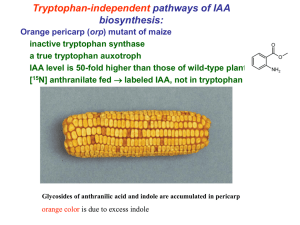
027 Chapter 27
advertisement

Chapter 27 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. Which of the following pertain to movement of plants? A. seismonastic movements B. sleep movements C. phototropism D. gravitropism E. all of the choices are correct 2. Which of the following ions are affected by gibberellins and is also involved in signal transduction? A. H+ B. Ca2+ C. Na+ D. Mg2+ 3. Pinching the top off a plant to create fuller growth involves which of the following hormones? A. auxins B. ethylene C. gibberellins D. cytokinins 4. The general sequence by which a plant responds to stimuli is A. chloroplast-vascular bundle-sap. B. reception-transduction-response. C. sensory nerve-interneuron-motor nerve. D. input-reflex-output. E. leaf-stem-root. 5. The Greek root word meaning "turning" is the basis for the term A. auxin. B. tropism. C. nastic. D. circadian. E. phytochrome. 6. Which of these external stimuli produces a growth of the plant toward light? A. negative gravitropism B. positive gravitropism C. thigmotropism D. negative phototropism E. positive phototropism 7. Which of these stimuli causes roots to grow downward? A. negative gravitropism B. positive gravitropism C. thigmotropism D. negative phototropism E. positive phototropism 8. Which of these stimuli causes a pea vine to twine around a wire support? A. negative gravitropism B. positive gravitropism C. thigmotropism D. negative phototropism E. positive phototropism 9. The Greek root words meaning "light" and "turning" are the basis for the term A. gravitropism. B. phototropism. C. nastic. D. circadian. E. thigmotropism. 10. Plant hormones are generally produced in _______ tissues. A. cortical (cortex) B. epidermal C. meristem D. vascular E. floral 11. The Latin root words meaning "about" and "day" are the basis for the term A. auxin. B. tropism. C. nastic. D. circadian. E. phytochrome. 12. Which statement about plant hormones is NOT true? A. Plant hormones include at least one form that is a gas. B. Each naturally occurring hormone has a specific chemical structure. C. Hormones are among the principal internal regulators of plant growth. D. Responses to plant hormones may be observed in nearly any part of a plant. E. All known growth regulators of plant activities are chemicals produced naturally in plants. 13. The Greek root word meaning "promoting growth" is the basis for the term A. auxin. B. tropism. C. nastic. D. circadian. E. phytochrome. 14. Which of these plant hormones is a growth inhibitor? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. gibberellin 15. Which of these plant hormones was studied in the 1880s by Charles and Francis Darwin in experiments on phototropism? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 16. Which plant hormone was discovered in infected rice seedlings that grew extremely tall and slender? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 17. The Latin root word meaning "bent" is the basis for the term A. auxin. B. gibberellin. C. ethylene. D. circadian. E. phytochrome. 18. Which plant hormone, developing in an apical bud, inhibits the growth of lower axillary buds? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 19. Indoleacetic acid (IAA) is the most commonly occurring form of which plant hormone? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 20. Dormancy in seeds and buds can be broken by application of which plant hormone? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 21. A hormone that causes cell division and is found in coconut milk or in dividing root tissue is A. abscisic acid. B. auxin. C. cytokinin. D. ethylene. E. gibberellin. 22. Which of the following is/are an effect(s) of auxin? A. Applied to a woody cutting, it causes roots to develop. B. Auxin production by seeds promotes the growth of fruit. C. Trees sprayed with auxin will keep mature fruit from falling to the ground. D. Under the effect of gravity, auxin moves to the lower surface of roots and stems, causing roots to curve downward and stems to curve upward. E. All of the choices are effects of auxin. 23. How does auxin actually work? A. In the presence of blue light, it triggers additional photosynthesis and growth. B. In the presence of light, it increases the turgor pressure of the cell and accelerates growth. C. In the presence of light, it increases the formation of hydrolytic enzymes that release energy needed for growth purposes. D. In the presence of light, it moves toward the light source and activates a protein that binds to DNA and starts enzyme production. E. In the presence of unidirectional light, it moves to the shady side and activates an ATP-driven proton pump that results in weakened cell walls and eventual elongation. 24. How does gibberellin actually work? A. In the presence of blue light, it triggers additional photosynthesis and growth. B. In the presence of light, it increases the turgor pressure of the cell and accelerates growth. C. In the presence of light, it increases the formation of additional DNA that codes for additional plant structures. D. In the presence of unidirectional light, it moves to the shady side and activates an ATP-driven proton pump that results in weakened cell walls and eventual elongation. E. It attaches to a plasma membrane receptor and results in gene activation to produce the enzyme amylase that releases sugars for additional cell growth, division, and elongation. 25. A chemical messenger from the embryo that apparently stimulates a seed to digest the endosperm is A. abscisic acid. B. auxin. C. cytokinin. D. ethylene. E. gibberellin. 26. The Greek root words meaning "cell" and "move" are the basis for the term A. senescence. B. tropism. C. nastic. D. cytokinin. E. phytochrome. 27. Application of which hormone prevents plant tissues from senescing, or aging? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 28. Which plant hormone is a gas? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 29. Which plant hormone stimulates the ripening of fruit and inhibits plant growth? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 30. The Latin root word meaning "cut off" is the basis for the term A. abscission. B. tropism. C. nastic. D. circadian. E. phytochrome. 31. Which plant hormone is called the stress hormone because it produces dormancy in seeds and buds? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 32. Which plant hormone is associated with the closure of the stomates in a plant under water stress? A. abscisic acid B. auxin C. cytokinin D. ethylene E. gibberellin 33. Which statement is NOT correct about a circadian rhythm? A. These rhythms tend to persist even in the absence of daily light cues. B. An example is the opening of stomates in the morning and their closing at night. C. If plants are maintained in total darkness or total light, their circadian rhythm acts on a faster time scale. D. The primary usefulness of circadian rhythms seems to be to measure day-length changes so plants respond appropriately to seasonal environmental changes. 34. Which is NOT a physiological change related to photoperiodism? A. seed germination B. root branching C. breaking bud dormancy D. some flowering E. onset of senescence 35. The prayer plant, Maranta leuconeura, folds up its leaves each night in accordance with a circadian rhythm. If we were to ship this plant halfway around the world to a location where it is daytime there when it is night here, the plant will A. slowly adjust to synchronize with the new day-night cycle. B. immediately switch to a new cycle and begin to open leaves in day and close them at night. C. detect the change but remain on its original cycle and therefore still fold leaves in day and open them at night. D. not detect the change and therefore remain on its original cycle. 36. Plants could readily develop seasonal responses based on temperature changes but have "elected" through evolution to manage their rhythms based on a comparison of daylight and darkness. Why has the day-night ratio system been selected? A. Temperature has no effect upon plant biochemistry. B. Temperature is a gradation but day/night is all-or-nothing. C. A plant's nervous system is tuned to light stimuli and not to temperature stimuli. D. Temperatures fluctuate widely across seasons and from year to year, but photoperiod comparisons are a more reliable indicator of season. 37. Which statement is NOT true about photoperiodism? A. A short-day plant flowers when the day length is shorter than some critical length. B. A day-neutral plant flowers according to some form of regulation other than photoperiodism. C. A long-day plant will flower even when the day period is not long enough if there is a short period of light during the dark period. D. The phytochrome form Pfr is converted to Pr in daylight, producing the active form that induces flowering in long-day plants. 38. It is the length of the dark period that controls flowering. Since in nature, short days go with long nights and vice versa, what critical observation supports this statement? A. Plants kept in 100% darkness do not flower. B. Plants kept in 100% daylight do not flower. C. Plants either are not dependent upon night length, or require a light period shorter or longer than a given amount, and a brief dark period triggers flowering. D. Plants either are not dependent upon day length, or require a dark period shorter or longer than a given amount, and a brief flash triggers flowering. 39. The Greek root words meaning "plant" and "color" are the basis for the term A. auxin. B. tropism. C. nastic. D. circadian. E. phytochrome. 40. How do some plants seeds "know" when it is day and night, and perhaps when to germinate? A. They chemically count the circadian cycles. B. All plant hormones are products of photosynthetic systems. C. Photosynthetic rates provide direct evidence of sun-produced food. D. Phytochromes cycle between red and far-red absorption and light levels can inhibit germination. E. All of the choices are correct. 41. Positive phototropism is due to A. elongation of cells on the shady plant side B. a pigment similar to riboflavin acts as a light photoreceptor C. auxin migrates from the bright side of the plant to the shaded plant side D. All of these cause positive phototropism. 42. Gravitropism in roots A. is positive when plant roots grow downward. B. is due to statliths in the root cap cells. C. is due to auxins. D. All of the choices are true. 43. Nastic movements in plants A. are independent of the direction of the stimulus. B. may be due to turgor pressure changes in some plants. C. is due to turgor pressure changes and changes in light and dark. D. All of the choices are associated with Nastic movements. 44. Apical dominance in plants is due to which of the following plant hormones? A. ethylene B. gibberellin C. auxins D. cytokinins 45. Which of the following is/are true regarding gibberillins? A. there are about 70 chemically different gibberellins B. are growth promoters causing cell elongation C. these hormones can break seed and bud dormancy D. all of the choices are true 46. Cytokinins A. are plant hormones that promote cell division. B. are used in combination with auxin to produce plants from undifferentiated callose tissue. C. also work with oligosaccharins to effect tissue differentiation. D. All of these are true regarding cytokinins. 47. The flowering of some plants is dependant upon the amount of red light received from sunlight. True False 48. Tropisms are due to some cells growing differently than others. True False 49. If a plant is laid on its side, cells on the lower side of the stem will respond to gravity and elongate, making the stem turn so that it continues to grow upward. True False 50. A hormone is produced in small amounts in a tissue, and it causes a physiological action within that same tissue soon after its production. True False 51. Went's experiment in 1926 with oat coleoptiles showed that agar that absorbed auxin from the tips would cause a tipless shoot to grow away from the side where he had placed the agar, suggesting that auxin causes cells to elongate. True False 52. In a plant seedling exposed to light on only one side, auxin produced in the tip moves to the lighted side and inhibits growth of cells there. True False 53. A cut woody stem exposed to a cytokinin solution will be induced to grow roots rapidly. True False 54. There are about seventy chemical forms of the hormone group called the gibberellins. True False 55. Plant growth is stimulated by the presence of auxins, ethylene, and abscisic acid. True False 56. An undifferentiated plant callus in tissue culture is stimulated to differentiate by the relative amounts of auxin and cytokinin present. True False 57. Ethylene stimulates leaf release, while auxin keeps leaves from falling. True False 58. In addition to regulating flowering in some plants, phytochrome also promotes seed germination and can inhibit stem elongation. True False 59. The plant aging process, senescence, is prevented by cytokinins. True False 60. Dormancy of plants occurs in relation to abscisic acid. True False 61. Thigmomorphogenesis is a touch response where the whole plant responds to an environmental stimulus. True False 62. Describe and give examples of three kinds of external stimuli that produce tropisms in plants. 63. Describe and give examples of three kinds of internal stimuli that produce plant movements. 64. The growth of tendrils around a fencepost is considered thigmotropism. However, there is also an insect called the earwig that expresses what is called thigmotropic behavior: it constantly moves through its environment by skirting open spaces and pressing itself against the surfaces of the substrate. The case of plants growing toward the source of light is positive phototropism. A caterpillar likewise shows the same response of moving toward a source of light, a benefit to moving further out on tree limbs to reach new buds. Although these are both considered "thigmotropism" and "positive phototropism," describe how the mechanism differs between the animal and the plant. Explain why some biologists prefer to call the animal behaviors "taxic movements" to distinguish these basic differences. Chapter 27 KEY 1. E 2. B 3. A 4. B 5. B 6. E 7. B 8. C 9. B 10. C 11. D 12. E 13. A 14. A 15. B 16. E 17. B 18. B 19. B 20. E 21. C 22. E 23. E 24. E 25. E 26. D 27. C 28. D 29. D 30. A 31. A 32. A 33. C 34. B 35. A 36. D 37. D 38. D 39. E 40. D 41. D 42. D 43. D 44. C 45. D 46. D 47. TRUE 48. TRUE 49. TRUE 50. FALSE 51. TRUE 52. FALSE 53. FALSE 54. TRUE 55. FALSE 56. TRUE 57. TRUE 58. TRUE 59. TRUE 60. TRUE 61. TRUE 62. Answers will vary. 63. Answers will vary. 64. Answers will vary.