Population Biology: Population Dynamics
advertisement

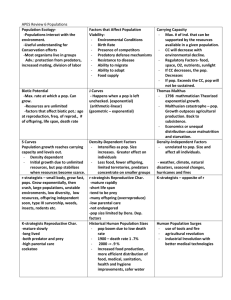
Population Biology: Population Dynamics Unit 2 Ecology / Ch. 5 / Sec. 5.1 How & why do populations grow? Methods of investigating: A. Placing a microorganism, such as a bacterium or yeast cell, into a tube or bottle of nutrient solution, & observing how rapidly the pop grows. B. Introducing a plant or animal species into a new environment that contains abundant resources, & observing the pop growth of that species 1. Population growth: The change in the size of a population with time Pops of organisms do not experience a liner growth; rather they produce a J-shaped curve. Initial increases in the # of organisms is slow b/c the # of reproducing organisms is small; they will soon grow rapidly b/c the total # of potentially reproducing organisms increases 2. Exponential growth: Explosive population growth in which the number of reproducing individuals increases by an ever-increasing rate Results in a pop explosion (Fig 5.3 / pg 115) 3. Carrying capacity: The number of organisms of a population a particular environment can support over an indefinite period of; Maximum, stable population size an environment can support over time Often represented by letter K; S-shaped curve (Fig 5.4) When pops are under the carrying capacity of a particular environment, births will exceed deaths until the carrying capacity is reached; when above, deaths exceed births until the carrying capacity is reached 4. Density-dependent factor: Factors that limit population density; examples include predation, disease, & competition for food, water, & territory Ex: Disease spreads more quickly in a pop whose members live close together than in smaller pop whose members live farther away 5. Density-independent factor: Most often weather-related occurrences such as storms & floods that affect populations, regardless of their density Most are abiotic factors like temp, storms, floods, drought, & habitat disruption No matter how many earthworms live in a field, they will all drown in a flood



![Population%20dynamics%20equations[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009173623_1-09271ff054ecf552593810773aee8fd9-300x300.png)