Intro to Protists and Protozoan Study Guide Relavent sections of text
advertisement

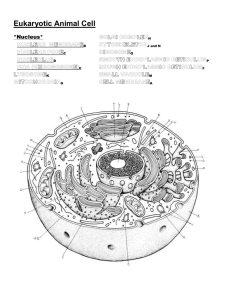
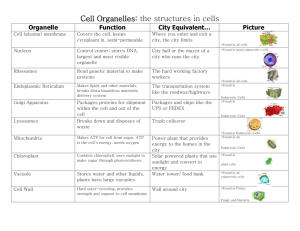
Intro to Protists and Protozoan Study Guide Relavent sections of text—THIS INCLUDES PROTOZOANS AND ALGAE: 25.3 (First Eukaryotes and origins of multicelluarity only) 28.1, 28.2-28.4 BUT only as needed for groups/examples we studied, 28.6 Objectives and Study Questions: 1. Is the term “protist” a taxa? What does the term ‘protist’ refer to? 2. What does the term protozoan refer to? 3. Are protists eukaryotic or prokaryotic? 4. Describe the characteristics of a eukaryotic cell. 5. How long ago did eukaryotic cells emerge? How does this relate to their diversity? 6. Explain how eukaryotic cells acquired mitochondria? How many different times has this occurred in the history of life on earth? Keep this answer specific to mitochondria. 7. Describe the origin of eukaryotic cells through endosymbiosis (this question is intended to be more general, but also more expansive than the preceding question which only focused on mitochondria)? 8. How does the cytoskeleton of eukaryotes differ from prokaryotes? 9. Describe some evidence that mitochondria and plastids arose in eukaryotic cells through endosymbiosis. 10. What common ancestral trait(s) is shared by all organisms in domain Eukarya? 11. What are the three common motility and/or feeding structures found in protozoans? Give examples of organisms with each. 12. What two parasitic protozoans did we discuss in lab? What diseases do they cause. 13. What are ciliates? What two examples did we look at in lab and how do they feed and move? 14. Describe forams including their tests and morphology and function of psuedopods 15. Describe radiolarians including their tests and morphology and function of psuedopods 16. Describe the feeding and movement of Tubulinid amoeba (i.e., amoeba within the Tubulinid group such as A. proteus) 17. Briefly state the roles of protists (protozoans and algae) in the environment.