SMART Career Goals Lesson Plan for Grade 12
advertisement

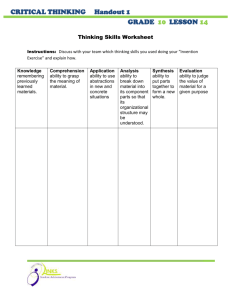
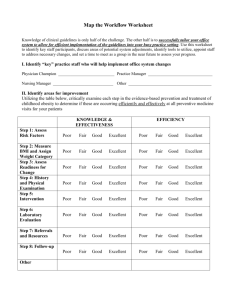
THEME: Goal Setting, Reflections and Self-Assessment Lesson: Setting SMART Career Goals Learning Outcomes Students will be able to identify career goals and develop action plans using the SMART goal setting process. Essential Question Do you have “SMART” career goals? Level Grade 12 Time 4 x 15 minutes Materials SMART Goals Handout Careers and Goal Setting Handout Setting Up Smart Goals Worksheet Procedure Lesson 1 – 15 minutes 1. Write essential question on the board. 2. Review the SMART goal setting acronym; ask students what each of the letters in the acronym represent. Review the S.M.A.R.T. principle to goal setting. (See SMART Goals Handout). Have students write examples of goals that follow the SMART goal principle. (See the blank area on the SMART Goals Handout, titled, “Your Example________________”). 3. Read through the “Tips to setting Effective Goals” on the SMART Goals Handout. Lesson 2 – 15 minutes 4. Briefly review the S.M.A.R.T. principle to goal setting (Once again, see the SMART Goals Handout). Handout Careers and Goal setting Handout. Have students complete this individually. 5. When students are finished the Career and Goal setting Handout, they will hare some of their goals with a partner or small group. Lesson 3 – 15 minutes 6. Ensure the students have complete the Career and Goal setting Handout. Give a few minutes to complete if needed. 7. Hand out Setting Up SMART Goals Worksheet. Students must choose one goal from their first list (See the Careers and Goal setting Handout) and write it at the top of this worksheet. Working individually, students must describe the necessary steps to achieve their goal, where they are now, and the potential obstacles and solutions. Lesson 4 – 15 minutes 8. Give some time to complete the Setting Up SMART Goals Worksheet. 9. After the Setting Up SMART Goals Worksheet is completed, they may share goals with a partner or small group. Extending Students may want to search online to investigate job opportunities as a first step towards achieving their career goals. Reference: http://ccd.me.edu/careerprep/CareerPrepCurriculum_LP-7.pdf S.M.A.R.T. GOALS Specific – The goal should identify a specific action or event that will take place. Is your goal well defined? Do you have short term goals to help you reach your long term goals? Example: It is difficult to pursue the goal to "work harder". It is easier to accomplish "Write a paper". Your Example: _____________________________________________________________ Measurable – The goal and its benefits should be quantifiable. Do you have steps you can check off on your way to your goal? Can you “measure” whether or not you attained your goal? Example: “Getting over 80 percent on your English paper” is measurable. Your Example: _____________________________________________________________ Action Oriented – The goal should be action oriented and attainable given available resources. Is this something you can work toward? What do I need to attain this goal? What do I need to do? Example: “I will work on my English paper every night for one hour this week.” Your Example: _____________________________________________________________ Realistic – The goal should be a challenge, but allow the likelihood of success. Is this something you can actually achieve? Have you looked at your past successes to decide if this goal is realistic? Example: “My overall average in English is currently 75 percent, so it is realistic to aim for over 80 percent on my next paper.” Your Example: _____________________________________________________________ Timely – The goal should state the time period in which it will be accomplished. Do you have enough time to complete your goal? Did you set a time limit to have your goal completed? Example: “I will complete the English paper and hand it in before the due date, which is ….” Your Example: _____________________________________________________________ Tips to setting Effective Goals… 1. Develop several goals. A list of 5 to 7 items gives you several things to work on over a period of time. 2. State goals as declarations of intention, not just items on a “wish list”. Ex: “I want to apply to three universities” lacks power, “I will apply to three universities” is intentional and powerful. 3. Attach a date to each goal. State what you intend to accomplish and by when. A good list should include some short term and long term goals. You may want a few goals for the year, and some for two or three month intervals. 4. Be specific. “To find a job” is too general; “to research and find 5 job opportunities before the end of the month” is better. A general goal may become the long term aim, however identify some more specific goals to get there. 5. Share your goals with another person. Sharing your intentions with parents, best friend or teach will provide steps towards reaching the goal. This “support network” will be there to help cheer you on as you pursue your goals. 6. Write down your goals and display them where you will be able to see them everyday. The more often you read your list, the more results you will get. 7. Review and revise your list. Experiment with different ways of stating your goals. Goal setting improves with practice! Careers and Goal Setting My key Occupation Objective or Career Goal: ______________________________________________________________________________ The following intermediate goals will be focused upon over the next ______ months. Education/Training Goals: Action Steps: Occupational Goals: Action Steps: Personal Health/Wellness Goals: Action Steps: Setting Up SMART Goals Worksheet Goal Statement: What do I need to do reach this goal? Where am I now? Obstacles Solutions