. Exptl. MW. Cal. MW. Exptl. I 14899.4 14899.5 14907.4 14907.5 Man5GlcNac2 II 15061.6 15061.5 15069.7 15069.5 Man6GlcNac2 III 15233.8 15223.5 15231.9 15231.5 Man7GlcNac2 IV 15386.0 15385.5 15394.0 15393.5 Man8GlcNac2 V 15548.2 15547.05 15556.2 15555.5 Man9GlcNac2 FIGURES Supplemental Figure 1. ESI/MS analysis of (A) non-reduced and (B) reduced RNase B. Left panel, low resolution V mode detection of molecular ions (M8+ - M12+); right panel: high resolution W mode detection of molecular ions (M13+). The mass difference between reduced and non-reduced molecular ions is 8 Da, corresponding to 4 disulfide bonds in RNase B. Supplemental Figure 2. ESI/MS analysis of (A) non-reduced and (B) reduced -lactoglobulin. Main panel, low resolution V mode detection of molecular ions; Inset, deconvoluted masses of lactoglobulin variants A and B. The mass difference between reduced and non-reduced molecular ions is 4 Da, corresponding to 2 disulfide bonds in BSA.