Biology 303 Midterm, Spring 2004
advertisement

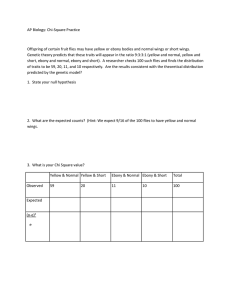
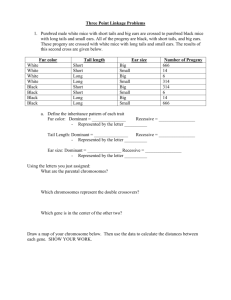
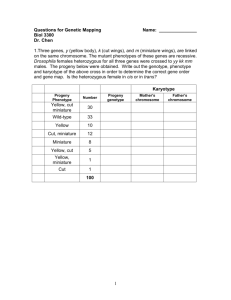
Biology 303 Midterm, Spring 2004 1. (4 points) a) When two AaBb individuals are crossed what are the expected phenotypic ratios of the progeny? Assume that A and B are not linked. b) If A and B are linked and 20 mu apart, what are the ratios of the gametes produced by an Ab / aB individual. 2. (4 points) In doodlewags, three separate genes affect coat color. The dominant allele S causes solid coat color and s causes spotted coat color. Black coat color B is dominant to brown (b), but these phenotypes are only expressed in a/a individuals. Doodlewags that are A/- are always yellow. A mating between a solid yellow male and a solid brown female results in the following progeny: 2 solid black, 1 spotted yellow, 1 spotted black, and 2 solid brown. a) What are the genotypes of the two parents? b) What is the probability that their next pup will be spotted brown? 3. (2 points) A recessive trait in garden peas causes the leaves to curl. A plant with yellow peas and curling leaves was crossed with a wild type plant with green peas and normal leaves. A testcross with an F1 plant yielded the following results: 107 green peas, normal leaves 88 yellow peas, curling leaves 90 green peas curling leaves 115 yellow peas, normal leaves Perform a chi square test to determine if the two genes are linked. 4. (10 points) In Drosophila, Dichaete (D) is a chromosome 3 mutation with a dominant effect on wing shape. It is lethal when homozygous. The genes ebony (e) and pink (p) are chromosome 3 recessive mutations affecting the body and eye color, respectively. Flies from a Dichaete stock are crossed to homozygous ebony, pink flies resulting in F1 progeny with a Dicheate phenotype. The F1 flies were backcrossed to the ebony, pink homozygotes with the following results: Dichaete ebony, pink Dichaete, ebony pink Dichaete, pink Dichaete, ebony, pink wild type 404 389 84 96 2 12 13 a) What is the order of the three genes? b) Calculate the recombination frequencies for each gene pair. c) Calculate the coefficient of coincidence. (observed/expected) 5. (6 points) A fruit fly with the genotype p+ q1 r+ / p- q2 r- was testcrossed and 12 p+ q+ r- progeny were observed among 6000 progeny. a) If the gene order is p - q - r, what is the order of q1 and q2 with respect to p and r? Explain your reasoning. b) What is the genetic distance between q1 and q2? 6. (10 points) The following results are ordered tetrad pairs from a cross between strain p+ and strain +q: 1 p+ p+ +q +q 41 2 p+ pq ++ +q 15 Tetrad Class 3 4 pq +q pq p+ ++ p+ ++ +q 1 3 5 p+ ++ pq +q 4 6 pq ++ pq ++ 3 7 p+ +q pq ++ 2 They are summarized by tetrad classes. a) b) c) d) Name the ascus type of each class from 1 to 7 (P, NP, or T). Calculate the gene-centromere distance for each locus. Calculate the distance between the two linked loci. Draw a linkage map, including the centromere. 7. (2 points) A phenotypically normal couple has two children. The daughter is phenotypically normal and the son has sickle cell disease. The daughter marries a phenotypically normal man whose mother suffered from sickle cell disease. What is the probability that their first child will have sickle cell disease? 8. (2 points) In fruit flies, allele l is sex-linked and recessive lethal. If a heterozygous female (L/l) is crossed with a normal male, what is the probability that the first two surviving progeny will be male?