tpj12456-sup-0011-DataS1
advertisement

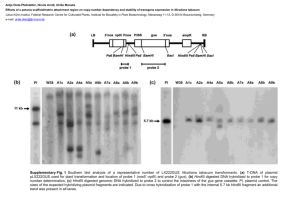
Construction of promoter:GUS and complementation constructs Promoters of CBL2 (1546 bp upstream of the CBL2 start codon) and CBL3 (2301 bp upstream of the CBL3 start codon) were amplified and cloned into pBluescriptII KS+ vector for sequencing and subcloned into pGPTVII.Bar vectors (Walter et al., 2004) for transformation in Arabidopsis. Col-0 wildtype plants were transformed with Agrobacterium strain GV3101 pMP90 (Voinnet et al., 2003) harboring the respective constructs using the floral dip method (Clough and Bent, 1998). GUS analysis was performed with homozygous T2 plants. To generate complementation constructs the udiA gene in existing promoter:GUS vectors was replaced either by CBL2 or CBL3 genomic sequence including the respective 3´UTR. An additional nucleotide sequence of AAA was added directly before the ATG of both constructs to ensure proper translation in plants. The CBL2 complementation construct was transformed in homozygous cbl2 SALK_115461 mutants and CBL3 complementation construct in homozygous cbl3 FLAG_294H06 mutants. T2 plants homozygous for either complementation construct were used for phenotypical analysis. For primer sequences see Table S1. GUS staining of seeds and plant tissues Seeds were dissected from siliques of different developmental stages under a binocular and fixed in 80 % ice cold aceton for 30 min and subsequently washed twice with 50 mM phosphate buffer containing 0,1 % Triton X-100. GUS staining of seeds and tissues was performed by adding GUS staining solution (50 mM phosphate buffer, 0,1 % Triton X-100, 100 mM 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-glucuronide, 200 mM K4FeCN6), followed by 2 vacuum infiltration steps for 10 min each. For the GUS reaction the infiltrated seeds were incubated for 24 h at 37°C in the dark. The staining solution was then removed and the clearing procedure was performed as described above. GUS staining was detected using a microscope with DIC module. Supporting References Clough, S.J. and Bent, A.F. (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacteriummediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J, 16, 735-743. Voinnet, O., Rivas, S., Mestre, P. and Baulcombe, D. (2003) An enhanced transient expression system in plants based on suppression of gene silencing by the p19 protein of tomato bushy stunt virus. Plant J, 33, 949-956. Walter, M., Chaban, C., Schutze, K., Batistič, O., Weckermann, K., Nake, C., Blazevic, D., Grefen, C., Schumacher, K., Oecking, C., Harter, K. and Kudla, J. (2004) Visualization of protein interactions in living plant cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant J, 40, 428-438.