A mineral is… A naturally-occurring inorganic substance with a
advertisement
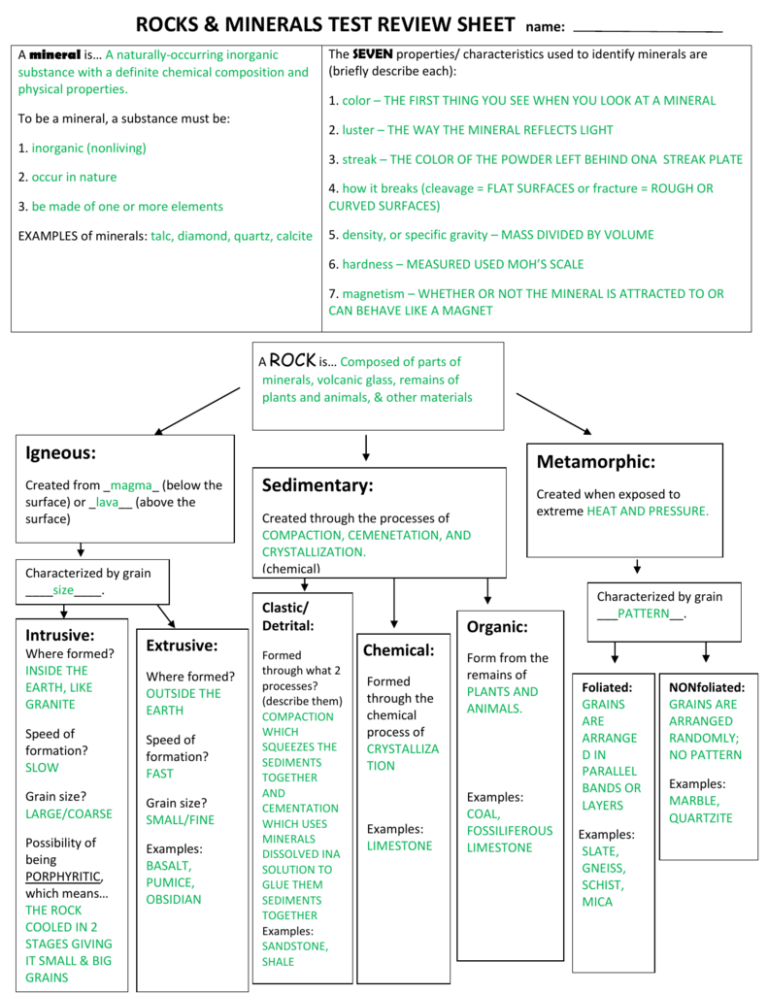
ROCKS & MINERALS TEST REVIEW SHEET A mineral is… A naturally-occurring inorganic substance with a definite chemical composition and physical properties. To be a mineral, a substance must be: name: The SEVEN properties/ characteristics used to identify minerals are (briefly describe each): 1. color – THE FIRST THING YOU SEE WHEN YOU LOOK AT A MINERAL 2. luster – THE WAY THE MINERAL REFLECTS LIGHT 1. inorganic (nonliving) 3. streak – THE COLOR OF THE POWDER LEFT BEHIND ONA STREAK PLATE 2. occur in nature 3. be made of one or more elements 4. how it breaks (cleavage = FLAT SURFACES or fracture = ROUGH OR CURVED SURFACES) EXAMPLES of minerals: talc, diamond, quartz, calcite 5. density, or specific gravity – MASS DIVIDED BY VOLUME 6. hardness – MEASURED USED MOH’S SCALE 7. magnetism – WHETHER OR NOT THE MINERAL IS ATTRACTED TO OR CAN BEHAVE LIKE A MAGNET A ROCK is… Composed of parts of minerals, volcanic glass, remains of plants and animals, & other materials Igneous: S Created from _magma_ (below the surface) or _lava__ (above the surface) Characterized by grain ____size____. Intrusive: Where formed? INSIDE THE EARTH, LIKE GRANITE Created through the processes of COMPACTION, CEMENETATION, AND CRYSTALLIZATION. (chemical) Clastic/ Detrital: Extrusive: Where formed? OUTSIDE THE EARTH Speed of formation? SLOW Speed of formation? FAST Grain size? LARGE/COARSE Grain size? SMALL/FINE Possibility of being PORPHYRITIC, which means… THE ROCK COOLED IN 2 B STAGES GIVING IT SMALL & BIG GRAINS Sedimentary: Examples: BASALT, PUMICE, OBSIDIAN Formed through what 2 processes? (describe them) COMPACTION WHICH SQUEEZES THE SEDIMENTS TOGETHER AND CEMENTATION WHICH USES MINERALS DISSOLVED INA SOLUTION TO GLUE THEM SEDIMENTS TOGETHER Examples: SANDSTONE, SHALE Metamorphic: Created when exposed to extreme HEAT AND PRESSURE. Characterized by grain ___PATTERN__. Organic: Chemical: Formed through the chemical process of CRYSTALLIZA TION Examples: LIMESTONE Form from the remains of PLANTS AND ANIMALS. Foliated: GRAINS ARE ARRANGE D IN PARALLEL BANDS OR LAYERS Examples: COAL, FOSSILIFEROUS LIMESTONE Examples: SLATE, GNEISS, SCHIST, MICA S NONfoliated: GRAINS ARE ARRANGED RANDOMLY; NO PATTERN Examples: MARBLE, QUARTZITE Answer the following questions using the diagram below. 1. How does sediment become a sedimentary rock? THROUGH COMPACTION AND CEMENTATION 2. How does a metamorphic rock become an igneous rock? MELTS TO MAGMA AND THEN COOLS TO BECOME IGNEOUS 3. Describe two ways in which an igneous rock can become a metamorphic rock. WAY 1: IGNEOUS ROCK IS EXPOSED TO EXTREME HEAT AND PRESSURE CHANGING IT INTO METAMORPHIC ROCK WAY 2: IGNEOUS ROCK IS WEATHERED AND ERODED TO SEDIMENTS. THEN, THE SEDIMENTS ARE COMPACTED AND CEMENTED TO BECOME A SEDIMENTARY ROCK, AND THEN THE SEDIMENTARY ROCK IS EXPOSED TO EXTREME HEAT AND PRESSURE AND IT BECOMES A METAMORPHIC ROCK. 4. How does magma become sediment? MAGMA COOLS TO BECOME AN IGNEOUS ROCK, AND THEN THE IGNEOUS ROCK WEATHERS AND ERODES TO SEDIMENT 5. What happens when an igneous rock is exposed to heat and pressure? IT BECOMES A METAMORPHIC ROCK EXTRA: 6. The processes of Weathering and Erosion create what? SEDIMENTS 7. How does an igneous rock become a sedimentary rock? IGNEOUS ROCK IS WEATHERED AND ERODED TO SEDIMENTS. THEN, THE SEDIMENTS ARE COMPACTED AND CEMENTED TO BECOME A SEDIMENTARY ROCK 8. When a rock is exposed to heat and pressure, what type of rock is formed? METAMORPHIC






