FSIS FSIS Procedure for the use of the Listeria monocytogenes BAX
advertisement

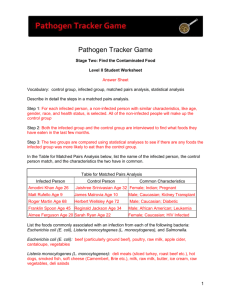
FSIS Procedure for the use of the Listeria monocytogenes BAX Screening Test - MLG 8A.05 SCOPE This method is applicable to processed meat and poultry products and environmental samples. PRINCIPLES This method uses a commercial PCR screening procedure. All samples identified as potentially positive for Listeria monocytogenes using this test must be confirmed using AS 5013.24.1 or MLG 8. The detection of Listeria monocytogenes is broken down into four stages: Pre-enrichment in non-selective liquid medium A 25 g ± 1 g portion is used for analysis of processed meat and poultry products. Primary enrichment is carried out in 225 ± 5 ml of modified University of Vermont broth (UVM) which is incubated at 30 ± 2C for 20 - 26 h. Environmental swab samples are enriched in 225± 5 ml of UVM and incubated at 30 ±2C for 20 - 26 h. Secondary enrichment and Primary enrichment plating Primary enrichment culture (0.1 ± 0.02 ml) is transferred to 10 ± 0.5 ml of MOPS-BLEB 1 broth. Secondary enrichment is carried out at 35 ± 2C for 18-24 h. Primary enrichment cultures are also streaked onto selective solid agar (MOX) after 20 – 26 h incubation. Selective agar, Modified Oxford agar (MOX), is incubated at 35 ± 2C for 26 ± 2 h. BAX system for screening Listeria Listeria monocytogenes is screened in the secondary enrichment broth following the manufacturer’s recommended protocol2. The BAX Listeria monocytogenes test is an automated method that uses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food and environmental samples. The system identifies a specific DNA fragment unique to Listeria monocytogenes. The DNA is combined with DNA polymerase, nucleotides, and primers. The mixture then undergoes a series of timed heating and cooling cycles. Heating denatures the DNA, separating it into single strands. As the mixture cools, the primers recognise and bind to the targeted DNA sequences. The DNA polymerase then uses the nucleotides to extend the primers, thus creating 2 copies of the targeted DNA fragment; repeating the cycle results in an exponential increase in the number of target DNA fragments. A fluorescent dye then binds with double-strand DNA and emits a fluorescent signal in response to light. After amplification, the BAX System begins a detection phase in which the fluorescent signal is measured. 1 Listeria enrichment broth (BBL) to which is added 3-[N-Morpholino]propane sulfonic acid (6.7 g/L) & its sodium salt (10.5 g/L). 2 The FSIS use DuPont Qualicon kits #17710609 held at 4 ± 2 C. Issue 2015 10 27 | Approved Methods Manual Export Standards Branch | Exports Division Department of Agriculture and Water Resources Page 1 of 3 Listeria Detection - FSIS BAX – MLG 8A.05 Confirmation BAX-negative samples that have typical colonies on 26 ± 2h MOX plates or BAX-positive, BAX-indeterminate or a BAX-signal-error the sample must be confirmed using AS 5013.24.1 or MLG 8 (starting at the appropriate stage of analysis i.e. plating out and identification). The MOPS-BLEB culture is streaked onto MOX and incubate at 35 ± 2C for 26 ± 2 h and then for a further 26 ± 2 h if growth is slight or if no colonies are observed after 26 h. Confirmation then proceeds as described in AS 5013.24.1 or MLG 8. Confirmation of Listeria spp Suspect colonies from selective agars are streaked onto plates of tryptone soya yeast extract agar (TSYEA) and incubated at 35 ± 1C 3 Error! Bookmark not defined. for 18 to 24 h or until growth is sufficient. Select a typical (convex, colourless and opaque with an entire edge) isolated colony and carry out confirmatory tests (catalase, gram stain, umbrella or tumbling motility, -haemolysis, utilisation of rhamnose and xylose and CAMP/CAMP factor test). MICRO-ID® Listeria or API®-Listeria and β-lysin CAMP factor discs (Remel #21-120, or equivalent) can be used or well established schemes (Compendium of methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods, Bacteriological Analytical Manual). Strains that are considered to be Listeria monocytogenes may be sent to a reference laboratory for further classification. MLG 8 All suspect colonies on MOX are streaked onto horse blood overlay agar at 35 ± 2C for 22 ± 4 h. Colonies showing -haemolysis are confirmed as L. monocytogenes using a commercially available bio-chemical test strip. Colonies should also be tested for tumbling motility and using the CAMP/CAMP factor test. Strains that are considered to be Listeria monocytogenes or are suspect but do not give definitive results must be sent to a reference laboratory for further classification. AS 5013.24.1 Suspect colonies from MOX are streaked onto plates of tryptone soya yeast extract agar (TSYEA) and incubated at 35 ± 1C for 18 to 24 h or until growth is sufficient. Typical colonies are selected (convex, colourless and opaque with an entire edge) and confirmed as Listeria monocytogenes (catalase, gram stain, umbrella or tumbling motility, -haemolysis, utilisation of rhamnose and xylose and CAMP/CAMP Factor test). Strains that are considered to be Listeria monocytogenes may be sent to a reference laboratory for further classification. 37 ± 1C can be used for incubation of agar plates depending on the availability of suitable incubators. Whichever temperature is selected it must be used for all Listeria monocytogenes determinations undertaken at the laboratory. 3 Issue 2015 10 27 | Approved Methods Manual Export Standards Branch | Exports Division Department of Agriculture and Water Resources Page 2 of 3 Listeria Detection - FSIS BAX – MLG 8A.05 CHECKLIST Primary enrichment Is an appropriate initial suspension prepared in UVM broth? Is UVM incubated at 30 ± 2C for 20 – 26 h? Is a positive control run with each batch of samples analysed? Are reference cultures inoculated into primary enrichment broth at a level of 10 to 100 cells? Secondary enrichment Is secondary enrichment in MOPS-BLEB? Is secondary enrichment carried out at 35 ± 2C for 26 ± 2 h? BAX screening Are positive and negative control run with each batch of samples? Are the manufacturers instructions reproduced in the laboratory manual and followed without modification? Plating out and identification Are primary enrichment cultures streaked onto MOX? Are MOX plates incubated at either 35 ± 2C for 26 ± 2 h? Are MOX plates incubated for a further 20 – 26 h if growth is slight or no colonies are observed after 26 h? Are descriptions of typical colony morphologies provided in the laboratories methods manual? Are MOPS-BLEB cultures streaked onto MOX for all BAX-positive, BAX-indeterminate or BAXsignal-error samples? Confirmation Is Listeria confirmed using AS 5013.24.1, MLG 8 or FDA BAM Chapter 10? (if applicable) If an external laboratory is used is it department approved? Issue 2015 10 27 | Approved Methods Manual Export Standards Branch | Exports Division Department of Agriculture and Water Resources Page 3 of 3