Ecosystems ecosystem is a natural system, in which the life cycles of
advertisement

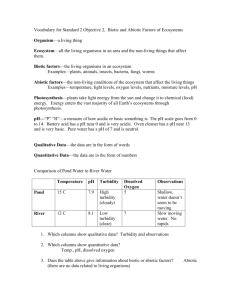
ECOSYSTEMS ecosystem flora fauna non-living environment living environment biomes is a natural system, in which the life cycles of its parts are closely lined to each other plants animals water – in the form of rain or water in the soil air – provides oxygen and carbon dioxide solar energy – primary source of energy, heat and light rocks – provide nutrients (permeable/impermeable) soils – vary in depth, acidity, nutrients and fertility plants, animals, insets and micro-organisms – harmony people – disharmony the world's major communities, classified according to the predominant vegetation and characterized by adaptations of organisms to that particular environment main source of energy is sunlight sunlight is absorbed by green plants and converted through photosynthesis energy passes through the ecosystem in the food chain it´s an open system plants/algae use carbon dioxide and water to make carbohydrates (energy) through the photosynthesis process photosynthesis food chain energy moves around within an ecosystem, from factor to factor, as producers and consumers are eaten and this flow of energy is what we call the food chain. recycling of nutrients some nutrients are part of a closed system plants take up nutrients from the soil they are returned back through dead bodies of animals micro – water droplet meso – freshwater pond, sand-dunes global – tropical rainforest, coniferous forest flow of energy levels of ecosystems ECOSYSTEMS An ecosystem is an environment containing a community of interdependent plants and animals. It is all the animals and plants in a particular area, and the way in which they are related to each other and to their environment. Food chains link animals to the plants/animals they eat and the animals that eat them. Communities Ecosystems are made up of both non-living (abiotic) and living (biotic) factors. • Abiotic factors are the elements of an ecosystem that are non-living. Nevertheless, they still have an affect on the ecosystem. Water, temperature, relief, soil type, fire, and nutrients are all examples of abiotic factors. • Biotic factors are the living elements of an ecosystem, i.e. plants and animals. All biotic factors require energy to survive. These living organisms form a community within an ecosystem. Biotic and abiotic factors are interrelated. If one factor is changed or removed, it impacts the availability of other resources within the system. Biotic and abiotic factors combine to create a system or more precisely, an ecosystem. An ecosystem is a community of living and nonliving things considered as a unit. If a single factor is changed, perhaps by pollution or natural phenomenon, the whole system could be altered The community within an ecosystem is linked together by food chains. Biotic factors become linked in a food chain when they eat one another. The start or bottom of a food chain is made up of producers, such as plants and algae. Producers are at the start, or the bottom, of the food chain because they do not eat other biotic factors to get the energy they need to survive. Instead of taking energy from food, producers get energy by converting it from carbon dioxide and water using sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis explains how energy from the sun is captured by green plants and used to make food. Most of this energy is used to carry on the plant's life activities. The rest of the energy is passed on as food to the next level of the food chain. Grass is a producer and gains its energy from photosynthesis Other biotic factors in the food chain survive by eating the producers. This gives them the energy that the producers obtained through photosynthesis. These biotic factors are called consumers because they eat other organisms to get their energy, rather than taking it direct from sunlight. Biotic factors that eat consumers are also consumers and they are often called carnivores. There are four types of consumer: 1. Herbivores are organisms that eat plant matter (producers) to gain energy. 2. Carnivores are organisms that eat meat to gain energy 3. Omnivores are organisms that eat both plant (producer) and animal (consumer) matter to gain energy. 4. Decomposers are organisms that feed on the remains of dead plant and animal matter. They help to speed up the process of decay. They also assist in recycling nutrients back to producers in nutrient cycles. Energy moves around within an ecosystem, from factor to factor, as producers and consumers are eaten. The flow of energy in this way is what we call the food chain. Biomes are defined as "the world's major communities, classified according to the predominant vegetation and characterized by adaptations of organisms to that particular environment" The importance of biomes cannot be overestimated. Biomes have changed and moved many times during the history of life on Earth. More recently, human activities have drastically altered these communities. Thus, conservation and preservation of biomes should be a major concern to all. FLOWS AND CYCLES As well as the flow of energy through a food chain, other flows and cycles can be found within ecosystems. Ecosystems have water cycles and nutrient cycles. So when an animal eats another animal or a plant it not only obtains that organism's energy, but its water and nutrients as well. Different nutrients are passed around an ecosystem as organisms consume other biotic and abiotic factors. Two important nutrients are carbon and nitrogen. The carbon cycle The carbon cycle describes how carbon circulates around an ecosystem. Carbon will change form. Sometimes it is an element and sometimes a compound. Carbon is passed between living organisms and between non-living and living systems. There are many different elements to the carbon cycle. • Producers, eg plants/algae use carbon dioxide and water to make carbohydrates (energy) through the photosynthesis process. • Animals can not photosynthesise. When animals consume the producers they use the carbohydrates to provide the energy for reproduction, growth and daily living. This process of creating energy is called respiration. It requires oxygen and carbohydrates and produces as a by-product carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The CO2 is exhaled by animals back into the atmosphere where the carbon cycle begins again. • When organisms die, they decompose. This releases nutrients into the soil, but carbon remains stored in the remains of the animals. It can remain stored for a very long time and can be still be used to provide energy - eg coal, oil. • When this energy is released by humans through burning (eg oil) in industrial processes, carbon gasses, such as carbon dioxide are released into the atmosphere. Water cycle The water cycle describes how water moves from the ocean, to the atmosphere (evaporation), to land (rain) and back to the ocean (rivers). On the way the water will be intercepted by plants and animals, both of which need water to survive. • plants need water for photosynthesis • animals use water to remove toxins and stay cool (sweat) • both plants and animals give off water as a by-product of respiration • animals drink water but can also obtain water by consuming plants and animals that have stored water