Synthetic and characterization data for all new compounds
advertisement

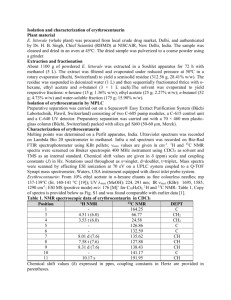
Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 Supporting Information for Preparation and Structure of 2-Iodoxybenzoate Esters: Soluble and Stable Periodinane Oxidizing Reagents Viktor V. Zhdankin,* Dmitry N. Litvinov, Alexey Y. Koposov, Department of Chemistry, University of Minnesota Duluth, Duluth, Minnesota 55812, USA Thanh Luu, Michael J. Ferguson, Robert McDonald, and Rik R. Tykwinski* Department of Chemistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G 2G2 Canada Contents: 1. Synthetic and characterization data for all new compounds 2. Experimental details on oxidation of alcohols with ester 4c General. All melting points were determined in an open capillary tube with a Mel-temp II melting point apparatus and are uncorrected. Infrared spectra were recorded neat, as a CCl4 mull, or as a KBr pellet on a Perkin-Elmer 1600 series FT-IR spectrophotometer. NMR spectra were recorded on a Varian UNITY INOVA 300 MHz NMR spectrometer at 300 MHz (1H NMR), and 75 MHz (13C NMR). Chemical shifts are reported in parts per million (ppm). 1H chemical shifts are referenced relative to the residual nondeuteriated solvent of chloroform at 7.24. The 13C chemical shifts are referenced relative to CDCl3 at 77.0. Mass-spectra were obtained with a Micromass Zabspec oaTOF or PE Biosystems Mariner TOF instrument. Microanalyses were carried out by Atlantic Microlab, Inc., Norcross, Georgia. All commercial reagents were ACS reagent grade and used without further purification. Methylene chloride was distilled from CaH2 immediately prior to use. Diethyl ether was distilled from Na/benzophenone. All other reagents and solvents were of commercial quality from freshly opened containers. Preparative chromatography separations were carried out on Acros silica gel (0.060-0.200 1 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 mm, pore diam. 4 nm). Reaction flasks were oven-dried at 200 oC, flame-dried and flushed with dry nitrogen prior to use. General procedure for preparation of 2-iodobenzoic acid esters. The appropriate alcohol (20 mmol) in dry ether (30 ml) was placed into a 50 ml round bottom flask equipped with magnetic stirrer and rubber septum. The 2.5M hexane solution of BuLi (8.0 ml, 20 mmol) was added into the flask dropwise at 0 oC in 5 minutes and the mixture was stirred for 30 min at room temperature under nitrogen. In a separate 25 ml flask, 2iodobenzoyl chloride (5.05 g, 19 mmol) was dissolved in 5 ml of dry ether and added dropwise at room temperature to the reaction flask. Immediate reaction takes place and the formation of a precipitate of lithium chloride is observed. The nitrogen line was disconnected, the reaction stirred overnight at room temperature, and then quenched with 10 ml of water. The top ethereal layer was separated, dried with MgSO4, and the solvent removed in vacuo. Crude esters of 2-iodobenzoic acid were purified by column chromatography (hexanes/ethyl acetate, 4:1, as eluent). 2-iodobenzoic acid ethyl ester 3b: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with ethanol according to general procedure afforded 4.45 g (85%) of product 3b. IR (KBr): 3065, 2981, 2904, 1727, 1290, 1251 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.00 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.78 (dd, J1 = 8 Hz, J2 = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (td, J1 = 7.6 Hz, J2 = 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.14 (td, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 1.41 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.6, 141.2, 135.5, 132.5, 130.8, 127.9, 94.0, 61.7, 14.2. Anal. Calcd for C9H9IO2: C, 39.16; H, 3.29; I, 45.97. Found: C, 38.90; H, 3.34; I, 45.67. 2-iodobenzoic acid isopropyl ester 3c: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with 2-propanol according to general procedure afforded 4.6 g (84%) of product 3c. IR (KBr): 3065, 2981, 2877, 1724, 1291, 1254 cm-1. 1 H NMR (CDCl3): 7.97 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.75 (dd, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (td, J1 = 7.7 Hz, J2 = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (td, J1 = 7.7 Hz, J2 = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 5.28 (m, 1H), 2 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 1.40 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 6H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.3, 141.2, 136.0, 132.5, 130.8, 128.0, 94.0, 69.7, 22.0. Anal. Calcd for C10H11IO2: C, 41.40; H, 3.82; I, 43.75. Found: C, 41.23; H, 3.85; I 43.57. 2-iodobenzoic acid tert-butyl ester 3d: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with 2-methyl-2-propanol according to general procedure afforded 4.85 g (84%) of product 3d. IR (KBr): 3064, 2978, 2932, 1726, 1252 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 7.93 (dd, J1 = 8.8 Hz, J2 = 0.7 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (d, J1 = 7.6 Hz, J2 = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (td, J1 = 7.6 Hz, J2 = 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (td, J1 = 7.6 Hz, J2 = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 1.62 (s, 9H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.2, 140.9, 137.4, 131.9, 130.4, 127.8, 93.4, 82.6, 28.1. Anal. Calcd for C11H13IO2: C, 43.44; H, 4.31; I, 41.73. Found: C, 43.83; H, 4.33; I, 41.35. 2-iodobenzoic acid (-)-menthyl ester 3e: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with (-)-menthol according to general procedure afforded 4.62 g (66%) of product 3e. IR (KBr): 3066, 2955, 2869, 1724, 1290, 1252 cm-1. 1 H NMR (CDCl3): 7.98 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (dd, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (t, J= 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 4.97 (td, J1 = 11 Hz, J2 = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 2.18 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 1H), 2.02 (m, 1H), 1.73 (m, 2H), 1.54 (m, 2H), 1.17 (m, 2H), 1.14 (m, 1H), 0.93 (m, 6H), 0.82 (d, J = 7 Hz, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.2, 141.2, 136.0, 132.3, 130.4, 127.8, 93.9, 75.9, 47.1, 40.8, 34.3, 31.5, 26.3, 23.3, 22.1, 20.8, 16.3. Anal. Calcd for C17H23IO2: C, 52.86; H, 6.0. Found: C, 53.02; H, 6.10. 2-iodobenzoic acid (+)-menthyl ester 3f: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with (+)-menthol according to general procedure afforded 4.33 g (62%) of product 3f. IR (KBr): 3066, 2956, 2868, 1724, 1290, 1251 cm-1. 1 H NMR (CDCl3): 7.98 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (dd, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (t, J= 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 4.97 (td, J1 = 11 Hz, J2 = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 2.19 (d, J = 12.7 Hz, 1H), 2.02 (m, 1H), 1.73 (m, 2H), 1.55 (m, 2H), 1.17 (m, 2H), 1.14 (m, 1H), 0.93 (m, 6H), 0.82 (d, J = 7 Hz, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.2, 141.2, 136.0, 132.3, 3 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 130.5, 127.8, 93.9, 75.9, 47.1, 40.8, 34.3, 31.5, 26.3, 23.3, 22.1, 20.8, 16.3. Anal. Calcd for C17H23IO2: C, 52.86; H, 6.0; I, 32.85. Found: C, 53.04; H, 6.08; I, 32.60. 2-iodobenzoic acid (±)-menthyl ester 3g: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with (±)-menthol according to general procedure afforded 5.17 g (74%) of product 3g. IR (KBr): 3066, 2955, 2869, 1724, 1290, 1252 cm-1. 1 H NMR (CDCl3): 7.97 (dd, J1 = 8.1 Hz, J2 = 1.2, 1H), 7.74 (dd, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (td, J1 = 7.5 Hz, J2 = 1.2, 1H), 7.13 (td, J1 = 7.7 Hz, J2 = 1.8, 1H), 4.97 (td, J1 = 11 Hz, J2 = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 2.19 (m, 1H), 2.02 (m, 1H), 1.72 (m, 2H), 1.54 (m, 2H), 1.17 (m, 2H), 1.13 (m, 1H), 0.93 (m, 6H), 0.82 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.3, 141.3, 136.2, 132.5, 130.6, 128.0, 94.1, 76.0, 47.3, 41.0, 34.4, 31.7, 26.4, 23.5, 22.2, 21.0, 16.5. Anal. Calcd for C17H23IO2: C, 52.86; H, 6.0; I, 32.85. Found: C, 53.02; H, 6.09; I, 32.58. 2-iodobenzoic acid [(1S)-endo]-(-)-bornyl ester 3h: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with [(1S)-endo]-(-)-borneol according to general procedure afforded 6.49 g (89%) of product 3h, mp 64-65 °C (recryst. from CH2Cl2/hexanes). IR (KBr): 2995, 2876, 1726, 1290, 1253 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): dd J1 = 7.9 Hz, J2 = 1.1 Hz, dd, J1 = 7.9 Hz, J2 = 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (td, J1 = 7.6 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (td, J1 = 7.8 Hz, J2 = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 5.15 (m, 1H), 2.50 (m, 1H), 1.75 (m, 2H), 1.35 (m, 4H), 0.96 (s, 3H), 0.94 (s, 3H), 0.91 (s, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.9, 141.3, 135.8, 132.4, 130.8, 127.9, 93.9, 81.8, 49.0, 48.0, 44.9, 36.7, 28.0, 27.4, 19.7, 18.9, 13.7. Anal. Calcd for C17H21IO2: C, 53.14; H, 5.51; I, 33.03. Found: C, 53.31; H, 5.59; I, 32.82. 2-iodobenzoic acid 2-adamantyl ester 3i: Reaction of 2-iodobenzoyl chloride with 2-adamantanol according to general procedure afforded 6.02 g (83%) of product 3i, mp 90-91 °C (recryst. from Et2O). IR (KBr): 2925, 2854, 1717, 1292, 1264 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 7.99 (dd, J1 = 7.9 Hz, J2 = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (dd, J1 = 8.0 Hz, J2 = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (td, J1 = 7.6 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (td, J1 = 7.7 Hz, J2 = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 5.22 (m, 1H), 2.18 (m, 4H), 1.89 (m, 6H), 1.77 (m, 2H), 4 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 1.65 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (CDCl3): 165.9, 141.3, 135.7, 132.4, 130.9, 127.9, 94.1, 78.8, 37.4, 36.4, 32.0, 27.2, 27.0. Anal. Calcd for C17H19IO2: C, 53.42; H, 5.01; I, 33.20. Found: C, 53.40; H, 5.05; I, 33.17. 2-iodobenzoic acid 1-adamantyl ester 3j: Reaction of 1-iodobenzoyl chloride with 2-adamantanol according to general procedure afforded 6.39 g (88%) of product 3j, mp 95-96 °C (recryst. from Et2O). IR (KBr): 3060, 2851, 1717, 1290, 1270 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 7.93 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H), 7.70 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.30 (m, 6H), 2.23 (m, 3H), 1.72 (m, 6H). 13C NMR (CDCl3): 165.9, 140.9, 137.3, 131.9, 130.5, 127.8, 93.5, 82.8, 41.3, 36.2, 30.9. Anal. Calcd for C17H19IO2: C, 53.42; H, 5.01; I, 33.20. Found: C, 53.44; H, 5.02; I, 33.38. General procedure for oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid esters. 20 ml of dichloromethane was added to a rigorously stirred suspension of the appropriate ester of 2-iodobenzoic acid 3 (5 mmol) and sodium hypochlorite solution (“bleach”, 5% NaOCl, 15 ml), and then acetic acid (5 ml) was added dropwise in 10 minutes at room temperature. A yellow solution was initially formed and later turned into a white precipitate or a colorless dichloromethane solution. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight and then extracted five times with 10 ml of dichloromethane. The extract was washed with saturated aqueous solution of NaHCO3 and dried with MgSO4, the solvent was evaporated and the product was dried in vacuo. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid methyl ester 4a: Oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid methyl ester 3a according to general procedure afforded 0.33 g (21%) of product 4a, mp 194 °C (decomp.). The lower preparative yield for this product is explained by its high solubility in water and low solubility in dichloromethane. Solubility in CH2Cl2: 0.061 g in 100 g of solvent (up to 0.003 M solutions); highly soluble in H2O and moderately soluble in acetonitrile. IR (KBr): 3063, 1687, 786, 755 cm-1. 1H NMR (DMSO–d6): 8.28 (dd, J1 = 7.7 Hz, J2 = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 8.10 (dd, J1 = 7.5 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (td, J1 = 7.5 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (td, J1 = 7.2 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 5 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 1H), 4.00 (s, 3H)13C NMR (DMSO–d6): 167.2, 150.6, 134.6, 131.7, 129.9, 125.7, 123.0, 53.6. Anal. Calcd for C8H7IO4•H2O: C, 30.79; H, 2.91; I, 40.67. Found: C, 30.81; H, 2.92; I, 40.42. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid ethyl ester 4b: Oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid ethyl ester 3b according to general procedure afforded 0.99 g (61%) of product 4b, mp 196 °C (decomp.; recryst. from acetonitrile). IR (KBr): 1633, 804, 732 cm-1. 1H NMR (DMSO–d6): 8.27 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 8.10 (dd, J1 = 7.4 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (td, J1 = 7.6 Hz, J2 = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.77 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 4.45 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 1.38 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). C NMR (DMSO–d6): 162.8, 146.6, 13 130.6, 127.8, 126.1, 122.1, 119.2, 58.9, 10.0. Anal. Calcd for C9H9IO4•H2O: C, 33.15; H, 3.40; I, 38.92. Found: C, 33.11; H, 3.41; I, 39.08. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid isopropyl ester 4c: Oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid isopropyl ester 3c according to general procedure afforded 1.43 g (89%) of product 4c, mp 156 °C (decomp.; recryst. from CH2Cl2/ether). Solubility in CH2Cl2: 69.7 g in 100 g of solvent (up to 2.86 M solutions). IR (KBr): 1673, 789, 743 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.34 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.01 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 5.31 (m, 1H) 1.35 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 6H). C NMR (CDCl3): 167.5, 149.6, 134.9, 131.8, 130.2, 126.8, 124.8, 71.9, 21.8. Anal. 13 Calcd for C10H11IO4: C, 37.29; H, 3.44; I, 39.40. Found: C, 37.21; H, 3.49; I, 39.36. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid tert-butyl ester 4d: Oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid tert-butyl ester 3d according to general procedure afforded 0.99 g (59%) of product 4d, mp 160 °C (decomp.; recryst. from CH2Cl2/hexanes). Solubility in CH2Cl2: 5.17 g in 100 g of solvent (up to 0.2 M solutions). IR (KBr): 3057, 2910, 2852, 1672, 1251, 771, 745. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.43 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.01 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.93 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 1.62 (s, 9H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 167.2, 147.8, 140.9, 131.9, 130.4, 128.0, 127.8, 6 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 85.9, 28.1. Anal. Calcd for C11H13IO4: C, 39.31; H, 3.90; I, 37.76. Found: C, 39.39; H, 4.03; I, 37.28. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid (-)-menthyl ester 4e: Oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid (-)-menthyl ester 3e according to general procedure afforded 1.50 g (69%) of product 4e, mp 101 °C (decomp.; recryst. from EtOAc/hexanes); []D20 = –63°. Solubility in CH2Cl2: 54.11 g in 100 g of solvent (up to 1.71 M solutions). IR (KBr): 1679, 774, 746 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.44 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (d, J = 7.4, 1H), 7.91 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.67 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 5.01 (td, J1 = 11.0 Hz, J2 = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 2.18 (d, J = 11 Hz, 1H), 1.88 (m, 1H), 1.75 (m, 2H), 1.58 (m, 2H), 1.11 (m, 3H), 0.92 (m, 6H), 0.75 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 167.6, 148.6, 135.0, 132.4, 130.3, 126.9, 125.1, 78.7, 47.1, 40.5, 34.1, 31.4, 26.4, 23.5, 21.9, 20.7, 16.5. Anal. Calcd for C17H23IO4•H2O: C, 46.80; H, 5.78. Found: C, 47.14; H, 5.47. ES MS: m/z (%) 859 (100), [2M+Na]+. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid (+)-menthyl ester 4f: Oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid (+)-menthyl ester 3f according to general procedure afforded 1.37 g (63%) of product 4f, mp 100 °C (decomp.; recryst. from EtOAc/hexanes); []D20 = +62°. IR (KBr): 1675, 773, 742 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.41 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.64 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 4.97 (td, J1 = 10.7 Hz, J2 = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 2.17 (m, 1H), 1.87 (m, 1H), 1.75 (m, 2H), 1.57 (m, 2H), 1.10 (m, 3H), 0.91 (m, 6H), 0.72 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 167.6, 148.6, 134.9, 132.3, 130.2, 126.9, 125.1, 78.5, 47.0, 40.3, 33.9, 31.2, 26.4, 23.4, 21.9, 20.7, 16.5. Anal. Calcd for C17H23IO4•H2O: C, 46.80; H, 5.78. Found: C, 47.11, H, 5.45. ES MS: m/z (%) 859 (100), [2M+Na]+, 419 (15), [M+H]+. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid (±)-menthyl ester 4g: Oxidation of 2-iodobenzoic acid (±)-menthyl ester 3g according to general procedure afforded 1.59 g (73%) of product 4g, mp 99-100 °C (decomp.; recryst. from MeCN/hexanes). IR (KBr): 1679, 774, 746. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.47 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.03 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.91 (m, 1H), 7 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 2.11(m, 1H), 1.82 (m, 1H), 1.73 (m, 2H), 1.55 (m, 2H), 1.07 (m, 3H), 0.91 (m, 6H), 0.68 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (CDCl3): 167.7, 148.9, 135.1, 132.2, 130.3, 127.0, 125.2, 78.6, 47.1, 40.5, 34.1, 31.6, 26.4, 23.5, 22.0, 20.8, 16.6. Anal. Calcd for C17H23IO4: C, 48.82; H, 5.54. Found: C, 48.71; H, 5.68. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid [(1S)-endo]-(-)-bornyl ester 4h: Oxidation of 2-iodoxybenzoic acid [(1S)-endo]-(-)-bornyl ester 3h according to general procedure afforded 1.31 g (63%) of product 4h, mp 164-165 °C (decomp.; recryst. from MeCN/hexanes). IR (KBr): 3057, 2882, 1678, 1296, 775, 750 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.41 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.05 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.87 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 5.11 (m, 1H), 2.46 (m, 1H), 2.03 (m, 1H), 1.77 (m, 2H), 1.40 (m, 1H), 1.26 (m, 1H), 1.14 (m, 1H), 0.95 (s, 3H), 0.91 (s, 3H), 0.87 (s, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 168.3, 149.4, 134.9, 131.9, 130.1, 126.8, 125.0, 83.8, 49.2, 47.9, 44.8, 36.6, 27.9, 27.7, 19.6, 18.9, 13.7. Anal. Calcd for C17H21IO4: C, 49.05; H, 5.09; I, 30.49. Found: C, 48.94; H, 5.26; I, 29.90. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid 2-adamantyl ester 4i: Oxidation of 2-iodoxybenzoic acid 2-adamantyl 3i according to general procedure afforded 1.72 g (83%) of product 4i, mp 138 °C (decomp.; recryst. from CH2Cl2/hexanes). IR (KBr): 3061, 2854, 1670, 1289, 763, 752 cm-1. 1H NMR(CDCl3): 8.46 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.13 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.94 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.69 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 5.30 (m, 1H), 2.10 (m, 4H), 1.96 (m, 6H), 1.79 (m, 2H), 1.64 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (CDCl3): 167.6, 148.1, 135.2, 132.4, 130.4, 127.0, 124.8, 81.3, 37.1, 36.3, 31.8, 27.1, 26.8. Anal. Calcd for C17H19IO4: C, 49.29; H, 4.62. Found: C, 49.19; H, 4.71. 2-iodoxybenzoic acid 1-adamantyl ester 4j: Oxidation of 2-iodoxybenzoic acid 1-adamantyl 3j according to general procedure afforded 1.37 g (66%) of product 4j, mp 120-121 °C (decomp.; recryst. from CH2Cl2/Hexanes). IR (KBr): 3061, 2855, 1670, 1290, 763, 752 cm-1. 1H NMR (CDCl3): 8.45 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.01 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.62 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 2.25 (m, 6H), 2.01 (m, 3H), 1.72 (m, 6H). 8 13 C NMR (CDCl3): 166.8, 148.1, Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 134.6, 132.2, 130.5, 128.1, 124.7, 85.3, 41.3, 35.9, 31.0. Anal. Calcd for C17H19IO4: C, 49.29; H, 4.62; I, 30.64. Found: C, 49.75; H, 4.77; I, 29.09. General procedure for oxidation of alcohols with ester 4c: To a solution of IBXester 5c (0.161 g, 0.5 mmol) in methylene chloride (5 ml) a solution of the appropriate alcohol (0.5 mmol) in methylene chloride (2 ml) was added, and then the trifluoroacetic acid (0.057 g, 0.5 mmol) (or BF3•Et2O (0.5 mmol) in entry 6) was added dropwise. The reaction mixture was stirred at 40 °C for 2 hours (unless specified in the table). A portion of the crude reaction mixture (1.5 ml) was passed through 1 cm of silica gel suspended in a pasteur pipet and eluted with CH2Cl2 (2-3 ml); then diluted to 10 ml and analyzed by GCMS. Entry Alcohol Additive Rxn time Temperature Yield (%) 1 OH CF3CO2H 11 hrs r.t 95 2 OH CF3CO2H 2 hrs 40 °C 95 CF3CO2H 2 hrs 40 °C 90 3 OH 4 OH CF3CO2H 2 hrs 40 °C 95 5 OH BF3•Et2O 15 min r.t. 95 CF3CO2H 1h 40 °C 100 CF3CO2H 2h 40 °C 50 6 OH 7 N OH Entry 1. Cyclohexanol was reacted with reagent 4c at r.t. for 11 hrs according to general procedure to produce cyclohexanone (95%, as determined by the integration of the area of the GCMS signal relative to internal standard). 9 Supplementary material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2003 Entry 2. Cyclohexanol was reacted with reagent 4c according to general procedure to produce cyclohexanone (95%, as determined by integration of the area of the GC signal relative to internal standard). Entry 3. Cycloheptanol was reacted with reagent 4c according to general procedure to produce cycloheptanone (90%, as determined by integration of the area of the GC signal relative to internal standard). Entry 4. Cyclooctanol was reacted with reagent 4c according to general procedure to produce cyclooctanone (95%, as determined by integration of the area of the GC signal relative to internal standard). Entry 5. Cyclooctanol was reacted with reagent 4c in the presence of BF3•Et2O at r.t. for 15 min. according to general procedure to produce cyclooctanone (95%, as determined by integration of the area of the GC signal relative to internal standard). Entry 6. Benzyl alcohol was reacted with reagent 4c according to general procedure to produce benzlylic aldehyde (100%, as determined by integration of the area of the GC signal relative to internal standard). Entry 7. 3-Pyridin-2-yl-propan-1-ol was reacted with reagent 4c according to general procedure to produce 3-pyridin-2-yl-propan-1-one (50%, as determined by integration of the area of the GC signal relative to internal standard). Typical procedure for oxidation of alcohols with ester 4c in the presence of KBr: To a solution of IBX-ester 4c (0.01 g, 0.031 mmol) in CDCl3 (0.5 ml) benzyl alcohol (5 l, 0.048 mmol) was added, and then an excess of KBr and 18-crown-6 (2 mg, 0.0075 mmol) were added. The reaction mixture was heated in NMR tube for 4 h at 50 °C to afford benzaldehyde in quantitative yield as judged by the integration of the area of the 1 H NMR signal at 10.03 ppm. 10