Earth History test 2 B
advertisement

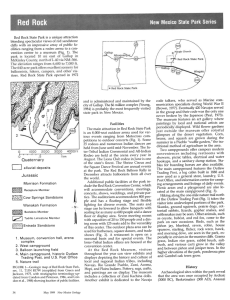
Name:______________________ Period: ________ Form A Earth History – Assessment #2 east Directions: Edit sentences 1-3. (Example: The Sun always rises in the west) 1. Sediments that settle in the water form a curved, vertical layer. 2. Each new layer of sediments mixes in with earlier layers. 3. The past is the key to the present; geological processes that we observe today most likely did not occur in the same way throughout Earth’s history. Directions: Answer the following questions. 4. Put a check next to each rock listed below that is a sedimentary rock. ___ limestone 5. ____ granite ___ obsidian ___ sandstone ___pumice ___shale Write a 1 next to the sediments listed below that are usually part of sandstone. Write a 2 next to the sediments listed below that are usually part of shale. ___pebbles ____ sand ___ silt ___ clay ___cobbles ___boulders 6. How is sandstone formed? Answer using sentences or a labeled diagram. Be sure to explain where the material comes from with scientific language. Include the terms weathering/erosion, transportation, deposition, and matrix. 7. A geologist discovers a new rock layer. When she observes the rock layer more closely, she finds fossils of corals and shells. She places a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid on the rock and observes fizzing. What inferences can she make about the origin of this rock? 8. Label the rock type of each layer in the diagram. Indicate which layer is the oldest, and which is the youngest. 9. Describe the environments that can be inferred when each rock layer was forming. Sandstone: Shale: Limestone: 10. Entrada Sandstone is a type of sandstone that features frosted grains of sand and fossilized reptile tracks. What ancient environment can you infer produced the Entrada Sandstone? a. Swamp or floodplain b. Sand dunes c. Marine or ocean Directions: Study the sample student work, and then answer question 11 below. 11. List one improvement each student should make so it is a better model of a geological timeline. Brent Josiah 12. Geological time extends from a. 500 million years ago to the beginning of human history b. Earth’s origin to present day c. The beginning of human history to present day d. Earth’s origin to the beginning of human history. 13. Why don’t geologists measure geological time in units such as days or months? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Directions: Use the rock columns to answer questions 20 & 21. 20. Which is older, the Moenkopi Formation or the Navajo Sandstone? ___________________ What is your evidence? _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 21. Which is older, the Moenkopi Formation or the Coconino Sandstone? ___________________ What is your evidence? _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Directions: Use the cross-section drawing to answer questions 14-17. 14. The Colorado River started eroding the Grand Canyon 6 million years ago. Which two layers did the Colorado River erode through first? _________________________ __________________________ 15. Explain why you think those two layers eroded first. 16. If you could return to the Grand Canyon one-million years from now, what layer of rock might you observe at river level? Explain why you think that layer will be at river level. 17. Change the drawing to show what the rock layers and the Grand Canyon might have looked like 6 million years ago. Explain here why you changed the drawing the way you did. 18. Explain why the Grand Canyon walls appear to have stripes. 19. Put the following in order of which came first and explain. The Grand Canyon The Colorado Plateau The Colorado River