Review Sheet – Monoploid, Diploid, Meiosis, Mitosis, Life Cycles
advertisement
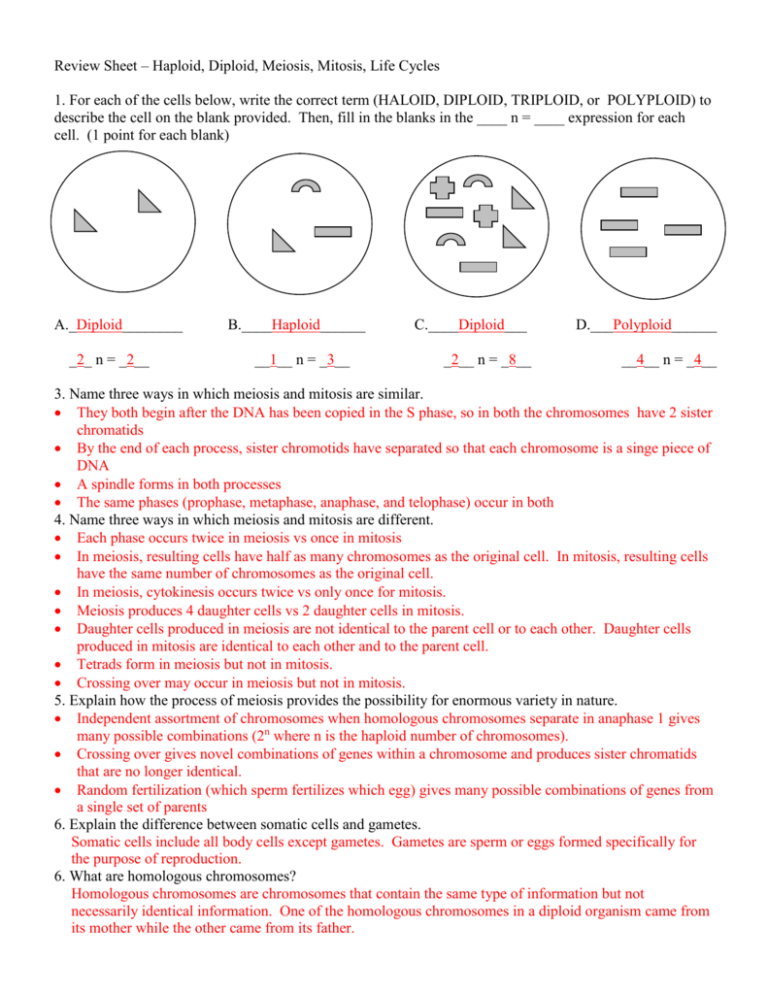
Review Sheet – Haploid, Diploid, Meiosis, Mitosis, Life Cycles 1. For each of the cells below, write the correct term (HALOID, DIPLOID, TRIPLOID, or POLYPLOID) to describe the cell on the blank provided. Then, fill in the blanks in the ____ n = ____ expression for each cell. (1 point for each blank) A._Diploid________ _2_ n = _2__ B.____Haploid______ __1__ n = _3__ C.____Diploid___ D.___Polyploid______ _2__ n = _8__ __4__ n = _4__ 3. Name three ways in which meiosis and mitosis are similar. They both begin after the DNA has been copied in the S phase, so in both the chromosomes have 2 sister chromatids By the end of each process, sister chromotids have separated so that each chromosome is a singe piece of DNA A spindle forms in both processes The same phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) occur in both 4. Name three ways in which meiosis and mitosis are different. Each phase occurs twice in meiosis vs once in mitosis In meiosis, resulting cells have half as many chromosomes as the original cell. In mitosis, resulting cells have the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. In meiosis, cytokinesis occurs twice vs only once for mitosis. Meiosis produces 4 daughter cells vs 2 daughter cells in mitosis. Daughter cells produced in meiosis are not identical to the parent cell or to each other. Daughter cells produced in mitosis are identical to each other and to the parent cell. Tetrads form in meiosis but not in mitosis. Crossing over may occur in meiosis but not in mitosis. 5. Explain how the process of meiosis provides the possibility for enormous variety in nature. Independent assortment of chromosomes when homologous chromosomes separate in anaphase 1 gives many possible combinations (2n where n is the haploid number of chromosomes). Crossing over gives novel combinations of genes within a chromosome and produces sister chromatids that are no longer identical. Random fertilization (which sperm fertilizes which egg) gives many possible combinations of genes from a single set of parents 6. Explain the difference between somatic cells and gametes. Somatic cells include all body cells except gametes. Gametes are sperm or eggs formed specifically for the purpose of reproduction. 6. What are homologous chromosomes? Homologous chromosomes are chromosomes that contain the same type of information but not necessarily identical information. One of the homologous chromosomes in a diploid organism came from its mother while the other came from its father. 7. When do homologous chromosomes come together? Homologous chromosomes come together to form tetrads in Prophase 1 of meiosis. 8. Explain what crossing over is. Crossing over occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange genes when they are in the tetrads. This creates new combinations of genes, some from the maternal chromosome and others from the paternal chromosome. Life Cycle Practice Sheet Fill in the blanks to indicate whether organisms are diploid (2n) or haploid (n) or to tell the name of a process. Then circle sexual or asexual to tell what kind of reproduction is used in the cycle. Life Cycle #1: Adult (2n) MITOSIS Circle one: MITOSIS SEXUAL or ASEXUAL Spore 2n (because mitosis does not change the chromosome #) This is not a life cycle typically found in nature. Fertilization ________________ (name of process) Life Cycle #2: Adult Male (2n) ____________ Meiosis (name of process) Adult Female (2n) ___________ Meiosis (name of process) Male gamete (n) 2n Zygote (___________) Female gamete (n) ____________ Mitosis Circle one: (name of process) SEXUAL or ASEXUAL Life Cycle #3: MITOSIS Spores n ______ MITOSIS Adult male n ______ Adult female MITOSIS Mitosis MITOSIS n ______ Female gamete n ______ MEIOSIS Spore case (2n) MITOSIS Zygote 2n ______ Male gamete n ______ Fertilization ___________________ (name of process) Circle one: SEXUAL or ASEXUAL Overall, this is a sexual life cycle, but it also has a point where a single cell becomes an entire organism. Note however that the spore was formed by meiosis so it is not genetically identical to the cell that made it. This life cycle shows alternation of generations.








