Psychology 445
advertisement

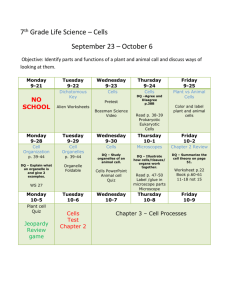
Week Date 9/29 9/30 10/1 10/2 Introduction to Social Psychology Introduction Methods Philosophy Introspectionism 10/6 10/7 10/8 10/9 Freudian Theory and Behaviorism Freud 1 Freud 2 Behaviorism 1 Behaviorism 2 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 10/13 10/14 10/15 10/16 Cognitive Behaviorism and Gestalt Psychology Behaviorism 3 Tolman Gestalt 1 TBA Week 4 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 10/20 10/21 10/22 10/23 Lewin Lewin 1 Lewin 2 Lewin 3 Lewin 4 Week 1 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Week 2 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Week 3 Week 5 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 10/27 10/28 10/29 10/30 Week 6 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 11/3 11/4 11/5 11/6 Week 7 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 11/10 11/11 11/12 11/13 Symbolic Interactionism Symbolic Interactionism The New Look in Perception Midterm Review Midterm Review continued MIDTERM EXAM Attitude Change 1 Attitude Change 2 Attitude Change 3 Attribution Theory No School Attribution 1 Attribution 2 Week 8 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 11/17 11/18 11/19 11/20 Interpersonal Attraction Attribution 3 Attraction 1 Attraction 2 Attraction 3 Week 9 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 11/24 11/25 11/26 11/27 Social Comparison Social Comparison 1 Social Comparison 2 TBA Thanksgiving Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 12/1 12/2 12/3 12/4 Cognitive Dissonance Theory Dissonance 1 Dissonance 2 TBA TBA Week 11 Monday Tuesday Wednesday 12/8 12/9 12/10 Friday 12/12 Week 10 Freud’s Influence Freud's Influence TERM PAPER DUE FINAL EXAM (8:30) References Allport, G. W. (1955). Becoming: Basic considerations for a psychology of personality. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. Anderson, N. H. (1965). Averaging versus adding as a stimulus-combination rule in impression formation. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 70, 394-400. Asch, S. E. (1946). Forming impressions of personality. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 41, 258-290. Asch, S. E. (1948). The doctrine of suggestion, prestige, and imitation in social psychology. Psychological Review, 55, 250-276. Baumeister, R. F., Bratslavsky, E., Muraven, M., & Tice, D. M. (1998). Ego depletion: Is the active self a limited resource? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74, 12521265. Bem, D. J. (1972). Self-perception theory. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 6, pp. 1-63). New York: Academic Press. (pages 15-32). Bushman, B. J. (2002). Does venting anger feed or extinguish the flame? Catharsis, rumination, distraction, anger, and aggressive responding. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 28, 724-731 Byrne, D. (1961). Interpersonal attraction and attitude similarity. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 62, 713-715. Deutsch, M., & Krauss, R. M. (1965). Theories in social psychology. New York: Basic Books. Eagly, A. H., & Chaiken, S. (1993). The psychology of attitudes. Orlando, FL: Harcourt, Brace, & Jovanovich. Fazio, R. H., & Cooper, J. (1983). Arousal in the dissonance process. In J. T. Cacioppo & R. E. Petty (Eds.), Social psychophysiology: A sourcebook (pp. 122-152). New York: The Guilford Press. Festinger, L. (1950). Informal social communication. Psychological Review, 57, 271-282. Festinger, L. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes. Human Relations, 7, 117-140. Festinger, L. (1957). A theory of cognitive dissonance. Evanston, IL: Row Peterson. (pp. 1-31) Greenberg, J., Martens, A., Jonas, E., Eisenstadt, D., Pyszczynski, T., & Solomon, S. (2003). Psychological defense in anticipation of anxiety: Eliminating the potential for anxiety eliminates the effect of mortality salience on worldview defense. Psychological Science, 14, 516-519. Gump, B. B., & Kulik, J. A. (1997). Stress, affiliation, and emotional contagion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 72, 305-319. Hall, C. S. (1954). A primer of Freudian psychology. New York: Mentor Books. (pp. 11-41) Heider, F. (1958). The psychology of interpersonal relationships. New York: Wiley. Hovland, C. I., Janis, I. L., & Kelley, H. H. (1953). Communication and persuasion: Psychological studies of opinion change. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. (Chapter 1) Lewin, K. (1935). A dynamic theory of personality. New York: McGraw-Hill. (pp. 1-43). Lewin, K. (1952). Group decision and social change. In G. Swanson, T. Newcomb, & G. Hartley (Eds.), Readings in social psychology (Revised ed., pp. 459-473). New York: Henry Holt & Co. Mook, D. W. (1983). In defense of external invalidity. American Psychologist, 38, 379-387. Rescorla, R. A. (1988). Pavlovian conditioning: It’s not what you think it is. American Psychologist, 43, 151-160. Schachter, S. (1959). The psychology of affiliation. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. (pp. 1-41) Schachter, S., & Singer, J. (1962). Cognitive, social, and physiological determinants of the emotional state. Psychological Review, 69, 379-399. Skinner, B. F. (1990). Can psychology be a science of mind? American Psychologist, 45, 12061210. Steele, C. M., & Lui, T. J. (1983). Dissonance processes as self-affirmation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45, 5-19. Stryker, S. & Statham, A. (1985). Symbolic interaction and role theory. In G. Lindzey & E. Aronson (Eds.), The handbook of social psychology (3rd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 311-378). New York: Random House. Taylor, S. E., & Lobel, M. (1989). Social comparison activity under threat: Downward evaluation and upward contacts. Psychological Review, 96, 569-575. Tolman, E. C. (1948). Cognitive maps in rats and men. Psychological Review, 55, 189-208. Watson, J. B. (1913). Psychology as the behaviorist views it. Psychological Review, 20, 158177. Wegner, D. M. (1994). Ironic processes of mental control. Psychological Review, 101, 34-52