Clouds and Precipitation
advertisement

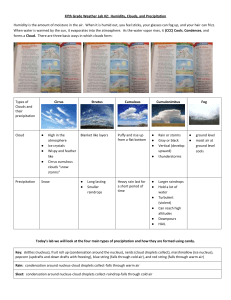
CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATION CLOUDS 489 Cloud a visible collection of water and other particles that are suspended in the air The water may be in the form of tiny water droplets or ice crystals. Classification Clouds are named based on their appearance and the height of their bases (bottoms). cirrus stratus cumulus numbus 489-492 CLOUD SHAPES whispy clouds layers, flat sheets puffy, cottonball shaped dark rain clouds CLOUD BASE HEIGHTS high-level = cirrus higher than 6 km ice thin, whispy cirrus, cirrostratus mid-level = alto 2 – 6 km water/ice altocumulus, altostratus low level = stratus 0 – 2 km water fog, stratus, nimbostratus, cumulostratus all level = cumulus low base, high top water/ice cumulonimbus, fair weather cumulus STORM CLOUDS nimbostratus dark, flat clouds near warm fronts long periods of steady precipitation cumulonimbus dark, puffy clouds thunderheads near cold fronts short periods of intense precipitation Resources U Illinois web page Clouds pdf http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides/mtr/cld/home.rxml http://nenes.eas.gatech.edu/Cloud/Clouds.pdf PRECIPITATION Precipitation 493 any form of condensed water or ice crystals that falls to the earth snow falling ice crystals that stay frozen sleet / ice pellets falling water droplets that freeze in the air and bounce when they hit the ground snow falls through warm air (melts) then cold air (refreezes) before landing freezing rain falling water droplets change to ice upon impact with cold ground (below 0°C) snow falls through warm air (melts) then freezes immediately when they hit the ground rain falling water droplets that stay liquid (ground is above 0°C) hail large balls of ice produced by updrafts in cumulonimbus clouds (July, August) see Figure 15.8 p. 494