Can`t Judge a Powder
advertisement

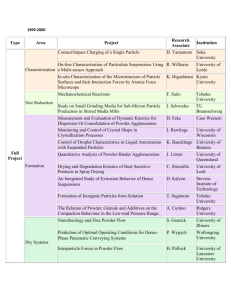
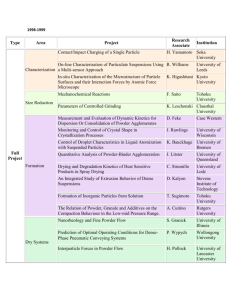
Can’t Judge a Powder What do the crystals look like? 1) Are they: a) colored, b) white, c) clear? d) Do the crystals seem to absorb water from the air? e) Or, were the crystals hygroscopic? Definition of hygroscopic: A substance having a tendency to absorb water from the atmosphere and become damp, but not form a solution 2) Density: D = m/v Using a graduated cylinder: The judge would have to provide a balance a) What is the calculated density of the solid? b) How many grams would 2mL of the solid weigh? c) How many mL would 3 grams 3) Relative density using a solvent: a) Does the solid sink or float in the solvent supplied by the judge? b) Is the solid more or less dense than the solvent supplied by the judge? c) Potential solvents: i) Hexane d = 0.6591 ii) Methanol d = 0.8100 wood alcohol, methyl alcohol iii) Ligroin d = 0.850- 0.870 painter’s naphtha 4) Solubility 5) Definition: The mass of a solid substance that can be dissolved in 100 g. of solvent to form a saturated solution. 6) Most ionic compounds are soluble in water by undergoing the process of solvation. 7) Most covalent compounds will not be soluble in water. 8) Solubility 9) Is the substance soluble, totally, partially, little, or not soluble? 10) Is the substance soluble in the extra solvent the judge provided? 11) Is the substance more or less soluble in either HCl or NaOH than it was in water? 12) Temperature Change: The judge would have to provide a thermometer 13) This must be done only with the aqueous solution 14) Need a larger sample size to obtain measurable results 15) Definitions: 16) Exothermic: a reaction that gives out heat to its surroundings, H is negative, because the system loses heat. 17) Endothermic: a reaction that takes in heat from its surroundings, H is positive, because the system gains heat 18) Temperature Change: cont 19) What was the temperature of the water (before the powder was added)? 20) What was the temperature of the solution after the powder was added? 21) Did the temperature of the water increase or decrease when the powder was added? 22) What was the temperature change for the solution after the powder was added? 23) Was the process of dissolving endothermic or exothermic? 24) Conductivity: 25) The SI unit for conductivity is Siemens (S). The scales on various devices will vary. The most important property of a conductor is the amount of current it will carry when a voltage is applied. Conductance is the inverse of resistance. i) Conductance = S= 1/ohm. 26) Electrolyte: Any compound which in solution conducts electric current. The solvent is usually water. Adjectives to describe electrolytes include: strong, weak, non. 27) Always test the solution of the powder in water (aqueous solution). 28) Do not test powder with NaOH or HCl. 29) Conductivity: cont 30) Did the aqueous solution conduct electricity? 31) Was the aqueous solution a strong, weak or non electrolyte? 32) pH of the solution 33) Only test aqueous solution 34) Correct use of pH paper 35) Definitions: 36) Acidic solutions have a pH <7 37) Basic solutions have a pH >7 38) What is the pH of the aqueous solution? 39) Was the aqueous solution acidic or basic? 40) Reaction with HCl or NaOH: 41) Is there any gas produced? 42) What is the odor of any gas? 43) Is there any color change? 44) Is there any precipitate formed? 45) Is the substance more or less soluble in either HCl or NaOH than it was in water? 46) Potential Questions with other reagents 47) Test solubility of powder in other reagents supplied. 48) Judge should indicate which reagent to use if there is more than 1 reagent 49) Is the substance soluble in the extra solvent the judge provided? 50) What might this indicate about the bonding in the powder? 51) Potential Questions with other reagents 52) Test for precipitate formation with addition a precipitation reagent 53) Judge should indicate reagent, if more than one reagent is available 54) Judge should tell students how much reagent to add 55) Potential Questions with other reagents 56) Test for precipitate formation, cont. 57) A solid formed from substances in solution. 58) Was a precipitate formed? 59) What color was the precipitate? 60) What was the form of the precipitate? 61) Was it a powder? 62) Or did it seem like jello? 63) Thoughts: Practice, Practice, Practice 64) Use common solids 65) Size of sample 66) Supply water in a wash bottle 67) Is temperature worth it? 68) Thoughts: 69) Perhaps supply a third liquid to test solubility 70) Perhaps supply a test reagent solution to look for precipitates 71) For #5 and #6 decide about waste problems 72) Is it worth is it? 73) Thoughts: 74) Where is waste from the students work to be disposed? 75) What about clean up of work area? 76) If judging decide on a powder and become familiar with that powder Can’t Judge a Powder by Its Color Scoring Sheet Names of Participants (please print) School Name: _______________________ __________________________ _______________________ Team Code # _________ 1 1 Question Values 5 4 3 2 5 4 3 2 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 Questions A. Is the substance in a powder or crystalline form? B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. What is the shape of the pieces of the powder? How much does 3 mL of this substance weigh? Is the powder soluble in water? Which solvent, water or methanol is the powder more soluble in? How well does the water, ALONE, conduct electricity? Is WATER a strong, weak or non-electrolyte? What is the conductivity of the aqueous solution of the powder? What is the pH of the aqueous solution of the powder? Were any gases observed? What is the color of solution formed when the powder is added to NaOH? What was the temperature change when the powder was added to the water? Is the powder soluble in hexane? When the powder is placed in hexane and stirred, does the powder float or sink to the bottom? What happened when silver nitrate was added to the aqueous solution of the powder? Use this letter to mark what you think is your best observation Total