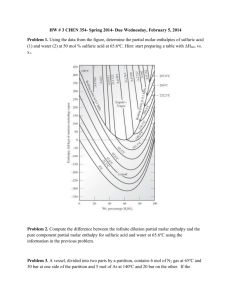
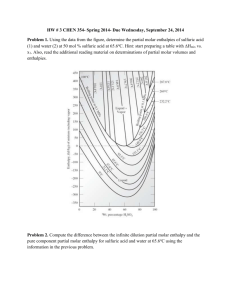
Problem Set 1 - First law of Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry
advertisement

CH 240 Problem Set 7.2 2010/11 First law of Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry: N.B. Where heat capacities (Cp) and standard enthalpies of formation ∆fH are not provided use the tabulated standard thermodynamic data from your textbooks. 1. How many joules of heat are required to change 100.0 g of ice at 0.0ºC to water at 40.0ºC? The heat of fusion (melting) for water is 333 J/g. 2. Using the tabulated standard enthalpies of formation, calculate the standard enthalpy of combustion of ethylene to give carbon dioxide and water vapor. 3. One mol of water is vaporized at 100 ºC and 1 atm. The heat of vaporization is 40.69 kJ/mol. Calculate the values of (i) w (ii) q (iii) ∆U (iv) ∆H. 4. The temperature dependence of the molar heat capacity of n-butane is expressed by the equation: Cp = 19.41 + 0.233T (J K-1 mol-1) Calculate the heat necessary to raise the temperature of 1 mol n-butane from 25 to 300 ºC. 5. One mol of argon is allowed to expand adiabatically from a pressure of 10 atm and 298.15 K to 1 atm. What is the final temperature and how much work can be done? 6. A tank contains 20 litres of compressed nitrogen at 10 atm and 25 ºC. Calculate the work obtained when the gas is allowed to expand to 1 atm pressure: (i) reversibly and isothermally. (ii) reversibly and adiabatically. 7. Calculate the temperature increase and the final pressure if one mol of helium is compressed adiabaticaly and reversibly from 44.8 litres at 0ºC to 22.4 liters. 8. One mol of ideal gas at 25ºC and 100 atm is allowed to expand reversibly and isothermally to 5 atm. Find: (i) the work done by the gas (ii) the heat absorbed and (iii) enthalpy change. 9. The empirical expression for the heat capacity of chlorine as function of temperature is: CP 37.03 6.70 104 T 2.84 105 T 2 JK-1mol-1 Calculate H, U, q and w when one mole of chlorine is heated from 298 to 1000 K at 1 atm, assuming chlorine behaves ideally. 10. 27 cal are evolved on completely neutralizing 20 ml of 0.1 M aq. HCl with NaOH. What is the H for the reaction: H+(aq) +OH-(aq) H2O(l) 11. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of cyanamide (CH2N2) given the following standard enthalpies of reaction. i) CH2N2(s) + 3/2.O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(l) + N2(g) Hº = -741.4 kJ/mol ii) H2(g) + 1/2.O2(g) H2O(l) Hº = -285.8 kJ/mol iii) C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) Hº = -393.5 kJ/mol 12. In a calorimetry experiment, 1.15 grams of glucose (molar mass = 180 g/mol) is burned in a calorimeter, causing the temperature to increase from 23.40ºC to 27.21ºC. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 958 J/K and the calorimeter contains 899.5 grams of water, calculate the amount of heat given off per mol of glucose under these conditions.