Zoo/Bot 3333
advertisement
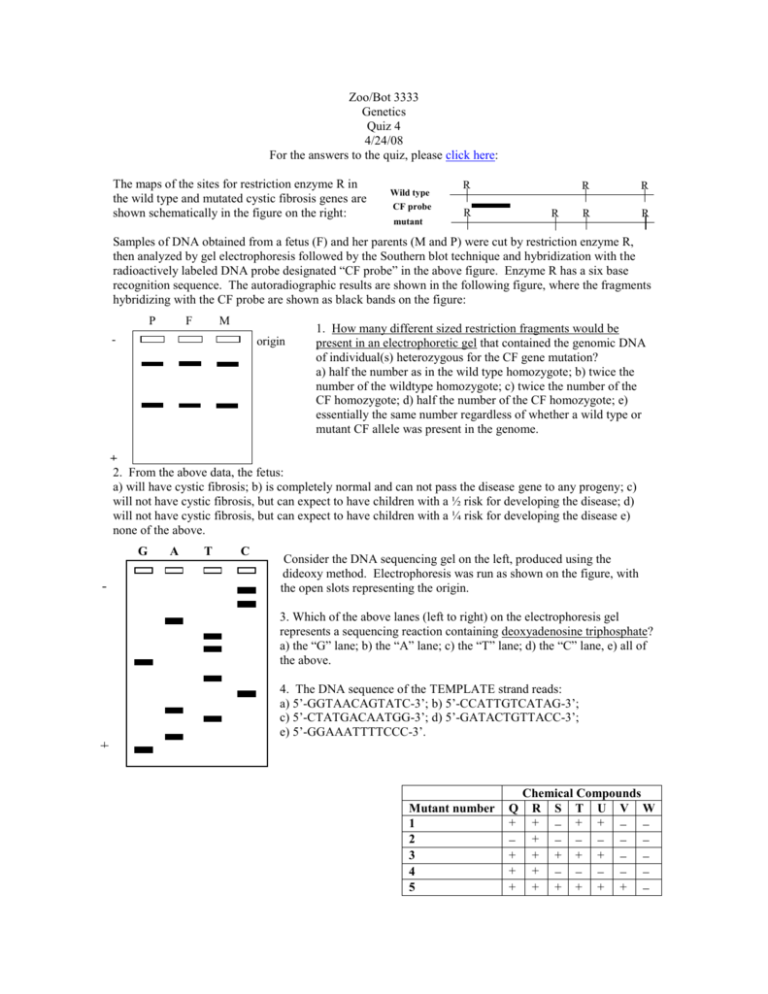
Zoo/Bot 3333 Genetics Quiz 4 4/24/08 For the answers to the quiz, please click here: The maps of the sites for restriction enzyme R in the wild type and mutated cystic fibrosis genes are shown schematically in the figure on the right: Wild type CF probe mutant R R R R R R R Samples of DNA obtained from a fetus (F) and her parents (M and P) were cut by restriction enzyme R, then analyzed by gel electrophoresis followed by the Southern blot technique and hybridization with the radioactively labeled DNA probe designated “CF probe” in the above figure. Enzyme R has a six base recognition sequence. The autoradiographic results are shown in the following figure, where the fragments hybridizing with the CF probe are shown as black bands on the figure: P F M - origin 1. How many different sized restriction fragments would be present in an electrophoretic gel that contained the genomic DNA of individual(s) heterozygous for the CF gene mutation? a) half the number as in the wild type homozygote; b) twice the number of the wildtype homozygote; c) twice the number of the CF homozygote; d) half the number of the CF homozygote; e) essentially the same number regardless of whether a wild type or mutant CF allele was present in the genome. + 2. From the above data, the fetus: a) will have cystic fibrosis; b) is completely normal and can not pass the disease gene to any progeny; c) will not have cystic fibrosis, but can expect to have children with a ½ risk for developing the disease; d) will not have cystic fibrosis, but can expect to have children with a ¼ risk for developing the disease e) none of the above. G C - A T C Consider the DNA sequencing gel on the left, produced using the dideoxy method. Electrophoresis was run as shown on the figure, with the open slots representing the origin. 3. Which of the above lanes (left to right) on the electrophoresis gel represents a sequencing reaction containing deoxyadenosine triphosphate? a) the “G” lane; b) the “A” lane; c) the “T” lane; d) the “C” lane, e) all of the above. 4. The DNA sequence of the TEMPLATE strand reads: a) 5’-GGTAACAGTATC-3’; b) 5’-CCATTGTCATAG-3’; c) 5’-CTATGACAATGG-3’; d) 5’-GATACTGTTACC-3’; e) 5’-GGAAATTTTCCC-3’. + Mutant number 1 2 3 4 5 Q + + + + Chemical Compounds R S T U V W + + + + + + + + + + + + + + Questions 5 and 6 pertain to the following. Six + + + 6 independently derived mutants (1-6) are recovered in Neurospora that are all able to grow on compound R. The mutants are then grown on minimal media supplemented with one of 6 chemicals all known to be precursors to R. A summary of the ability of the mutants to grow on media containing these chemicals is indicated below, where a “+” sign indicates growth and a “-” sign indicates no growth. 5. The immediate precursor to compound Q (i.e. the metabolite before it in the pathway) is: a) T; b) S; c) R; d) U; e) none of the above. 6. A mutation in gene 5 should lead to an accumulation of which metabolite in the pathway? a) T; b) S; c) R; d) U; e) none of the above. 7. Studies on the human photoreceptor proteins associated with vision: a) indicate the blue-receiving protein is most closely related to the green-receiving protein; b) show they are all linked together on the X chromosome; c) indicate that color blindness arises through unequal crossing-over; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. Questions 8-9 pertain to the following. Plant breeders studying genes affecting leaf shape in the plant Arabidopsis identified six independent recessive mutations that resulted in mutant serrated leaves rather than wild type smooth leaves. They began to perform complementation tests, but some of the tests could not be completed due to a fire in the greenhouse. Their results are indicated in the table on the right: mutations 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 – 2 + – 3 – 4 * – – – 5 + 6 – ** – + – 8. The asterisks in the table represent two complementation tests that were not performed. What would be expected? a) * would show complementation and ** would not show complementation; b) both * and ** would show complementation; c) both * and ** would not show complementation; d) * would not show complementation and ** would show complementation. 9. How many different cistrons are represented in this collection of mutants? a) 1; b) 2; c) 3; d) 4; e) 5. 10. The genome size of E. coli is 3.2 x 106 bp. The BamHI restriction endonuclease cuts at the following sequence: 5’-GGATCC-3’ 3’-CCTAGG-5’ Assuming that the genome contains equal proportions of all four nucleotides, and their distribution is random, approximately how many fragments would be produced on BamHI digestion of the E. coli genome? a) 28; b) 780; c) 5.3 x 104; d) 7.3 x 105; e) 1.9 x 107. 11. The accompanying table shows the presence or absence of seven sequence-tagged sites (STS’s) numbered 1-7, in each of six BAC clones, designated A-F. A “+” in the table means that PCR primers specific to the STS are able to amplify the sequence from the clone, “-“ means that the sequence can not be amplified from the clone. BAC Clone A B C D 1 + + 2 + - 3 + - STS marker 4 + - 5 + - 6 + 7 + - E F - + - + - + + - The relative order of the STS sites within the cloned genome can be ordered as: a) 3427165; b) 1527634; c) 3514276; d) 2541673; e) 3461527. -