Review Answers
advertisement

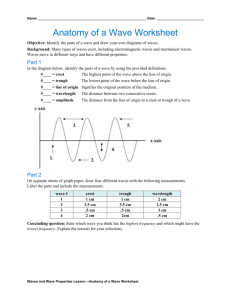
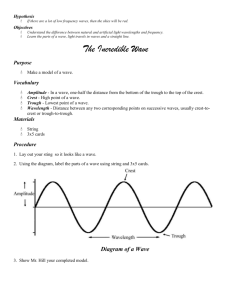
Name: _____________ Conceptual Physics: Wave & Sound Unit Review Worksheet 1. TRUE or FALSE: In order for John to hear Jill, air molecules must move from the lips of Jill to the ears of John. Explain your reasoning… No. The air molecules just have to transfer the energy to the next molecule they run into. 2. Draw a longitudinal wave and label the wavelength, compression and rarefactions (stretches). Picture. 3. A science fiction film depicts inhabitants of one spaceship (in outer space) hearing the sound of a nearby spaceship as it zooms past at high speeds. Critique the physics of this film. Sounds need air (or some medium) in order to travel. Space doesn’t have any medium. 4. Consider the diagram below in order to answer the following questions. a. The wavelength of the wave in the diagram above is given by letter __A_. b. The amplitude of the wave in the diagram above is given by letter __D_. 5. A wave has amplitude of 2 cm and a frequency of 12 Hz, and the distance from a crest to the nearest trough is measured to be 5 cm. Determine the period of such a wave. T = 1/12 s = 0.083 6. A fly flaps its wings back and forth 150 times each second. The period of a wing flap is_____. T = 1/150 s = 0.0067 7. A tennis coach paces back and forth along the sideline 10 times in 2 minutes. The frequency of her pacing is ________ (cycles per minute). F = 10 cycles /120 seconds = 0.083 Hz 8. The frequency of rotation of a second hand on a clock is _______. 1 cycle/ 60 s = 0.0167 Hz 9. A kid on a playground swing makes a complete to-and-fro swing each 2 seconds. The frequency of swing is _________. 1 cycle/ 2 seconds = 0.5 Hz 10. In problem #9, the period of swing is __________. T = 1/f = 2 s 11. As the frequency of a wave increases, the period of the wave ___________. Decrease 12. A transverse wave is found to have a vertical distance of 8 cm from a trough to a crest, a frequency of 12 Hz, and a horizontal distance of 6 cm from a crest to the nearest trough. Determine the amplitude, period, wavelength and speed of such a wave. A = 4 cm; T = 1/12 = 0.083 s; λ = 12 cm; v = 144 m/s 13. An automatic focus camera is able to focus on objects by use of an ultrasonic sound wave. The camera sends out sound waves, which reflect off distant objects and return to the camera. A sensor detects the time it takes for the waves to return and then determines the distance an object is from the camera. If a sound wave (speed = 340 m/s) returns to the camera 0.150 seconds after leaving the camera, how far away is the object? 25.5 m 14. A transverse wave is found to have a distance of 4 cm from a trough to a crest, a frequency of 12 Hz, and a distance of 5 cm from a crest to the nearest trough. Determine the amplitude, period, wavelength and speed of such a wave. A = 4 cm; T = 1/12 = 0.083 s; λ = 10 cm; v = 120 m/s 15. Several positions along the medium are labeled with a letter. Categorize each labeled position along the medium as being a position where either constructive or destructive interference occurs. Constructive at G, J, M, & N Destructive at H, I, K, L & O 16. The number of nodes in the standing wave shown in the diagram below is 8 17. Twin water bugs Jimminy and Johnny are both creating a series of circular waves by jiggling their lgs in the water. The waves undergo interference and create a pattern represented in the diagram. The thick lines represent the crests of the waves and the thin lines represent the troughs. Several positions are labeled with a letter. Categorize each as destructive or constructive interference. Constructive: A, B, & E Destructive: C, D, & F 18. Why is light (transmitted by stars) shifted toward the red end of the spectrum? The stars are moving away from us. 19. Draw what would happen if the two waves with different frequencies encountered the barriers below. Drawing should illustrate Huygen’s Principle. 20. Draw what would happen if the waves encountered the situations below. Drawing should illustrate reflection and Huygen’s Principle. 21. What happens as a plane approaches the sound barrier and what happens when it crosses over the sound barrier. Waves build up in front of the plane so that a large pressure wave is being pushed by the plane. When it exceeds the speed of sound if effectively moves through the pressure wave which expands behind the plane. The pressure wave is what we experience as a sonic boom. 22. Explain how a brass, string, and reed instrument make sound. Make sure to mention the words “forced vibration”, “resonance”, and natural frequencies. Brass and reed instruments vibrate the air column by vibrating a mouthpiece or reed. As the air column vibrates at a natural frequency (determined by the air column) sound is generated from the instrument. A stringed instrument vibrates the string at its natural frequency, which forces the instrument’s sound chamber to vibrate. This causes the air in contact with the sound chamber to vibrate and generate sound. 23. What is a beat? If you hear two instruments that have a beat equal to 2 times per second, what can you tell about the frequencies of the sounds? Their frequencies are off by 2 Hz.