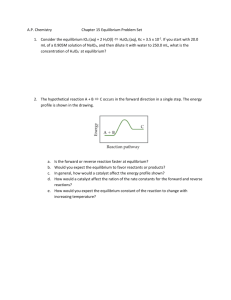
1. Specify the total number of orbitals possible with the principal
advertisement

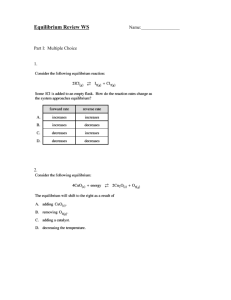
1. Specify the total number of orbitals possible with the principal quantum n=3. A) 1 B) 3 C) 8 D) 9 E) 18 2. What effect will adding additional O2 (g) to the following equilibrium system, once equilibrium is reestablished? 2 CO2 (g) ? 2 CO (g) + O2 (g) ?H° = -514 kJ A) The concentration of CO (g) will increase. B) The concentration of CO2 (g) will decrease. C) The equilibrium constant for the reaction will increase. D) The equilibrium constant for the reaction will decrease. E) The concentration of CO2 (g) will increase. 3. For the following reaction: 4CuO(s) + CH4 (g) ? CO2 (g) + 4Cu(s) + 2H2O(g) Kc= 1.10 at 25 °C. What is the value of Kp for this reaction? A) 2.20 B) 4.63 C) 46.3 D) 372 E) 658 4. Which of the statements following is true? A) Ionic solids are highly conductive. B) Molecular solids are always very high melting. C) Metallic solids are electrically conductive D) Metallic solids are consistently low melting. E) Ionic solids are not soluble in water. 5. Consider the reactions given below. In which case(s) will the reaction proceed more to the right by decreasing the pressure? I. 2 CO (g) + O2 (g) ? 2 CO2 (g) II. 2 NO (g) ? N2 (g) + O2 (g) III. N2O4 (g) ? 2 NO2 (g) IV. Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) ? Ni(CO)4 (g) V. N2 (g) + 3 H2 ? 2 NH3 (g) A) I B) II C) III D) I, II and III E) I, IV and V 6. Identify the correct equilibrium expression for the following reaction. 6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) ? C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g) A) [C6H12O6][O2]6 / [CO2]6[H2O]6 B) [CO2]6[H2O]6 / [C6H12O6] [O2]6 C) [CO2]6 / [O2]6 D) [O2]6 / [CO2]6 E) [O2]6 / [CO2]6[H2O]6 7. For the following reaction: 3 H2 (g) + CO (g) ? CH4 (g) + H2O The equilibrium constant is 3.93 at 1200 K. If the equilibrium concentrations are [CO] = 0.0613 M, [H2] = 0.1839 M and [CH4] = 0.0387 M. What is the [H2O]? A) 0.0387 B) 0.0323 C) 0.0233 D) 0.0201 8. At equilibrium, the concentrations of H2, I2, and HI were found to be 0.15 M, 0.33 M, and 0.55 M respectively. What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? H2 (g) + I2 (g) ? 2HI (g) A) 11.1 B) 9.0 × 10-3 C) 23 D) 111 E) 6.1 9. At equilibrium which statement is true? A) All chemical processes have ceased B) The rates of the forward reaction and reverse reaction are equal. C) The rate constants for the forward reaction and reverse reaction are equal. D) The rates and the rate constants for the forward reaction and the reverse reaction are equal. E) None of the above. 10. When 1.00 mol C6H6 and 3.00 mol H2 are put into a 1 L container and allowed to reach equilibrium, the resulting mixture contains 0.137 mol C6H12. What is the equilibrium amount of H2 in moles? C6H6 (g) + 3H2 (g) ? C6H12 (g) A) 2.86 B) 2.59 C) 1.37 D) 0.411 E) 0.0457 11. The equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 2.0 x 10-10 at 100°C. COCl2 (g) ? CO (g) + Cl2 (g) What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction shown below? CO (g) + Cl2 (g) ? COCl2 (g) A) -2.0 x 10-10 B) 5.0 x 109 C) 2.0 x 1010 D) -5.0 x 109 12. For the following reaction: CO (g) + 3H2 (g) ? CH4 (g) + H2O (g) The equilibrium constant is 3.93 at 1200 K. If [CO] = 0.0450 M, [H2] = 0.132 M, [CH4] = 0.0620 M and [H2O] = 0.0550 M one can conclude that: A) Q > K and the reaction will proceed to the right. B) Q < K and the reaction will proceed to right. C) Q > K and the reaction will proceed to the left. D) Q < K and the reaction will proceed to the left. E) The reaction is at equilibrium and no change will occur. 13. Consider the following reactions at equilibrium and determine which reaction(s) will shift to the right in response to a decrease in volume. I. 2 Fe2O3(s) ?4 Fe (s) +3 O2 (g) II. 2 HCl (g) ?H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) III. H2 (g) + I2 (g) ? 2 HI (g) IV. 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)? 2 SO3 (g) V. N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) ?2 NH3 (g) A) I and II B) II and III C) IV and V. D) I and V. E) I, III, and V. 14. What is the consequence of heating the following equilibrium system to a higher temperature? 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ? 2 SO3 (g) ?H° = -99 kJ/mol A) The concentration of SO3 will decrease, and the equilibrium constant will decrease. B) The concentration of SO2 will decrease, and the equilibrium constant will decrease. C) The concentration of SO3 will increase, and the equilibrium constant will increase. D) The concentration of SO3 will decrease but the equilibrium constant will not change. E) The concentration of SO3 will increase but the equilibrium constant will not change. 15. If 131 g of NOCl (g) (65.5 g/mol) was placed in a 4.00 L flask. What is the equilibrium concentration of Cl2 (g) for this reaction? 2NOCl (g) ? 2 NO (g) + Cl2 (g) Kc = 3.0 x 10-7 A) 2.30 x 108 M B) 1.52 x 104 M C) 3.79 x 10-3 M D) 2.66 x 10-3 M E) 1.71 x 10-11 M 16. For the endothermic reaction: CaCO3 (s) ? CaO (s) + CO2 (g) Le Châtelier's principle predicts that __________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of CO2. A) decreasing the temperature B) removing some of the CaCO3 (s) C) increasing the pressure D) increasing the temperature E) adding more CaCO3 (s) 17. Which of the following statements are true, regarding the equilibrium constant (K) for a reaction and the reaction quotient (Q): I. If Q > K, the reaction is not at equilibrium, and will reach equilibrium by shifting products over to reactants II. If K= 3.2 x 10-6, the reaction is product favored III. If K= 5.2 x 104, the reaction is product favored IV. If Q = K, the reaction is already at equilibrium. A) I and II only B) I, II, and IV only C) I, III, and IV only D) III and IV only E) II and IV only 18. Consider the following reaction at equilibrium. Which of the following situations would cause the maximum number of moles of N2 (g) at equilibrium? 2NH3 (g) ? N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) ?H° = +92.4 kJ/mol A) High temperature and high volume B) High temperature and low volume C) Low temperature and high volume D) Low temperature and low volume 19. Indicate the reaction which shifts to the right upon decreasing the volume to half of the original value: A) CH4 (g) +2 O2 (g) ?CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) B) 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ?2 SO3 (g) C) N2O (g) + NO2(g) ? 3 NO (g) D) 2 HCl (g) ?Cl2 (g) + H2 (g) 20. In which of the following reactions would increasing pressure at constant temperature not change the concentrations of reactants and products, based on Le Châtelier's principle? A) 2N2 (g) + O2 (g) ? 2N2O (g) B) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ? 2NH3 (g) C) N2 (g) + O2 (g) ? 2NO (g) D) N2O4 (g) ? 2NO2 (g) E) N2 (g) + 2O2 (g) ? 2NO2 (g)