NaCl Solubility Product Constant Lab Report
advertisement

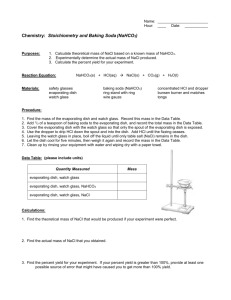
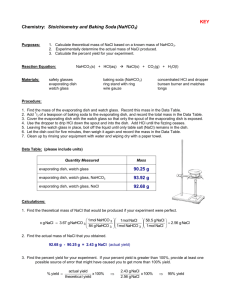
Lab-The Solubility Product Constant of Sodium Chloride Ksp of NaCl Objectives: -Prepare a saturated solution of NaCl -Determine the solubility product constant of NaCl Materials: 25 ml graduated cylinder 150 and 100 ml beaker balance evaporating dish ringstand with ring tongs Bunsen burner spatula water NaCl wire gauze Safety: -Follow general safety procedures -When heating the saturated salt solution, remember to reduce the size of the flame as the solution is close to dryness Procedure: 1. Prepare a saturated solution of NaCl : Measure 25 ml of water in the graduated cylinder. Pour this water into the 150 ml beaker. Measure 10.0 g of NaCl and add this to the beaker of water. Stir for one minute. There should be some undissolved solid on the bottom of the beaker. Allow the solid to settle, and then decant the clear, saturated solution into the 100 ml beaker. 2. Determine the mass of the evaporating dish to the nearest 0.01 g. 3. Use the graduated cylinder to measure approximately 10 ml of the saturated salt solution. Record this volume to the nearest 0.1 ml. Pour this portion of the saturated solution into the evaporating dish. 4. Assemble the ring stand, ring, wire gauze and Bunsen burner. Clamp the ring assembly several centimeters above the flame so that you can heat gently and avoid spattering. Place the evaporating dish on the wire gauge and heat the solution to evaporate it. When the solution is close to dryness, reduce the burner to a very low flame and continue heating for 10 minutes. 5. When heating is complete, remove the evaporating dish with tongs and place it on the base of the ring stand to cool. Then determine the mass of the evaporating dish and solid residue to the nearest 0.01 g. Data and Analysis: Create a data table with to record the following information: mass of the empty evaporating dish, volume of the saturated NaCl solution and mass of evaporating dish and NaCl Conclusion: (Be sure to show your work in order to receive credit!) 1. Determine the mass of dry NaCl residue in the evaporating dish. 2. Calculate the moles of dry NaCl. (convert mass in grams of NaCl to moles) 3. Calculate the concentration of the original 10 ml of NaCl before drying. (calculate the moles/L) 4. Write the equilibrium equation for the saturated solution. Hint: 1 mole of NaCl dissociates into 1 mole of Na+ ions and 1 mole of Cl- ions) 5. Write the Ksp for the system. 6. Calculate the Ksp for the system. 7. The actual Ksp for NaCl is 28.8. Calculate your percent error.