Techniques of HPLC - Agilent Technologies
advertisement

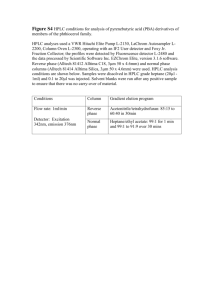
User Information Plan Template Form Rev. Feb 25, 1999 Document Information: Filename USERINFO.DOC Current Owner Deborah Perkins Product Identifier Techniques of HPLC. H1186A Project Identifier SS980032 Current Lifecycle Test Phase Revision Log: Version Date A.00 99/05/19 A.01 99/11/09 Reason For Update Initial user information plan. Preliminary Final update Course Description H1186A Techniques of HPLC with Instrumentation H1186A is a 4-day, instructor-led, hands-on course providing the student with knowledge of techniques of HPLC including details of the separation process, general HPLC procedures, gradient elution, instrumentation, troubleshooting, quantification, modes of HPLC, and method development. To prepare for the course, you will need to provide instruments equipped with ChemStations, order needed supplies, and tools. The following items are provided by SSD: An instructor manual with laboratory and lecture details (as hidden text) A student manual Powerpoint slides Product Delivery Requirements 1. Course Description: H1186A is a 4-day, instructor-led, hands-on course providing the student with knowledge of techniques of HPLC including details of the separation process, general HPLC procedures, gradient elution, instrumentation, troubleshooting, quantification, modes of HPLC, and method development. 2. Course Outline with correlation to file names: Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only DAY 1 Module 1 Introduction to HPLC mod1.doc, mod1.ppt Module 2 HPLC Instrumentation mod2.doc, mod2.ppt, Laboratory: Solvent Delivery Systems mod2lab1.doc Laboratory: Autosampler and Detector mod2lab2.doc Module 3 Practical HPLC Procedures mod3.doc, mod3.ppt Module 4 Chromatographic Resolution and the Separation mod4.doc, mod4.ppt Laboratory: HPLC Parameters mod4lab.doc Common Troubleshooting mod5.doc, mod5.ppt Module 6 Gradient Elution Laboratory: Gradient Elution mod6.doc, mod6.ppt mod6lab.doc Module 7 Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis mod7.doc,mod7.ppt Module 8 Column Hardware mod8.doc, mod8.ppt Laboratoy: Column Hardware mod8lab.doc DAY 2 Module 5 DAY 3 (optional, pick 1 of last 3 labs) DAY 4 Module 9 Reversed- Phase HPLC Module 10 Reversed-Phase Separations of Ionic Samples mod9.doc, mod9.ppt mod10.doc, mod10.ppt Laboratory: Separation of Weakly Ionic Compounds(optional) mod10lab.doc Module 11 Ion Exchange HPLC mod11.doc, mod11.ppt Module 12 Normal Phase HPLC mod12.doc, mod12.ppt Module 13 Size Exclusion Chromatography mod13.doc, mod13.ppt Module 14 Method Development mod14.doc, mod14.ppt Laboratory: Develop a Quantitative Method For the Separation of Caffeine in Beverages (optional) Module 15 Method Validation(appendix, optional) Hewlett-Packard Company mod14lab.doc mod15.doc, mod15.ppt For Internal Use Only Bibliography biblio.doc Complete Manual H1186A.doc Manual Cover Cover.doc PostScript Student Manual H1186Ast.ps Student Manual Cover Stcover.ps PostScript Instructor Manual H1186Ains.ps Instructor Manual Cover Inscover.ps 3. For marketing purposes of this product see the Product Release Bulletin (if available): Product Release Bulletin available? Yes Product Release Bulletin location: SSD Website http://cagsso.atl.hp.com/development/main.htm Find H1186A then the file prodrel.doc. 4. Instructor or Delivery Agent skills and training required to deliver the product: Care should be taken to ascertain instructor experience and expertise for this course. This course leans heavily towards the chemistry/methods development side of HPLC techniques. The following are guidelines: At least 10 years of HPLC method development experience in an industrial setting, or Analytical Chemistry faculty at a college or university whose research area is separations. Instructor should have direct, significant experience in at least three modes of HPLC. The instructor can test his/her readiness to teach the course by answering the following questions: 1. Describe the separation process using analogy. 2. Describe the main modes of HPLC and their strengths and weaknesses. Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only 3. Describe how to maintain an HPLC and prepare samples for injection. 4. Be able to relate resolution to efficiency, selectivity, and capacity. 5. Describe how to perform method development in reversed-phase HPLC based upon a scouting gradient. 6. Describe how check valves work in an HPLC pumping system. 7. Describe typical HPLC detectors and give advantages of each kind. 8. Describe HPLC detectors which give 3 dimensional data. 9. Troubleshoot the HPLC based on chromatographic data. 10. Know the basis of quantification and when area or height is most suitable. 11. Know the advantages and disadvantages of reduced particle size and narrow bore columns. 12. Know how to select the right stationary phase for reversed-phase HPLC. 13. Know how to optimize ion-pair HPLC. 14. Describe how to optimize separations on an ion exchange column. 15. Know how to determine the molecular weight from SEC. 16. Know how to optimize the performance of SEC. 17. Know the latest advances in HPLC columns. 18. Lead discussions on method development strategies. 19. Describe rugged method validation procedures. 5. Equipment (Instrumentation and Software) required for product delivery: This course is designed with laboratories requiring an instrument for every two customers. The course is designed for the HP 1100 Series Modules. Each Liquid Chromatograph requires: Solvent degassing A binary or quaternary pump Autosampler Column Oven Diode Array Detector ChemStation Current HPLC 3D ChemStation Configuration and Software: A.06, or A.07 G2170AA Single Instrument LC2d ChemStation Software Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only A.0, A.07 G2180AA Spectral Processing Software Pentium 233 64 Mb RAM CD-ROM drive Speakers (to listen to directions from maintenance and repair CD-ROM) 17 inch monitor (at least 600 x800) Laserjet Printer NT Windows 4.0 3 ½ inch floppy drive Classroom Projection System (at least 800 x 600 resolution) Classroom Computer for slide presentation and software demonstration. pH meter and associated calibration buffers (If performing optional lab Separation of Weakly Ionic Compounds by Reversed-Phase). Balance 6. Consumables required for product delivery: Purchase the following consumables to complete the entire course. 1/instrument 1per2 instruments 3 um column 1 per 2 instruments narrow bore column 1/instrument XDB column 1 4L methanol 1 4L acetonitrile 1 4L HPLC grade water Acetate Buffer Antioxidant sample from Supelco Part Number Vitamin samples Part Number Spare Parts Capillaries Spare waste tubing Standard Checkout Column Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only Pump Seals Wear Retainers Pistons Frits Solvent inlet filters Rotors Needles Needle Seats lamps 7. Samples and Materials required for each laboratory : You will need the following materials and samples for each laboratory: Laboratory 1: Solvent Delivery Systems Instrument: required as described above Tools: ¼” wrench 4 mm hexagonal key Spare Parts: Optional: pump seals (5062-8576) Wear retainers (01018-22706) Samples: None Columns: No specific column required. Suggest that the columns required for exercise 3 be in place. Solvents: HPLC grade water in channel A, Acetonitrile in channel B Make certain that if quaternary system, all channels have some mobile phase. Special Instructions: The lab allows for the students to replace the pump seals or just look at the pump seals without replacing them. Tell them which you would like them to Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only do before the lab starts. Your supervision will be required while the students locate the components of the HPLC and describe their function. You may want to do this as a group. This laboratory is done after the completion of the solvent delivery section of the Instrumentation module. Laboratory 2: Autosampler and Detector Instrument: As described above. Tools: ¼” wrench 2.5 mm hexagonal key 9/64” hexagonal key Pozidrive #1 screwdriver Spare Parts: Have a few on hand in case someone breaks something. Needle G1313-87201 Rotor Seal 0100-1853 Deuterium Lamp 2140-0590 Samples: None Columns: No specific column required. Suggest that the columns required for exercise 3 be in place. Solvents: HPLC grade water in channel A HPLC grade acetonitrile or isopropanol in channel B If channel C or D, Isopropanol for pressure test: note: water may be substituted for the pressure test. Special Instructions: Remind the students not to touch the deuterium lamp with their fingers. Many students experience problems removing the needle without bending it. This lab may is done after the completion of the detectors section of the Instrumentation module. Laboratory 3: HPLC Parameters Instrument: As described above. Tools: None specifically required. Spare Parts: Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only Same as general selection of spare parts. Samples: You will need: Vials and caps Crimper Pasteur pipettes and bulb Graduated cylinder to measure dilution (don’t need any more accuracy than this) 1 vial isocratic test mix per instrument, part number 01080-68704 Stock Solution of Uracil (uracil may be obtained from a variety of sources including Preparation: Dilute each vial of HP isocratic test mix 1:3. Spike with uracil stock solution (the amount is not critical just as long as a peak can be seen from the baseline). Uracil Stock: Weigh out 33 mg of uracil. Dissolve in 20 mL of water with sonication. Dilute with 80 mL of methanol or acetonitrile. Dilute solution 1:50. Add approximately 1 mL for each 1:3 dilution. Columns: 1 SB-C18, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3.5 micron column, part number 863953-902/instrument. Solvents: HPLC grade water in channel A HPLC grade acetonitrile in channel B Note: experiment is not greatly affected by use of methanol instead of acetonitrile. Special Instructions: You will need to review the lab results carefully. Unfortunately, with this sample, the efficiency doesn’t decrease with increasing temperature. Point out the shape of the curve N vs. T where N increases with temperature at first, levels off, then slightly falls. Make certain that the students return the column oven down before going back to the classroom. Laboratory 4: Gradient Elution Instrument: as described above. Tools: None specifically required. Spare Parts: Same as general selection of spare parts. Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only Samples Place gradient test mix, part number 01080-68794 in labeled vials. Columns: 1 SB-C18, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3.5 micron column/instrument part number 863953-902. Solvents: HPLC grade water in channel A, HPLC grade acetonitrile in channel B, you may have other assorted solvents for students to try if desired: methanol, THF, isopropanol. Special Instructions: We often make this lab into a contest with a simple prize such as an HPLC textbook or an Agilent Technologies mug or T-shirt. That often makes this the most popular laboratory. You may want to postpone this laboratory exercise to the end of the course after method development as it can apply there as well. Skip the method development and weakly ionic compound labs. That will make a very relaxed pace course where you can explain each lecture in a little more detail. In other words, do the two instrument labs, the HPLC separations lab, the column hardware lab and the gradient lab at the end of the course. Students can then spend as much time optimizing as they like. Also, if you have an even more complicated sample, the same instructions can apply, but the lab will be more challenging. Laboratory Exercise 5: Column Hardware Instrument: as described above Tools: The students will need wrenches to change the columns. Spare Parts: Standard spare parts. Sample Use the sample from the HPLC Separations laboratory or just isocratic test mix: 0108068704. Columns: 1 for every 3 instruments SB-C18, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 micron column, part number 883975902 1 for every instrument (same as used in other laboratories) SB-C18 4.6 x 150 mm, 3.5 micron column part number 863953-902. 1 for every 3 instruments SB-C18 2.1 x 150 mm, 5 micron column, part number 883700922. Solvents: Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only HPLC grade water in channel A, HPLC grade acetonitrile in channel B. Special Instructions: To save money, buy only a couple of the 2.1 and 4.6(5 micron) columns. The students can do the experiments out of order and swap columns. Make certain that they understand this before they start the lab. Laboratory 6: Separation of Weakly Ionic Compounds by Reversed Phase Note: This laboratory is optional. You must have a pH meter. Hypersil columns or any brand that has more residual silanols are more appropriate than the Zorbax columns. With the hypersil columns, the lab demonstrates the behavior of weakly ionic species. Instruments: same as described above. Tools: The instructor will need a balance and a pH meter. Several containers for buffers. Samples: From stock solution, combine equal amounts of aniline, benzoic acid, and benzaldehyde into vials. Also, provide vials of standards for aniline and benzoic acid. They can infer the benzaldehyde peak. Stock Solutions: Aniline: mix 5 mL of aniline with 95 mL acetonitrile or methanol. Dilute 1:100 with 65/35 acetonitrile/water. Benzoic Acid: 9.77 g dissolved in 100 mL acetonitirle or methanol. Dilute 1:100 with 65/35 water/methanol or acetonitrile. Benzaldehyde: 4.0 mL in 96 mL of methanol or acetonitrile. Dilute 1:500 with 65/35 water /acetonitrile or methanol. These stock solutions will keep for years. Buffers: Make 0.010 M Sodium Acetate Buffers in 500 mL quantities at the following pH’s. Use Acetic acid to adjust the pH. pH = 5.5, 4.7, and 4.0 The final buffer solution, make it 0.010 M sodium acetate, add 10 mM triethyamine, then pH to 4.00 with acetic acid. The students can do the first three buffer solutions in any order as long as the columns are Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only well equilibrated. The TEA buffer must be done last. Columns: Select a column with many residual silanols. The Zorbax columns do not work well. This may be a discussion point about the lack of problem with certain columns. A hypersil column 4.6 x 100 , 5 micron 79916OD-554 works okay. Non-endcapped sil type columns work the best, such as Lichrospher. Solvents: Above Buffers channel A, acetonitrile channel B. Special Instructions: If the students do not spend the appropriate time equilibrating the columns, this lab does not work well. Have the students look at the changes in the UV spectrum as well. Make certain that the students flush the columns and instruments at the end of this lab. Laboratory 7: Develop a Quantitative Method for the Separation of Caffeine in Beverages. Instrument: as described above. Tools: The students will need wrenches to change the columns. Spare Parts: Standard spare parts. Samples: You will need the following: Samples of two or three beverages that contain caffeine. Suggestions: Coca-Cola, Dr. Pepper, Pepsi, coffee, tea, etc. It is better to filter the samples, but do not dilute. A vial of each per instrument. Caffeine standards, 3 levels/ instrument at the following levels: Weigh out 70 mg into a 100 mL volumetric. Dilute with a 50/50 mixture of water/acetonitrile to the mark. Repeat with 20 mg and 10 mg. This range of standards should cover beverages from soft drinks to brewed coffee. Columns: The 4.6 x 150, 3.5 micron SB-C18 column as in previous experiments. Solvents: HPLC grade Water in channel A, HPLC grade Acetonitrile in channel B. Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only Special Instructions: The problem with this lab is the difficulty encountered with the ChemStation calibration tables. If you really don’t want to get into that, use graph paper. Tools: large column wrenches7/16 x ½ and ½ x 9/16 small column wrenches ¼ x 5/16 pozidrive #1 pozidrive #2 ZDV union Capillary Small screw driver Flat wrenches (HP 1050 and HP 1100) 4mm and 14 mm Allen wrench set 1.5 mm 2.5 mm 3 mm 4 mm 5 mm Blanking nut Small beaker Safety glasses Sand paper (small strip) HP 1100 priming tool HP 1100 Maintenance and Repair CD-ROM (01100-60002) Floppy disk Tweezers Empty capped vial 9/64” hex key 8. Electronic Files required for product delivery: None required Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only 9. Activities required prior to product delivery. Determine which laboratories you will be conducting. Order supplies. Make any stock solutions or buffers. Set-up HPLC’s and ChemStations . Check out HPLC’s. Run standard isocratic test mix on all HPLC’s prior to class. Set-up classroom projector for slide presentations. Make up required samples. 10. Activities required during product delivery. Monitor students during laboratory exercises. Dispose of solvent waste as needed. 11. Activities required after product delivery. Make certain that students fill out the evaluation forms. Dispose of solvents and samples properly. Hewlett-Packard Company For Internal Use Only