constellation wars
advertisement

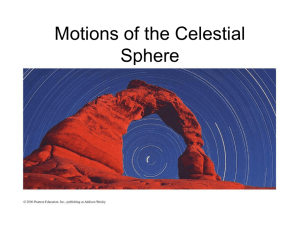
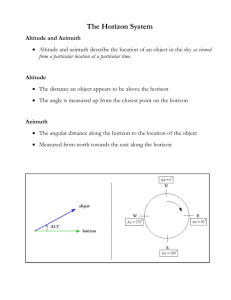
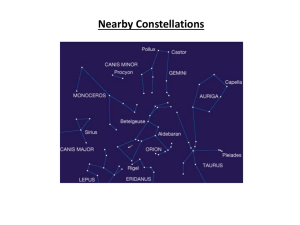
CONSTELLATION WARS A LONG TIME AGO IN A GALAXY FAR, FAR AWAY (OR ….WELL NOT TO FAR FROM HERE) http://www.newforestobservatory.com/category/publications/astonomynowmagazine/page/ 2/ Good night: see about 3000 points of light (unless you live here in WA) Different cultures have all looked for patterns in the stars The brightest stars visible were fit into patterns called constellations Constellation: the pattern of stars seen in the sky, and refer to a specific region in the sky Ancient Astronomers named constellations: • Mythological beings • Heroes (Orion) • Animals (Leo, Scorpio, etc.) http://sankofa.loc.edu/savur/web/astronomy.html Different cultures grouped some of the same basic stars. Often varying interpretations • Example: “The Big Dipper (North America) • “The Wagon” or “The Plough” (Western Europe) • Tail of the “The Great Bear” (Ancient Greeks) • Leg of an Ox (Egyptians) • “Stag” (Siberians) http://aar-vee.blogspot.com/2011/06/niftyastrology-lunar-cycle-time-cycle.html http://arayanastrology.com/images/horoscope2.jpg Many began to believe that the relative position of the stars and planets at a person's birth could determine that person’s destiny Helping them to “see” into the future http://s77.beta.photobucket.com/user/hollyoung_200 http://www.vaastushaastra.com/chineseastrology. html Polaris (Located in Little Dipper): • Help indicate the direction of north • Near constant location in the sky helped travelers for centuries • Location is nearly at the northern horizon year-round while other stars circle around it. • Polaris does not rise or set Why is its locating consistent? • The axis of the Earth is pointed almost directly at it http://my.execpc.com/60/B3/culp/astronomy/Winter/Bears.html Constellations: • Help astronomers to specify large areas of the sky (geologists and continents) • Primitive calendars predicting/planning harvest and planting seasons. Ancient cultures knew when certain stars appeared on the horizon before daybreak, it would be the beginning of spring Example of a spring star chart for the Northern Hemisphere http://mail.colonial.net/~hkaiter/astronomyimagesC/Spring_star_chart.jpg The stars that make up any constellation are not actually close together in space • They are bright enough to be observed with the naked eye • They happen to lie in the same direction in the sky as seen from Earth • PERSPECTIVE!!!! Roughly 88 constellations in all • Most are visible from North America at some time during the year http://skywatchingworld.com/finding-big-dipper-constellation/ http://krystalschultheiss.com/stuff/wp-admin/star-constellation-orion Humans lack depth perception we look into space: • Our perspective is that all the stars lie same distance The ancient Greeks mistook this illusion for reality • Believed Earth to be surrounded by a great Celestial Sphere Constellations seem to move across the sky from East to West • Ancient astronomers understood that the relative locations of stars remained unchanged • Conclusion: the stars were firmly attached to a Celestial Sphere that surrounded the Earth. Celestial Sphere: surrounds the Earth, is a canopy of stars resembling an astronomical painting on a heavenly ceiling Star Trails: show how all stars appear to move in circles around a point very close to the star Polaris http://www.perthnow.com.au/stunning-photographs-of-star-trails-over-outback-australia/story-e6frg4nl-1226411728115 http://www.bluemoon.bz/astrology/sun-ingress/libra/ Today we understand: • Earth does not lie in a the center of a great ball • Apparent motion of the stars is the result the Earth’s rotation, not the sphere’s rotation. Celestial Poles: The points where Earth’s axis intersects the celestial sphere Celestial Equator: Midway between the north and south celestial poles http://www.herongyang.com/astrology_horoscope/celestial_sphere.jpg Today: • that the Earth does not really lie in the center of a giant ball Names given to certain locations: • North Celestial Pole (NCP): The point directly above the Earth’s North Pole • South Celestial Pole (SCP): The point directly above the Earth’s South Pole • Celestial Equator: represents the Earth’s equator into space • Ecliptic Ecliptic: the ecliptic is the plane of Earth's orbit around the Sun • The apparent path of the Sun on the celestial sphere • as seen from the Earth's center • Sun’s path is not normally noticeable from the Earth's surface • Earth rotates • Carrying the observer through the cycle of sunrise and sunset, concealing the apparent position of the Sun against the background stars. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecliptic http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EjMNNpIksaI