Chemistry Review 3 Answer Key - High School Chemistry
advertisement
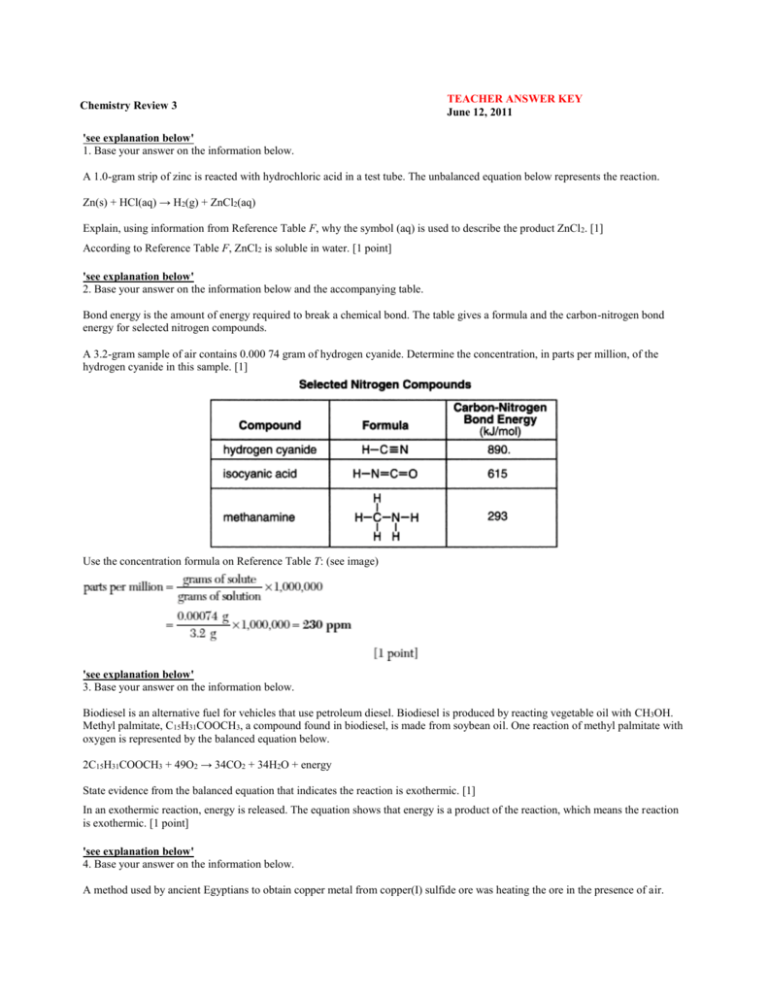
Chemistry Review 3 TEACHER ANSWER KEY June 12, 2011 'see explanation below' 1. Base your answer on the information below. A 1.0-gram strip of zinc is reacted with hydrochloric acid in a test tube. The unbalanced equation below represents the reaction. Zn(s) + HCl(aq) → H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq) Explain, using information from Reference Table F, why the symbol (aq) is used to describe the product ZnCl2. [1] According to Reference Table F, ZnCl2 is soluble in water. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 2. Base your answer on the information below and the accompanying table. Bond energy is the amount of energy required to break a chemical bond. The table gives a formula and the carbon-nitrogen bond energy for selected nitrogen compounds. A 3.2-gram sample of air contains 0.000 74 gram of hydrogen cyanide. Determine the concentration, in parts per million, of the hydrogen cyanide in this sample. [1] Use the concentration formula on Reference Table T: (see image) 'see explanation below' 3. Base your answer on the information below. Biodiesel is an alternative fuel for vehicles that use petroleum diesel. Biodiesel is produced by reacting vegetable oil with CH3OH. Methyl palmitate, C15H31COOCH3, a compound found in biodiesel, is made from soybean oil. One reaction of methyl palmitate with oxygen is represented by the balanced equation below. 2C15H31COOCH3 + 49O2 → 34CO2 + 34H2O + energy State evidence from the balanced equation that indicates the reaction is exothermic. [1] In an exothermic reaction, energy is released. The equation shows that energy is a product of the reaction, which means the reaction is exothermic. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 4. Base your answer on the information below. A method used by ancient Egyptians to obtain copper metal from copper(I) sulfide ore was heating the ore in the presence of air. Later, copper was mixed with tin to produce a useful alloy called bronze. Calculate the density of a 129.5-gram sample of bronze that has a volume of 14.8 cubic centimeters. Your response must include a correct numerical setup and the calculated result. [2] Use the density formula given on Reference Table T: (see image) One point is awarded for a correct numerical setup, and one point is awarded for a calculation that is consistent with the numerical setup. [2 points] 'see explanation below' 5. Base your answer on the information below. Heat is added to a sample of liquid water, starting at 80.oC, until the entire sample is a gas at 120.oC. This process, occurring at standard pressure, is represented by the balanced equation below. H2O(l) + heat → H2O(g) In the box provided or on a separate piece of paper, using the key, draw a particle diagram to represent at least five molecules of the product of this physical change at 120.oC. [2] The product of this reaction is water in the gas phase. Such molecules are widely separated in the container. See the accompanying diagram: One point is awarded for showing at least five water molecules, and one point is awarded for drawing all the particles in the gas phase. [2 points] 'see explanation below' 6. Base your answer on the accompanying information. Explain, in terms of molecular polarity, why hydrogen chloride is more soluble than methane in water at 20. oC and standard pressure. [1] Water is a polar substance, and solubility in it depends on the polarity of the solute. Hydrogen chloride is polar and is very soluble in water. Methane is nonpolar and is hardly soluble in water. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 7. Base your answer on the accompanying information. Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, why ammonia has a higher boiling point than the other compounds in the table. [1] The boiling point of a substance depends on the strength of the intermolecular forces present in the liquid. Since ammonia has a higher boiling point, it must have stronger intermolecular forces than either liquid methane or liquid hydrogen chloride. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 8. Base your answer on the information below. Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, is a water-soluble compound. The concentration of an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution that is 3% by mass H2O2 is used as an antiseptic. When the solution is poured on a small cut in the skin, H 2O2 reacts according to the balanced equation below. 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 Calculate the total mass of H2O2 in 20.0 grams of an aqueous H2O2 solution that is used as an antiseptic. Your response must include both a numerical setup and the calculated result. [2] The equation used to find percent concentration is a slight modification of the percent composition equation given on Reference Table T: (see image) One point is awarded for a correct numerical setup, and one point is awarded for a response consistent with the numerical setup. [2 points] 4 9. How do the boiling point and freezing point of a solution of water and calcium chloride at standard pressure compare to the boiling point and freezing point of water at standard pressure? 1. Both the freezing point and boiling point of the solution are higher. 3. The freezing point of the solution is higher and the boiling point of the solution is lower. 2. Both the freezing point and boiling point of the solution are lower. 4. The freezing point of the solution is lower and the boiling point of the solution is higher. 4 When calcium chloride is dissolved in water, the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than the vapor pressure of pure water. As a result, the solution has a lower freezing point and a higher boiling point than those of pure water. 3 10. Under which conditions of temperature and pressure does a sample of neon behave most like an ideal gas? 1. 100 K and 0.25 atm 3. 400 K and 0.25 atm 2. 100 K and 25 atm 4. 400 K and 25 atm 3 Real gases behave most ideally when the volume of the gas particles is negligible and the particles have enough kinetic energy to overcome intermolecular forces. These occur under conditions of high temperatures and low pressures. Of the choices given, choice (3), 400 K and 0.25 atm, has the highest temperature and the lowest pressure. 4 11. What is the mass of NH4Cl that must dissolve in 200. grams of water at 50.oC to make a saturated solution? 1. 26 g 3. 84 g 2. 42 g 4. 104 g 4 Use Reference Table G. At 50oC, the solubility of NH4Cl is 52 grams of solute per 100 grams of water. In order to saturate 200 grams of water, twice the mass of NH4Cl, 104 grams, must be used. This problem can also be solved by using the factor-label method: (see image) 4 12. Which graph represents the relationship between pressure and volume for a sample of an ideal gas at constant temperature? 4 At constant temperature, the pressure of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its volume. As the pressure increases, the volume decreases and vice versa. Of the choices given, only the graph in choice (4) displays this trend. 3 13. Which unit can be used to express the concentration of a solution? 1. L/s 3. ppm 2. J/g 4. kPa 3 The concentration of a solution can be measured as a percentage (%), as molarity (M), and as parts per million (ppm). Wrong Choices Explained: (1) L/s measures volume flow. (2) J/g measures heat transfer per unit of mass (such as heat of fusion). (4) kPa measures pressure. 3 14. Which formula represents a mixture? 1. C6H12O6(l) 3. LiCl(aq) 2. C6H12O6(s) 4. LiCl(s) 3 A solution is a homogeneous mixture. The designation LiCl(aq) represents an aqueous solution of LiCl. 2 15. Which gas sample at STP has the same total number of molecules as 2.0 liters of CO 2(g) at STP? 1. 5.0 L of CO2(g) 3. 3.0 L of H2S(g) 2. 2.0 L of Cl2(g) 4. 6.0 L of He(g) 2 Avogadro's hypothesis states that equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules. All of the gases in this question are at STP. In other words, they are all at the same temperature and pressure. Of the choices given, only choice (2), 2.0 L of Cl2(g), occupies the same volume as 2.0 L of CO2. 4 16. Which compound is insoluble in water? 1. KOH 3. Na3PO4 2. NH4Cl 4. PbSO4 4 Use Reference Table F. Although sulfates (SO42-) are generally soluble in water, the combination of this ion with Pb 2+ is an exception. PbSO4 is an insoluble compound. Wrong Choices Explained: (1), (3) K+ and Na+ are Group 1 ions; their compounds are always soluble in water. (2) Compounds containing the NH4+ ion are always soluble in water. 4 17. A gas sample is at 25oC and 1.0 atmosphere. Which changes in temperature and pressure will cause this sample to behave more like an ideal gas? 1. decreased temperature and increased pressure 3. increased temperature and increased pressure 2. decreased temperature and decreased pressure 4. increased temperature and decreased pressure 4 Real gases behave most ideally when their molecules are far enough apart to make their molecular volumes negligible (low pressure) and are moving fast enough to overcome any intermolecular forces (high temperature). 2 18. A cylinder with a movable piston contains a sample of gas having a volume of 6.0 liters at 293 K and 1.0 atmosphere. What is the volume of the sample after the gas is heated to 303 K, while the pressure is held at 1.0 atmosphere? 1. 9.0 L 3. 5.8 L 2. 6.2 L 4. 4.0 L 2 Use the combined gas law equation found on Reference Table T: (see image) 3 19. What is the minimum amount of heat required to completely melt 20.0 grams of ice at its melting point? 1. 20.0 J 3. 6680 J 2. 83.6 J 4. 45 200 J 3 Use the heat of fusion of ice given on Reference Table B and the heat of fusion equation found on Reference Table T: (see image) 'see explanation below' 20. Base your answer on the information below. A portable propane-fueled lantern contains a mesh silk bag coated with metal hydroxides. The primary metal hydroxide is yttrium hydroxide. When the silk bag is installed, it is ignited and burned away, leaving the metal hydroxide coating. The coating forms metal oxides that glow brightly when heated to a high temperature. During a test, a propane lantern is operated for three hours and consumes 5.0 moles of propane from the lantern's tank. The balanced equation below represents the combustion of propane. C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O + energy Determine the total number of moles of CO2 produced during the lantern test. [1] Use the appropriate coefficients of the balanced equation and the factor-label method: [1 point] 'see explanation below' 21. Base your answer on the information below. The equation shown (see image) represents the reaction between butanoic acid and an unidentified reactant, X. Write the molecular formula of the organic product in the equation. [1] Count the total number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in the structural formula to determine the molecular formula: C6H12O2. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 22. Base your answer on the information below. A piece of magnesium ribbon is reacted with excess hydrochloric acid to produce aqueous magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. The volume of the dry hydrogen gas produced is 45.6 milliliters. The temperature of the gas is 293 K, and the pressure is 99.5 kilopascals. Balance the equation on the answer sheet or on a separate piece of paper, using the smallest whole-number coefficients. [1] The balanced equation is: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) Note that using a coefficient of "1" in front of Mg, MgCl 2, or H2 is acceptable for credit. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 23. Base your answer on the information below. A portable propane-fueled lantern contains a mesh silk bag coated with metal hydroxides. The primary metal hydroxide is yttrium hydroxide. When the silk bag is installed, it is ignited and burned away, leaving the metal hydroxide coating. The coating forms metal oxides that glow brightly when heated to a high temperature. During a test, a propane lantern is operated for three hours and consumes 5.0 moles of propane from the lantern's tank. The balanced equation below represents the combustion of propane. C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O + energy Calculate the total mass of propane consumed during the lantern test. Your response must include both a correct numerical setup and the calculated result. [2] The molar mass of propane (C3H8) is calculated as follows: (3·(12 g/mol)) + (8·(1 g/mol)) = 44 g/mol Since 5.0 moles of propane are consumed, the total mass of the consumed propane is equal to: (5.0 mol)·(44 g/mol) = 220 g One point is awarded for a correct numerical setup, and one point is awarded for a calculation that is consistent with the numerical setup. [2 points] 'see explanation below' 24. Base your answer on the information below. Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, is a water-soluble compound. The concentration of an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution that is 3% by mass H2O2 is used as an antiseptic. When the solution is poured on a small cut in the skin, H 2O2 reacts according to the balanced equation below. 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 Identify the type of chemical reaction represented by the balanced equation. [1] This reaction can be classified in either of two ways. Since there is one reactant and two products, this is a decomposition reaction. Since the oxidation numbers change during the reaction, this is also a redox reaction. Note that only one type needs to be given in order to receive credit. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 25. Base your answer on the information below. Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, is a water-soluble compound. The concentration of an aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution that is 3% by mass H2O2 is used as an antiseptic. When the solution is poured on a small cut in the skin, H 2O2 reacts according to the balanced equation below. 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 Determine the gram-formula mass of H2O2. [1] Use the accompanying table to calculate the gram-formula mass (molar mass) of H2O2: [1 point] 'see explanation below' 26. Base your answer to the question on the accompanying potential energy diagram. What is the heat of reaction for the forward reaction? Refer to the diagram accompanying this question. The heat of reaction is the difference between the potential energy of the reactants, located at 40 kJ, and the potential energy of the products, located at 120 kJ: 'see explanation below' 27. Base your answer to the question on the accompanying potential energy diagram. What is the activation energy for the forward reaction with the catalyst? Refer to the diagram accompanying this question. The activation energy of the forward catalyzed reaction is the difference between the potential energy of the reactants and the peak of the dotted curve, located at 140 kJ: 'see explanation below' 28. Base your answer to the question on the accompanying potential energy diagram. Explain, in terms of the function of a catalys, why the curves on the potential energy diagram for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions are different. A catalyst provides an alternate pathway for the reaction. This pathway has a lower activation energy than that of the uncatalyzed reaction. [1 point] 'see explanation below' 29. State two methods to increase the rate of a chemical reaction and explain, in terms of particle behavior, how each method increases the reaction rate. [2] Any two of the following methods are acceptable for maximum credit. Increase the temperature. This causes the reacting particles to move faster and collide more frequently. Increase the concentrations of the reacting particles. This causes an increase in the number of collisions. Increase the surface area of a solid reactant. This exposes more reacting particles to collisions with other reactants. Add a catalyst. This provides the reacting particles with an alternate pathway that has a lower activation energy. One point is awarded for each acceptable response. [2 points] 'see explanation below' 30. State two methods to increase the rate of a chemical reaction and explain, in terms of particle behavior, how each method increases the reaction rate. [2] Any two of the following methods are acceptable for maximum credit. Increase the temperature. This causes the reacting particles to move faster and collide more frequently. Increase the concentrations of the reacting particles. This causes an increase in the number of collisions. Increase the surface area of a solid reactant. This exposes more reacting particles to collisions with other reactants. Add a catalyst. This provides the reacting particles with an alternate pathway that has a lower activation energy. One point is awarded for each acceptable response. [2 points] 'see explanation below' 31. Base your answer on the information below. Heat is added to a sample of liquid water, starting at 80.oC, until the entire sample is a gas at 120.oC. This process, occurring at standard pressure, is represented by the balanced equation below. H2O(l) + heat → H2O(g) On the diagram or on a separate piece of paper, complete the heating curve for this physical change. [1] As heat is added to liquid water, its temperature rises until it reaches the boiling point. The temperature then remains constant until all of the liquid water has changed to gas. From that point on, the temperature rises once again. An example of an acceptable heating curve is shown in the accompanying diagram: [1 point] 'see explanation below' 32. Base your answer on the information below. The catalytic converter in an automobile changes harmful gases produced during fuel combustion to less harmful exhaust gases. In the catalytic converter, nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen and carbon dioxide. In addition, some carbon monoxide reacts with oxygen, producing carbon dioxide in the converter. These reactions are represented by the balanced equations below. Reaction 1: 2NO2(g) + 4CO(g) → N2(g) + 4CO2(g) + 1198.4 kJ Reaction 2: 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 566.0 kJ The potential energy diagram (see image) represents reaction 1 without a catalyst. On the same diagram or a separate piece of paper, draw a dashed line to indicate how potential energy changes when the reaction is catalyzed in the converter. [1] Catalysts speed reactions by lowering their activation energies. The dashed curve in the accompanying potential energy diagram represents the effect of a catalyst on the reaction. [1 point] 1 33. What is the formula of titanium(II) oxide? 1. TiO 3. Ti2O 2. TiO2 4. Ti2O3 1 The charges of the titanium (II) and oxide ions are, respectively, 2+ and 2-. In a (neutral) compound, the sum of the charges must add to zero. Therefore, the correct formula is TiO. 3 34. What is the IUPAC name for the compound FeS? 1. iron(II) sulfate 3. iron(II) sulfide 2. iron(III) sulfate 4. iron(III) sulfide 3 In the compound FeS, Fe has an oxidation state of +2. According to the IUPAC, the name of this ion is iron(II). In the compound FeS, the oxidation state of S is -2. According to the IUPAC, the negative ion in a binary compound takes on the suffix -ide, meaning the name of the ion is sulfide. Therefore, the name of the compound is iron(II) sulfide. 3 35. Which equation represents a double replacement reaction? 1. 2 Na + 2 H2O --> 2 NaOH + H2 3. LiOH + HCl --> LiCl + H2O 2. CaCO3 --> CaO + CO2 4. CH4 + 2 O2 --> CO2 + 2 H2O 3 In a double replacement reaction, the positive and negative ions "switch" places. Write the equation as though all of the substances were ionic: Li+[OH]- + H+Cl- + L+Cl- + H+[OH]Note: H2O is not really an ionic substance; it is a covalently bonded molecule. It was written this way to illustrate the double replacement. Wrong Choices Explained: (1) This equation represents a single replacement reaction. (2) This equation represents a decomposition reaction. (4) This equation represents a combustion reaction. 2 36. Note: This question may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. Given the incomplete equation: 4Fe + 3O2 --> 2X Which compound is represented by X? 1. FeO 3. Fe3O2 2. Fe2O3 4. Fe3O4 2 There are a total of 4 Fe atoms and 6 O atoms on the left side of the equation. Since the product is 2X, the formula unit X must be Fe2O3. 3 37. A compound is made up of iron and oxygen, only. The ratio of iron ions to oxide ions is 2:3 in this compound. The IUPAC name for this compound is 1. triiron dioxide 3. iron(III) oxide 2. iron (II) oxide 4. iron trioxide 3 The formula of the compound is Fe2O3. In this compound, Fe has an oxidation state of +3, and the oxidation state of the oxygen is -2. According to the IUPAC, the name of Fe3+ ion is iron(III), and the name of the O2- ion is oxide. Therefore, the name of the compound is iron(III) oxide. 2 38. Given the balanced equation shown: What is the total number of moles of CO2 formed when 20. moles of HCl is completely consumed? 1. 5.0 mol 3. 20. mol 2. 10. mol 4. 40. mol 2 The mole ratio of CO2 : HCl is given by the coefficients of the equation, 1 mole : 2 moles. Use the factor-label method to solve the problem:(see image) 2 39. A hydrate is a compound with water molecules incorporated into its crystal structure. In an experiment to find the percent by mass of water in a hydrated compound, the following data were recorded: What is the percent by mass of water in the hydrate? 1. 8.0% 3. 72.% 2. 50.% 4. 96.% 3 40. Given the unbalanced equation: . . . (see image) What is the coefficient of O2 when the equation is balanced correctly using the smallest whole-number coefficients? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2 41. The chemical formula for nickel (II) bromide is 1. Ni2Br 3. N2Br 2. NiBr2 4. NBr2 4 42. Given the reaction: . . . (see image) How many moles of C6H12O6(s) are needed to produce 24 moles of carbon dioxide? 1. 1.0 mole 3. 24 moles 2. 12 moles 4. 4.0 moles 3 43. Which formula is an empirical formula? 1. C2H6 3. H2O 2. C4H10 4. H2O2 2 44. What is the percent by mass of oxygen in Ca(OH)2? [formula mass = 74.1] 1. 21.6% 3. 45.9% 2. 43.2% 4. 54.1% 4 45. The gram-formula mass of (NH4)2CO3 is 1. 46.0 g 3. 78.0 g 2. 64.0 g 4. 96.0 g 4 46. What is the total number of moles of atoms contained in 1 mole of NH3? 1. 1 mole 3. 3 moles 2. 2 moles 4. 4 moles 4 47. The percent by mass of hydrogen in NH3 is equal to 4 48. A compound has a gram formula mass of 56 grams per mole. What is the molecular formula for this compound? 1. CH2 3. C3H6 2. C2H4 4. C4H8 1 49. What is the total number of oxygen atoms in the formula MgSO4•7 H2O? [The • represents seven units of H2O attached to one unit of MgSO4.] 1. 11 3. 5 2. 7 4. 4 4 50. Given the reaction: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6 O2 What is the total number of moles of water needed to make 2.5 moles of C 6H12O6? 1. 2.5 3. 12 2. 6.0 4. 15 4 51. Given the reaction: (see image) What is the total number of moles of NaCl formed when 2 moles of Na2CrO4 react completely? 1. 1 mole 3. 3 moles 2. 2 moles 4. 4 moles 'see explanation below' 52. Base your answer on the information below. Heat is added to a sample of liquid water, starting at 80.oC, until the entire sample is a gas at 120.oC. This process, occurring at standard pressure, is represented by the balanced equation below. H2O(l) + heat → H2O(g) On the diagram or on a separate piece of paper, complete the heating curve for this physical change. [1] As heat is added to liquid water, its temperature rises until it reaches the boiling point. The temperature then remains constant until all of the liquid water has changed to gas. From that point on, the temperature rises once again. An example of an acceptable heating curve is shown in the accompanying diagram: [1 point] 'see explanation below' 53. Base your answer on the information below. The catalytic converter in an automobile changes harmful gases produced during fuel combustion to less harmful exhaust gases. In the catalytic converter, nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen and carbon dioxide. In addition, some carbon monoxide reacts with oxygen, producing carbon dioxide in the converter. These reactions are represented by the balanced equations below. Reaction 1: 2NO2(g) + 4CO(g) → N2(g) + 4CO2(g) + 1198.4 kJ Reaction 2: 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 566.0 kJ The potential energy diagram (see image) represents reaction 1 without a catalyst. On the same diagram or a separate piece of paper, draw a dashed line to indicate how potential energy changes when the reaction is catalyzed in the converter. [1] Catalysts speed reactions by lowering their activation energies. The dashed curve in the accompanying potential energy diagram represents the effect of a catalyst on the reaction. [1 point] 2 54. Note: This question may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. Given the incomplete equation: 4Fe + 3O2 --> 2X Which compound is represented by X? 1. FeO 3. Fe3O2 2. Fe2O3 4. Fe3O4 2 There are a total of 4 Fe atoms and 6 O atoms on the left side of the equation. Since the product is 2X, the formula unit X must be Fe2O3. 3 55. A compound is made up of iron and oxygen, only. The ratio of iron ions to oxide ions is 2:3 in this compound. The IUPAC name for this compound is 1. triiron dioxide 3. iron(III) oxide 2. iron (II) oxide 4. iron trioxide 3 The formula of the compound is Fe2O3. In this compound, Fe has an oxidation state of +3, and the oxidation state of the oxygen is -2. According to the IUPAC, the name of Fe3+ ion is iron(III), and the name of the O2- ion is oxide. Therefore, the name of the compound is iron(III) oxide. 2 56. Given the balanced equation shown: What is the total number of moles of CO2 formed when 20. moles of HCl is completely consumed? 1. 5.0 mol 3. 20. mol 2. 10. mol 4. 40. mol 2 The mole ratio of CO2 : HCl is given by the coefficients of the equation, 1 mole : 2 moles. Use the factor-label method to solve the problem:(see image) 2 57. A hydrate is a compound with water molecules incorporated into its crystal structure. In an experiment to find the percent by mass of water in a hydrated compound, the following data were recorded: What is the percent by mass of water in the hydrate? 1. 8.0% 3. 72.% 2. 50.% 4. 96.% 3 58. Given the unbalanced equation: . . . (see image) What is the coefficient of O2 when the equation is balanced correctly using the smallest whole-number coefficients? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2 59. The chemical formula for nickel (II) bromide is 1. Ni2Br 3. N2Br 2. NiBr2 4. NBr2 4 60. Given the reaction: . . . (see image) How many moles of C6H12O6(s) are needed to produce 24 moles of carbon dioxide? 1. 1.0 mole 3. 24 moles 2. 12 moles 4. 4.0 moles 3 61. Which formula is an empirical formula? 1. C2H6 3. H2O 2. C4H10 4. H2O2 2 62. What is the percent by mass of oxygen in Ca(OH)2? [formula mass = 74.1] 1. 21.6% 3. 45.9% 2. 43.2% 4. 54.1% 4 63. The gram-formula mass of (NH4)2CO3 is 1. 46.0 g 3. 78.0 g 2. 64.0 g 4. 96.0 g 4 64. What is the total number of moles of atoms contained in 1 mole of NH 3? 1. 1 mole 3. 3 moles 2. 2 moles 4. 4 moles 4 65. The percent by mass of hydrogen in NH3 is equal to 4 66. A compound has a gram formula mass of 56 grams per mole. What is the molecular formula for this compound? 1. CH2 3. C3H6 2. C2H4 4. C4H8 1 67. What is the total number of oxygen atoms in the formula MgSO4•7 H2O? [The • represents seven units of H2O attached to one unit of MgSO4.] 1. 11 3. 5 2. 7 4. 4 4 68. Given the reaction: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6 O2 What is the total number of moles of water needed to make 2.5 moles of C6H12O6? 1. 2.5 3. 12 2. 6.0 4. 15 4 69. Given the reaction: (see image) What is the total number of moles of NaCl formed when 2 moles of Na2CrO4 react completely? 1. 1 mole 3. 3 moles 2. 2 moles 4. 4 moles 1 70. What is the formula of titanium(II) oxide? 1. TiO 3. Ti2O 2. TiO2 4. Ti2O3 1 The charges of the titanium (II) and oxide ions are, respectively, 2+ and 2-. In a (neutral) compound, the sum of the charges must add to zero. Therefore, the correct formula is TiO. 3 71. What is the IUPAC name for the compound FeS? 1. iron(II) sulfate 3. iron(II) sulfide 2. iron(III) sulfate 4. iron(III) sulfide 3 In the compound FeS, Fe has an oxidation state of +2. According to the IUPAC, the name of this ion is iron(II). In the compound FeS, the oxidation state of S is -2. According to the IUPAC, the negative ion in a binary compound takes on the suffix -ide, meaning the name of the ion is sulfide. Therefore, the name of the compound is iron(II) sulfide. 3 72. Which equation represents a double replacement reaction? 1. 2 Na + 2 H2O --> 2 NaOH + H2 3. LiOH + HCl --> LiCl + H2O 2. CaCO3 --> CaO + CO2 4. CH4 + 2 O2 --> CO2 + 2 H2O 3 In a double replacement reaction, the positive and negative ions "switch" places. Write the equation as though all of the substances were ionic: Li+[OH]- + H+Cl- + L+Cl- + H+[OH]- Note: H2O is not really an ionic substance; it is a covalently bonded molecule. It was written this way to illustrate the double replacement. Wrong Choices Explained: (1) This equation represents a single replacement reaction. (2) This equation represents a decomposition reaction. (4) This equation represents a combustion reaction. 1 73. Which statement best describes the shape and volume of an aluminum cylinder at STP? 1. It has a definite shape and a definite volume. 3. It has no definite shape and a definite volume. 2. It has a definite shape and no definite volume. 4. It has no definite shape and no definite volume. 1 Aluminum is a solid at STP. Any solid has a definite shape and a definite volume. Wrong Choices Explained: (3) A liquid has a definite volume but not a definite shape. (4) A gas has neither a definite shape nor a definite volume. 2 74. An atom of potassium-37 and an atom of potassium-42 differ in their total number of 1. electrons 3. protons 2. neutrons 4. positrons 2 Isotopes, such as potassium-37 and potassium-42, differ in their total number of neutrons. An atom of potassium-37 contains 19 protons, 19 electrons, and 18 neutrons. An atom of potassium-42 contains 19 protons, 19 electrons, and 23 neutrons. 3 75. What is the mass number of an atom that has six protons, six electrons, and eight neutrons? 1. 6 3. 14 2. 12 4. 20 3 The mass number of an atom is the sum of the protons and neutrons in its nucleus. An atom that has 6 protons and 8 neutrons in its nucleus has a mass number of 14. 2 76. Which diagram represents the nucleus of an atom of 2713Al? 2 The symbol 27 13Al represents an isotope of aluminum. The lower number (13) is the atomic number of the atom, that is, the number of protons in its nucleus. The upper number (27) is the mass number of the atom, which is the sum of the protons and neutrons. Therefore, the nucleus of this atom contains 13 protons and 14 (27 - 13) neutrons. This combination is represented in choice (2). 1 77. Which list of elements from Group 2 on the Periodic Table is arranged in order of increasing atomic radius? 1. Be, Mg, Ca 3. Ba, Ra, Sr 2. Ca, Mg, Be 4. Sr, Ra, Ba 1 Use the Periodic Table of the Elements and Reference Table S. Of the choices given, only choice (1), Be, Mg, and Ca, are Group 2 elements listed in order of increasing atomic radius. 4 78. Which Period 4 element has the most metallic properties? 1. As 3. Ge 2. Br 4. Sc 4 Refer to the Periodic Table of the Elements. As one proceeds left to right across a period, the metallic properties of the elements decrease. Of the choices given, choice (4), Sc, lies furthest to the left and has the most metallic properties. 2 79. Which statement explains why ozone gas, O3, and oxygen gas, O2, have different properties? 1. They are formed from different elements. 3. They have different oxidation numbers. 2. They have different molecular structures. 4. They have different electronegativities. 2 The physical and chemical properties of a substance depend on the molecular structure of the substance. Since ozone gas (O 3) and oxygen gas (O2) have different molecular structures, they have different properties. 3 80. Which element has both metallic and nonmetallic properties? 1. Rb 3. Si 2. Rn 4. Sr 3 Refer to the accompanying diagram, which represents a portion of the Periodic Table of the Elements: The metalloids—those elements that have both metallic and nonmetallic properties—are found in the shaded boxes. Of the choices given, only choice (3), Si, is a metalloid. 4 81. The carbon atoms in graphite and the carbon atoms in diamond have different 1. atomic numbers 3. electronegativities 2. atomic masses 4. structural arrangements 4 Graphite and diamond are known as allotropes—forms of an element in which the atoms have different structural arrangements in space. 3 82. Which statement describes a chemical property of the element magnesium? 1. Magnesium is malleable. 3. Magnesium reacts with an acid. 2. Magnesium conducts electricity. 4. Magnesium has a high boiling point. 3 A chemical property is one in which the substance is changed when the property is investigated. In other words, a chemical reaction occurs. When magnesium atoms react with an acid, hydrogen gas and magnesium ions are formed. Wrong Choices Explained: (1), (2), (4) Malleability, conductivity, and boiling point are physical properties. The magnesium atoms are not changed by these properties. 1 83. Which statement explains why sulfur is classified as a Group 16 element? 1. A sulfur atom has 6 valence electrons. 3. Sulfur is a yellow solid at STP. 2. A sulfur atom has 16 neutrons. 4. Sulfur reacts with most metals. 1 The group numbers of the representative elements are related to the number of valence electrons in an atom of the element, as shown in the accompanying table: 1 84. How do the atomic radius and metallic properties of sodium compare to the atomic radius and metallic properties of phosphorus? 1. Sodium has a larger atomic radius and is more metallic. 3. Sodium has a smaller atomic radius and is more metallic. 2. Sodium has a larger atomic radius and is less metallic. 4. Sodium has a smaller atomic radius and is less metallic. 1 See Reference Table S and the Periodic Table of the Elements. Sodium has a larger atomic radius than phosphorus. Sodium is classified as a metal, and phosphorus is classified as a nonmetal. 1 85. Which group on the Periodic Table of the Elements contains elements that react with oxygen to form compounds with the general formula X2O? 1. Group 1 3. Group 14 2. Group 2 4. Group 18 1 Refer to the Periodic Table of the Elements. In the formula X2O, oxygen has an oxidation state of –2. Therefore, the substance X must have an oxidation state of +1, which places it in Group 1. 2 86. An atom of which element has the largest atomic radius? 1. Fe 3. Si 2. Mg 4. Zn 2 Use Reference Table S. Of the choices given, choice (2), Mg (atomic number 12), has the largest atomic radius. 3 87. Which element requires the least amount of energy to remove the most loosely held electron from a gaseous atom in the ground state? 1. bromine 3. sodium 2. calcium 4. silver 3 The energy needed to remove the most loosely held electron from a gaseous atom in the ground state is known as the first ionization energy. Use Reference Table S. Of the choices given, choice (3), sodium (atomic number 11), has the smallest first ionization energy. 4 88. At STP, which element is solid, brittle, and a poor conductor of electricity? 1. Al 3. Ne 2. K 4. S 4 A solid element that is brittle and a poor conductor of electricity is most likely a nonmetal. Refer to the Periodic Table of the Elements. Of the choices given, only choice (4), S, is a solid, nonmetallic element. Wrong Choices Explained: (1), (2) Al and K are metallic elements. (3) Ne is nonmetallic, but it is a gas at STP. 3 89. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown in the accompanying graph. Each interval on the axis labeled "Potential Energy (kJ)" represents 40 kilojoules. What is the heat of reaction? 1. -120 kJ 3. +40 kJ 2. -40 kJ 4. +160 kJ 3 Refer to the graph below: Note that the difference between the reactants and products (labeled "Heat of Reaction") is one interval high. The magnitude of the heat of reaction is 40 kJ. Since the products have more energy than the reactants, this is an endothermic reaction. The heat of reaction is +40 kJ. 3 90. Given the reaction at equilibrium: . . . (see image) Which change will cause the equilibrium to shift? 1. increase in pressure 3. addition of heat 2. increase in volume 4. addition of a catalyst 2 91. Given the equilibrium at 101.3 kPa: . . . (see image) At what temperature does this equilibrium occur? 1. 100 K 3. 298 K 2. 273 K 4. 373 K 1 92. Given the accompanying diagram that shows carbon dioxide in an equilibrium system at a temperature of 298 K and a pressure of 1 atm: Which changes must increase the solubility of the carbon dioxide? 1. increase pressure and decrease temperature 3. decrease pressure and decrease temperature 2. increase pressure and increase temperature 4. decrease pressure and increase temperature 2 93. Given the equation representing a reaction: Which statement describes this reaction at equilibrium? 1. The concentration of N2O4(g) must equal the concentration of NO2(g). 3. The rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. 2. The concentration of N2O4(g) and the concentration of NO2(g) 4. The rate of the reverse reaction is greater than the rate of the must be constant. forward reaction. 2 At equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. As a result, the concentrations of N 2O4(g) and NO2(g) do not change. 3 94. Given the balanced equation representing a reaction: 2HCl(aq) + Na2S2O3(aq) --> S(s) + H2SO3(aq) + 2NaCl(aq) Decreasing the concentration of Na2S2O3(aq) decreases the rate of reaction because the 1. activation energy decreases 3. frequency of effective collisions decreases 2. activation energy increases 4. frequency of effective collisions increases 3 The rate of a chemical reaction depends on the frequency of effective collisions among the reacting particles. Any factor that decreases the collision frequency will decrease the rate of the reaction. Such factors include decreasing the concentration of the reactants and lowering the temperature. Wrong Choices Explained: (1), (2) Activation energy does not depend on the concentration of the reactants. It depends on the nature of the reactants. 4 95. Given the equation representing a phase change at equilibrium: (see accompanying image) Which statement describes this equilibrium? 1. The H2O(s) melts faster than the H2O(l) freezes. 3. The mass of H2O(s) must equal the mass of H2O(l). 2. The H2O(l) freezes faster than the H2O(s) melts. 4. The mass of H2O(l) and the mass of H2O(s) each remain constant. 4 When a system reaches a state of equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions become equal. In this example, the rate at which the ice melts is equal to the rate at which the water freezes. As a result, the masses of the water and the ice become constant, though not necessarily equal to each other. 4 96. In a chemical reaction, the difference between the potential energy of the products and the potential energy of the reactants is equal to the 1. activation energy 3. heat of fusion 2. entropy of the system 4. heat of reaction 4 Refer to the accompanying potential energy diagram. An inspection of this diagram reveals that the difference in potential energy between the reactants and products is equal to the heat of reaction (ΔH). In this case, the heat of reaction is negative. 1 97. Given the potential energy diagram and equation representing the reaction between substances A and D: (see accompanying diagram) According to Table I, substance G could be 1. HI(g) 3. CO2(g) 2. H2O(g) 4. C2H6(g) 1 The diagram in this question indicates that substance G has a higher potential energy than substances A and G. This reaction is endothermic and has a positive ΔH. Use Reference Table I. Of the choices given, only the product in choice (1), HI(g), has a positive ΔH. 4 98. Given the equation representing a system at equilibrium: (see accompanying image) Which changes occur when the temperature of this system is decreased? 1. The concentration of H2(g) increases and the concentration of N2(g) increases. 3. The concentration of H2(g) decreases and the concentration of NH3(g) decreases. 2. The concentration of H2(g) decreases and the concentration of N2(g) increases. 4. The concentration of H2(g) decreases and the concentration of NH3(g) increases. 4 In the forward reaction, energy appears as a product, i.e., it is an exothermic reaction. If the temperature of the system is lowered, Le Chatelier's principle predicts that the system will shift to the right in order to produce more heat energy. As a result, the concentration of both H2(g) and N2(g) will decrease and the concentration of NH3(g) will increase. 1 99. The solid and liquid phases of water can exist in a state of equilibrium at 1 atmosphere of pressure and a temperature of 1. 0oC 3. 273oC 2. 100oC 4. 373oC 3 100. Given the equilibrium reaction in a closed system as shown: What will be the result of an increase in temperature? 1. The equilibrium will shift to the left and [H2] will increase. 3. The equilibrium will shift to the right and [HI] will increase. 2. The equilibrium will shift to the left and [H2] will decrease. 4. The equilibrium will shift to the right and [HI] will decrease. 4 101. Which information about a chemical reaction is provided by a potential energy diagram? 1. the oxidation states of the reactants and products 3. the change in solubility of the reacting substances 2. the average kinetic energy of the reactants and products 4. the energy released or absorbed during the reaction 4 Refer to the potential energy diagram shown (see image). 4 102. Given the reaction system in a closed container at equilibrium and at a temperature of 298 K: (see image) The measurable quantities of the gases at equilibrium must be 1. decreasing 3. equal 2. increasing 4. constant 4 When a reaction system reaches equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant. 4 103. Based on Reference Table H, which sample has the highest vapor pressure? 1. water at 20oC 3. ethanol at 50oC 2. water at 80oC 4. ethanol at 65oC 2 104. Given the potential energy diagram of a chemical reaction: . . . (see image) Which arrow represents the potential energy of the reactants? 1. A 3. C 2. B 4. D 2 105. Given the reaction at equilibrium: . . . (see image) Which change will shift the equilibrium to the right? 1. increasing the temperature 3. decreasing the amount of SO2(g) 2. increasing the pressure 4. decreasing the amount of O2(g) 3 106. What occurs when the temperature is increased in a system at equilibrium at constant pressure? 1. The rate of the forward reaction increases, and the rate of the reverse reaction decreases. 3. The rate of the endothermic reaction increases. 2. The rate of the forward reaction decreases, and the rate of the reverse reaction increases. 4. The rate of the exothermic reaction decreases. 1 107. Ammonia is produced commercially by the Haber reaction: . . . (see image) The formation of ammonia is favored by 1. an increase in pressure 3. removal of N2(g) 2. a decrease in pressure 4. removal of H2(g) 1 108. Given the equilibrium reaction at STP: . . . (see image) Which statement correctly describes this system? 1. The forward and reverse reaction rates are equal. 3. The concentrations of N2O4 and NO2 are equal. 2. The forward and reverse reaction rates are both increasing. 4. The concentrations of N2O4 and NO2 are both increasing. 2 109. Which process is accompanied by a decrease in entropy? 1. boiling of water 3. subliming of iodine 2. condensing of water vapor 4. melting of ice 1 110. A catalyst is added to a system at equilibrium. If the temperature remains constant, the activation energy of the forward reaction 1. decreases 3. remains the same 2. increases 2 111. As carbon dioxide sublimes, its entropy 1. decreases 3. remains the same 2. increases 3 112. A solution that is at equilibrium must be 1. concentrated 3. saturated 2. dilute 4. unsaturated 3 When a solution is in equilibrium, the rate at which excess solute dissolves must equal the rate at which the dissolved solute leaves the solution. Since these two rates are equal, dissolving additional solute at a given temperature and pressure is not possible. In other words, the solution is saturated. 2 113. Given the reaction: Which change would cause an immediate increase in the rate of the forward reaction? 1. increasing the concentration of NO(g) 3. decreasing the reaction temperature 2. increasing the concentration of N2(g) 4. decreasing the reaction pressure 2 Increasing the concentration of N2(g) would increase the number of effective collisions between N2(g) and O2(g), leading to an increase in the rate of the forward reaction. Wrong Choices Explained: (1) Increasing the concentration of NO(g) would lead to an increase in the rate of the reverse reaction. (3) Decreasing the temperature always decreases the rates of both the forward and the reverse reactions. (4) Decreasing the reaction pressure effectively decreases the concentrations of (gaseous) reactants and products. As a result, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions would decrease. 2 114. Systems in nature tend to undergo changes toward 1. lower energy and lower entropy 3. higher energy and lower entropy 2. lower energy and higher entropy 4. higher energy and higher entropy 2 Changes in nature are directed by two factors: energy and entropy. Systems in nature will tend to undergo spontaneous changes if the energy of the system is decreased and the entropy (disorder) of the system is increased. 4 115. A 1.0-gram piece of zinc reacts with 5 milliliters of HCl(aq). Which of these conditions of concentration and temperature would produce the greatest rate of reaction? 1. 1.0 M HCl(aq) at 20.oC 3. 2.0 M HCl(aq) at 20.oC 2. 1.0 M HCl(aq) at 40.oC 4. 2.0 M HCl(aq) at 40.oC 4 Reaction rates depend on temperature and the concentration of reactants. A reaction that occurs at 40°C will be faster than the reaction at 20°C. Furthermore, 2.0 M HCl is more concentrated than 1.0 M HCl. Using 2.0 M HCl will produce a faster reaction than using 1.0 M HCl. 5 116. Which expression represents the ΔH for a chemical reaction in terms of the potential energy, PE, of its products and reactants? 1. PE of products + PE of reactants 3. PE of products × PE of reactants 2. PEof products - PE of reactants 4. PE of products ÷ PE of reactants 2 The heat of a reaction, ΔH, is the difference between the potential energies of the products and reactants. 2 117. At 20.oC, a 1.2-gram sample of Mg ribbon reacts rapidly with 10.0 milliliters of 1.0 M HCl(aq). Which change in conditions would have caused the reaction to proceed more slowly? 1. increasing the initial temperature to 25oC 3. using 1.2 g of powdered Mg 2. decreasing the concentration of HCl(aq) to 0.1 M 4. using 2.4 g of Mg ribbon 2 Three factors that affect reaction rate are concentration, surface area, and temperature. As the concentration increases, the rate increases. Therefore, a 0.1 M solution of HCl will produce a slower rate than a 1.0 M solution of HCl. Wrong Choices Explained: (1) If the temperature is increased, the rate will increase. (3) If the surface area is increased, the rate will increase. (4) Using more Mg ribbon will have no affect on the rate since the concentration of the magnesium is unchanged. 3 118. A closed container holds 3.0 moles of CO2 gas at STP. What is the total number of moles of Ne(g) that can be placed in a container of the same size at STP? 1. 1.0 mole 3. 3.0 moles 2. 1.5 moles 4. 0.0 moles 3 119. Which statement best describes a chemical reaction when it reaches equilibrium? 1. The concentrations of reactants and products are the same. 3. The forward and reverse reaction rates are the same. 2. The concentrations of the reactants decrease to zero. 4. The forward reaction rate decreases to zero. 1 120. Which reaction has the greatest increase in entropy? 1 121. In a potential energy diagram, the difference between the potential energy of the products and the potential energy of the reactants is equal to the 1. heat of reaction 3. activation energy of the forward reaction 2. entropy of the reaction 4. activation energy of the reverse reaction 2 122. As the concentration of reacting particles increases, the rate of reaction generally 1. decreases 3. remains the same 2. increases 2 123. As the temperature of a gas increases at constant pressure, the volume of the gas 1. decreases 3. remains the same 2. increases 4 124. If 4.00 moles of oxygen gas, 3.00 moles of hydrogen gas, and 1.00 mole of nitrogen gas are combined in a closed container at standard pressure, what is the partial pressure exerted by the hydrogen gas? 1. 1.00 atm 3. 3.00 atm 2. 0.125 atm 4. 0.375 atm 3 125. Which compound has molecules that form the strongest hydrogen bonds? 1. HI 3. HF 2. HBr 4. HCl








