Weathering - Fair Lawn Schools
advertisement

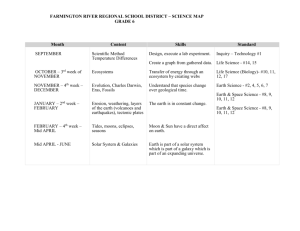
Weathering Agent of Weathering Physical Weathering Ice wedging Water abrasion Wind abrasion Exfoliation Plant roots Animals Chemical Weathering Carbonic Acid Oxidation Plant Acids Water Example of Weathering Caused by Agent Falling rock zone along a highway in Spring Rounded rocks in a stream Smooth-surface rocks in a dessert Exposed granite peeling on a mountain Trees growing out of cracks in rocks Burrowing animals bring rocks to the surface Caverns in limestone rock Iron rust in rocks Acids produced by water running over dead plants Feldspar decomposes when water mixes with it 1. How would you define weathering based on the information in the chart above? 2. How does physical and chemical weathering differ? The Seasons Vernal Equinox – The sun is directly over the Equator. The length of night and day is the same all over the world. Summer Solstice – The sun is directly over the Tropic of Cancer Autumnal Equinox – The sun is directly over the Equator. The length of night and day is the same all over the world. Winter Solstice – The sun is directly over the Tropic of Capricorn. 1. Write the bold face terms next to appropriate part of the diagram above. 5. How are they different? 2. How are the Vernal and Autumnal Equinoxes similar? 6. When would the North Pole tilt the greatest amount toward the sun? 3. How are they different? 4. How are the Summer and Winter Solstices similar? 7. At which point does the Northern Hemisphere have its shortest day and the Southern Hemisphere have its longest day? ROCKS You have found a dark gray rock that is smooth and flat. On its surface are impressions of plants that look like ferns. You want to add the rock to your collection, but you need to fit it into one of the following categories. In which would you place it? a. b. c. d. Igneous Rock with a fossil impression of a fern. A conglomerate rock, made from pebbles, stones and other sizes. A rock made from crystals being melted and pressed together. A rock made from sediment, like mud. Things to think about… Would a fern be preserved in a lava rock? Why or why not? What does a conglomerate rock look like? Does that match the question? Could this rock be made from crystals? Why or why not? Could this rock be made from mud? Why or why not? Look at this picture of sedimentary rocks, which are formed from sediment which become compacted together. 1. Which rock layer is older, D or C? 2. Which rock layer represents the surface of the earth? Eclipses The word “eclipse” means to block. There are two kinds of eclipses, solar and lunar. 1. What does the word solar refer to? 2. What does the word lunar refer to? In a solar eclipse, something blocks the light from the sun. In a lunar eclipse, something blocks the sunlight from reaching the moon. The three objects involved in these eclipses are always the sun, moon and the earth. 3. In the space below, draw a diagram and explain the positions that the earth, sun, and moon would have to be in for there to be a solar eclipse. 4. Look at the diagram below. How is this different from a solar eclipse? Tides The water level along the ocean rises and falls about twice a day. These changes are called tides. When water is at its highest, it is a high tide. When it is at its lowest, it is a low tide. These tides are cause by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on the waters of the ocean. This gravitational pull of a body like the sun or the moon depends on the mass of that body and how close that body is to the Earth. The more massive and closer the object is, the stronger is it’s gravitational pull. The distance between the two bodies has a greater affect on gravity than the mass of the object. 1. Why do you think that the moon’s gravitational pull on the ocean is greater than that of the Sun? Explain your answer. 2. A group of people who live near the beach have been measuring the tides for the last ten months. Their records show a repeating pattern of high tides which are higher than average, occurring every 14 days. Which is the most likely explanation of this? a. b. c. d. The earth, moon, and sun are aligned twice a month. There have been heavy storms at sea every 14 days. Ocean currents bring in large amounts of water every two weeks. A series of solar flares on the sun are affecting tides. 3. Look at the image above. What is this diagram showing? Plate Boundaries 1. Label the plate boundaries above as convergent, divergent, or transform. 2. Which boundaries can produce earthquakes? 3. Which can produce volcanoes? 4. At which are the sea floor created? 5. At which are the sea floor destroyed?