Quiz #1

REACTOR TECHNOLOGY COURSE
FOR UTILITY EXECUTIVES
Quiz #1
June 12, 2007
Name________________________
Part One: Short Answer (7 questions, 30 points)
1.
(5 points) Describe how neutrons “thermalize” (slow down) in a nuclear reactor. Why is it important for neutrons to thermalize in a Light Water Reactor (LWR)?
2.
(3 points at 1 points each) After being born from fission in a LWR core, what three things can happen to a neutron?
3.
(4 points at 2 points for definition and 2 points for fission explanation) In your own words, define the nuclear physics term "binding energy." Use the concept of binding energy to describe why the fission of heavy nuclei (e.g. Uranium) releases energy.
4.
(4 points) Why must vigilance of a nuclear reactor be maintained after shutdown?
Briefly explain the unique phenomenon that prevents “walking away from” a nuclear reactor after shutdown.
RTC 2007 Quiz #1 Page 2 of 7
5.
(5 points total) a.
(2 points) What is meant by “defense in depth?” b.
(3 points at 1 point each) What physical barriers exist to prevent fission product release from LWR fuel to the environment?
6.
(3 points at 1 points each) List three lessons learned from the TMI-2 accident.
7.
(6 points) List one of the reactivity feedback effects that contributes to the safety and controllability of a LWR and briefly explain how it works.
RTC 2007 Quiz #1 Page 3 of 7
Part Two: Matching (3 problems, 16 points)
In each of the following, match the word with its definition.
8.
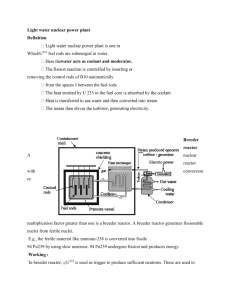
(7 points at 1 point each) Match each of the PWR plant components with its primary function:
A.
Steam generator
B.
Pressurizer
______ Adjusts reactivity in the reactor core
______ Ultimate barrier to the release of radioactivity from
C.
D.
Control rod
Reactor coolant pumps the fuel to the environment
______ Converts steam to liquid for reuse in the secondary system; removes waste heat
______ Transfers heat from the primary to the secondary
E.
Steam turbine
F.
Condenser
G.
Containment building coolant loops
______ Circulates the primary coolant
______ Converts thermal energy of steam to electricity
______ Controls the pressure in the primary system
9.
(4 points at 1 point for each) Match the type of radiation with the material that would provide the most efficient shielding:
A.
Alpha
B.
Beta
C.
Neutron
D.
Gamma
______ Lead blocks
______ Clothing
______ A sheet of paper
______ Tank of water
10.
(5 points at 1 point for each) Match each material with its function in a reactor:
______ Fuel A.
Boron
B.
Uranium
C.
Hafnium
D.
Zirconium
E.
Xenon
______ Structural
______ “Parasitic” poison produced by fission
______ Neutron absorber used in control rods
______ Soluble poison, also can be used in control rods
RTC 2007 Quiz #1 Page 4 of 7
Part Three: Multiple Choice (22 points, 11 problems at 2 points each)
In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best answer from those given.
11.
The boiling crisis of concern in a Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) is: a) Departure from Nucleate Boiling (DNB) b) different from that of a Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) c) the basis for some of our design and operating limits d) all of the above
12.
In thermal hydraulics, the “quality” of a flow is: a) its ability to absorb neutrons b) the fraction of vapor (steam) in the vapor/liquid mixture c) the temperature at which nucleate boiling begins d) a kind of boiling crisis that we try to protect against in BWRs
13.
What is the primary source of decay heat in the hours after reactor shutdown? a) b) c) delayed neutrons
235
U and
239
Pu the radioactive decay of fission products d) the control rods
14.
In a LWR fuel rod, the temperature is highest: a) at the center of the fuel pellet b) midway between the center and the outer diameter of the fuel pellet c) in the gas gap d) at the outer surface of the fuel rod
15.
In most commercial LWRs the delayed neutron fraction,
, is approximately equal to: a) 0.65 (65% of fission neutrons) b) 0.1 (10% of fission neutrons) c) 0.0065 (0.65% of fission neutrons) d) 10
-24
(10
-22
% of fission neutrons)
RTC 2007 Quiz #1 Page 5 of 7
16.
Which of the following best describes the energy of a thermal neutron in a LWR: a) 2 MeV b) 100 keV c) 1 keV d) 0.025 eV
17.
Fuel melting in a reactor is bad because: a) significant money must be spent to re-solidify the fuel at the end of the cycle b) the efficiency of heat transfer from the fuel to the coolant will improve c) the fuel becomes more dense, so not as much thermal power can be generated d) the fuel deforms, increasing strain on the fuel rod cladding and increasing the chance of cladding failure and fission product release
18.
During the TMI-2 incident, reactor coolant escaped from the primary loop via: a) a hole in the reactor pressure vessel b) a stuck open Pilot Operated Relief Valve (PORV) c) a failed Reactor Coolant Pump (RCP) seal d) a ruptured steam generator U-tube weld
19.
Approximately how much energy is released in one 235 U fission? a) 1/40 eV b) 1 eV c) 200 MeV d) 1 Joule
20.
For a single radiation interaction with human tissue, biological damage depends on: a) the type of radiation b) the energy deposited by the radiation c) the half-life of the isotope emitting the radiation d) both (a) and (b) e) all of the above
RTC 2007 Quiz #1 Page 6 of 7
21.
Delayed neutrons are important for reactor control because: a) they are produced at higher energy than prompt neutrons b) they lower the radiation levels in existing reactor plants c) they represent a large fraction of the neutrons available to produce fission d) they significantly increase the average neutron lifetime
The following questions are BONUS (maximum 5 extra points)
22.
The average dose that a person within a 50 mile radius of the TMI-2 plant received compared to the dose that a person receives annually from background (i.e. natural) radiation is: a) 1.5 mrem (from TMI-2) compared to 100-300 mrem (from background per year) b) 300 mrem (from TMI-2) compared to 500 mrem (from background per year) c) 1.5 rem (from TMI-2) compared to 100-300 rem (from background per year) d) 300 rem (from TMI-2) compared to 500 rem (from background per year)
23.
In thermal hydraulics, saturation is: a) the point at which the plasma phase is formed b) the amount of heat transferred from the fuel to the cladding c) the temperature difference across the steam generator U-tubes d) the temperature and pressure combination at which liquid and vapor phases coexist
24.
Please fill in the blanks. What happens to the reactivity (increase, decrease, or no
change) if the following LWR parameters change?
A.
Fuel 235 U enrichment increased
B.
Boric acid added to primary coolant
C.
Control rods are withdrawn from core
_________________________
_________________________
_________________________
RTC 2007 Quiz #1 Page 7 of 7