Microorganisms, Fungi, and Plants
advertisement

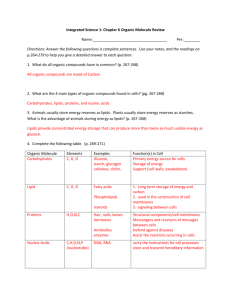
Microorganisms, Fungi, and Plants Chapter 1 Lesson 2: The Necessity of Life * Almost all organisms have the same basic needs: water, air, shelter, food A. Water (p.8) 1. The human body is made up of approximately 70% water. 2. Most chemical reactions involved in metabolism (all of an organism’s chemical processes) require water. B. Air (p.8) 1. Most living things use oxygen in the chemical process that releases energy from food. 2. Organisms living on land get oxygen from the air while organisms living in water take in dissolved oxygen from the water or come to the surface to get oxygen. 3. Plants produce food and oxygen by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis converts energy in sunlight to energy stored in food. C. A Place to Live (p.9) 1. Organisms need a place to live that contains all of the things they need to survive. 2. Since there is limited space on Earth, many animals find a place to live and then try to keep other animals away. D. Food (p.9) 1. Food gives organisms energy and materials needed to carry on life processes. 2. Nutrients from food are used to replace cells and build body parts. 3. Organisms are grouped into three different groups depending on how they get their food: a. producers - make food ex. plants use energy from sun to make food b. consumers – eat other organisms/plants ex. frogs get energy from eating insects c. decomposers – eat dead organisms or animal waste ex. mushroom E. Putting It All Together (p.10) 1. All organisms need to break down food in order to use the nutrients in the food. 2. A molecule is a substance made when two or more atoms combine. Compounds are molecules made of different kinds of atoms. 3. Molecules found in living things usually are made of six elements: a. carbon b. hydrogen c. nitrogen d. oxygen e. phosphorus f. sulfur * These six elements combine to form: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, ATP, and nucleic acids. F. Proteins (p.10) 1. Proteins are large molecules that are made up of smaller molecules called amino acids. 2. Proteins are broken down in food to supply cells with amino acids. Amino acids are put together to form new proteins. 3. Proteins have different functions: a. form structures that can be seen ex. spider webs, hair, horns, feathers b. help cells do their job c. protect cells d. (enzymes) start or speed up chemical reactions in cells G. Carbohydrates (p.11) 1. Carbohydrates are molecules made of sugar. Carbohydrates are used as a source of energy and for energy storage. 2. Cells break down carbohydrates to release energy stored in them. 3. Two kinds of carbohydrates: a. simple carbohydrates – made up of one or a few sugar molecules ex. table sugar, sugar in fruits b. complex carbohydrates – made of hundreds of sugar molecules ex. potato (starch) H. Lipids (p.12) 1. Lipids are compounds that cannot mix with water. ex. fats and oils 2. Lipids: a. store energy b. form the membranes of cells 3. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. Phospholipids are the molecules that form much of the cell membrane. 4. After all carbohydrates are used, organisms can get energy from the fats and oils that store energy. I. ATP (p.12) 1. ATP is a molecule that is the major energy-carrying molecule in the cell. Energy must be transferred (from carbohydrates and lipids) to ATP which provides fuel for cell activities. J. Nucleic Acids (p.13) 1. Nucleic acids are large molecules made up of smaller molecules called nucleotides. Nucleic acids are called the blueprints of life because it contains all the information a cell needs to make a protein. 2. DNA is a nucleic acid that tells the cell the order of amino acids that are put together to make a protein. Microorganisms, Fungi, and Plants Chapter 1 Lesson 1: Characteristics of _______________ _______________ A. Living Things Have ___________ (p.4) 1. All living things are __________ of one or more cells. 2. A _________ is a structure that contains all of the materials necessary for ____________. The __________ surrounds a cell and separates the contents of the cell from the cell’s environment. 3. Most cells are too __________ to be seen with the naked eye. 4. In an organism with many cells, different _______ perform different functions. In a organism with only one cell, different _________ of the cell perform different functions. B. Living Things __________ and ____________ to Change (p.5) 1. All organisms can sense change in their ________________ and respond to that change. 2. A change that affects the activity of the organism is called a ____________________. ex. chemicals, ____________, light, ____________, hunger 3. Even if an organisms _______________ changes, its _________ inside must stay the same. Chemical reactions __________ an organism help it to maintain a _________ internal condition. The maintenance of a stable internal environment is called _________ 4. When your body gets ________, your body responds by sweating. When your body gets cold, it responds by _________________. 5. Animals control their body temperature by __________ from one environment to another. ex. too warm – move to _________ too __________ – move to sunlight C. Living Things ________________ (p.6) 1. Organisms make other organisms ____________ to themselves in two ways: a. sexual reproduction – two parents produce offspring that will _________ characteristics of both parents b. asexual reproduction – a single parent produces offspring that are _____________ to the parent D. Living Things Have DNA (p.6) 1. Cells of all living things contain DNA. _______ controls the structure and ____________ of cells. 2. The passing of ____________ from one generation to the next is called heredity. E. Living Things Use _____________ (p.6) 1. Energy is used to carry out the activities of _______ in organisms. ex. _________ food, breaking down food, moving materials in and out of cells, ____________ cells 2. An organism’s ______________ is the total of all of the chemical activities that the organism performs. F. Living Things Grow and _____________ (p.7) 1. All living things ________. a. single-celled organisms – _______ gets larger and divides b. many-celled organisms – _________ of cells gets larger and organism get bigger Microorganisms, Fungi, and Plants Chapter 1 Lesson 2: The ________________ of Life * Almost all organisms have the same _______ needs: water, air, shelter, food A. Water (p.8) 1. The human body is made up of approximately _______% water. 2. Most chemical reactions involved in metabolism (all of an organism’s chemical processes) require __________. B. Air (p.8) 1. Most living things use __________ in the chemical process that releases ___________ from food. 2. Organisms living on land get oxygen from the ____ while organisms living in ________ take in dissolved oxygen from the water or come to the surface to get oxygen. 3. Plants produce _______ and oxygen by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis converts energy in sunlight to _________ stored in food. C. A __________ to Live (p.9) 1. Organisms need a place to ________ that contains all of the things they need to ___________. 2. Since there is ____________ space on Earth, many animals find a place to live and then try to keep other animals _________. D. Food (p.9) 1. Food gives organisms _________ and materials needed to carry on ________ processes. 2. ______________ from food are used to replace cells and build body parts. 3. Organisms are grouped into three different groups depending on ______ they _______ their food: a. _____________ - make food ex. plants use _________ from sun to make food b. _____________ – eat other organisms/plants ex. frogs get energy from eating insects d. _____________ – eat dead organisms or animal waste ex. ________________ E. Putting It All Together (p.10) 1. All organisms need to ________ _________ food in order to use the nutrients in the food. 2. A molecule is a _________ made when two or more atoms combine. _____________ are molecules made of different kinds of atoms. 3. Molecules found in living things usually are made of six elements: a. carbon b. ________________ c. nitrogen d. ________________ e. phosphorus f. ________________ * These six elements combine to form: ___________, carbohydrates, ____________, ATP, and nucleic acids. F. Proteins (p.10) 1. ______________ are large molecules that are made up of smaller molecules called ___________ acids. 2. Proteins are broken down in food to __________ cells with amino acids. Amino acids are put _____________ to form new proteins. 3.Proteins have different ________________: a. form structures that can be ___________ ex. spider webs, hair, horns, ____________ b. help _________ do their job c. ___________ cells d. (___________) start or speed up chemical reactions in cells G. Carbohydrates (p.11) 1. Carbohydrates are molecules made of _______. Carbohydrates are used as a source of __________ and for energy storage. 2. Cells break down ____________ to release energy stored in them. 3. _______ kinds of carbohydrates: a. _________ carbohydrates – made up of one or a few sugar molecules ex. table sugar, sugar in fruits b. _________ carbohydrates – made of hundreds of sugar molecules ex. potato (___________) H. Lipids (p.12) 1. Lipids are ______________ that cannot mix with water. ex. fats and _________ 2. Lipids: a. store _________ b. form the ________________ of cells 3. All cells are ______________ by a cell membrane. Phospholipids are the molecules that _________ much of the cell membrane. 4. After all carbohydrates are used, organisms can get __________ from the _________ and oils that store energy. I. ATP (p.12) 1. _______ is a molecule that is the major energy-carrying molecule in the cell. Energy must be _________________ (from carbohydrates and lipids) to ATP which provides ________ for cell activities. J. Nucleic Acids (p.13) 1. Nucleic acids are _______ molecules made up of smaller molecules called nucleotides. Nucleic acids are called the _______________ of life because it contains all the ______________ a cell needs to make a protein. 2. _______ is a nucleic acid that tells the cell the order of amino acids that are put _______________ to make a protein.