51_SWP_Southern Blotting_JW
advertisement

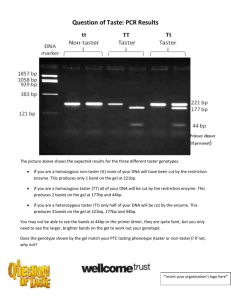
OHS026 Safe Work Procedure Faculty/Division School of Medical Sciences Document number SOMS.CGM.SWP051 Initial Issue date 26.6.09 School/ Divisional Unit School of Medical Sciences, Oncology Research Unit/Neuromuscular and Regenerative Medicine Unit Current version Current Version Next review date 1.0 26.6.12 Issue date 26.6.09 The Writing Safe Work Procedures Guideline (OHS027) should be consulted to assist in the completion of this form. Safe Work Procedure Title and basic description Title: Southern blotting Description: Southern blot is used to detect specific DNA fragment in the mixture of double-stranded DNA fragments generated by restriction endonuclease treatment. This protocol outlines the separation of the DNA fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis, the capillary blotting transfer of DNA onto nitrocellulose membrane and the radioactive labeling hybridization with the specific DNA probe. Associated risk assessment title and location:51_RA_Southern blotting_JW Describe the activity or process SOLUTIONS required: Depurination solution For 1 L volume, mix: 11 ml concentrated HCl 989 ml distilled water f.c. 250 mM Denaturation buffer For 1 L volume, dissolve: 87.66 g NaCl f.c. 1.5 M 20 g NaOH f.c. 0.5 M in approximately 800ml distilled water. Make up to a final volume of 1L with water 20X SSC For 1 L volume, dissolve: 175.3 g of NaCl f.c. 3 M 88.2 g of Sodium citrate f.c. 0.3 M in approximately 700mL distilled water then pH to 7.0 with a few drops of 10N NaOH. Make up to a final volume of 1L. 1M NaHPO4 pH 7.2 For 500 mL volume, dissolve in distilled water : 70.98g Na2HPO4 ~2ml 85% H3PO4 (phosphoric acid) Church (hybridization) Buffer 0.5M Na2HPO4 pH 7.2 (25ml of 1M stock) 1% BSA (fraction V) (5ml of 10% stock) 7% SDS (17.5ml of 20% stock) 1mM EDTA (0.1ml of 0.1M stock) 2.4ml H2O (up to 50ml total) DNA digest and gel electrophoresis: ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 1 of 5 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007 Digest genomic DNA (normally, a total of 10 μg) with the appropriate enzyme under manufacturer’s recommended conditions. Use a 10x excess of enzyme for 4 hours to overnight incubation with final volume between 20-30 l. Make 0.7–0.8% TAE agarose gel (see SWP on DNA agarose ethidium bromide). Add 1x loading buffer to each digested DNA sample then load samples into the gel, along to a DNA molecular weight marker. Begin electrophoresis at 120 volts until the dye enters the gel, then either keep running for 1-2 hours or turn down to 25-35 volts for 10-18 hours until the bromophenol blue marker reaches the bottom of the gel. Photograph gel with ruler next to the gel for sizing the molecular weight markers (see Gel documentation system in SWP on UV Equpiment - Transilluminator) Rinse the gel briefly in deionised water. Depurination step is optional for fragments >15 kb. By taking the purines out, hence cutting the DNA into smaller fragments, this improves the transfer to the blotting membrane. Place the gel in depurination solution for 10 minutes in gentle agitation then rinse briefly in deionised water. Denaturation: soak the gel in denaturation buffer for 30 minutes in gentle agitation. Southern Transfer: Cut a piece of membrane and 4x Whatmann 3MM filter paper to the size of the gel and a longer piece for the wick. Set up capillary blotting in the following order (as shown in the picture): o Half fill a tray of suitable size with 10xSSC (the transfer buffer) o Make a platform and cover with a wick made from Whatmann filter paper. Stack one smaller filter paper (of the size of the gel) on top. o Place the gel upside down on the wick platform. Remove any air bubbles between gel on the wick by using a clean pipette or glass rod over the surface. Surround the gel with parafilm to prevent the transfer buffer being absorbed directly onto the paper towels. o Place membrane on top of the gel. Avoid trapping any air bubbles. o Place 3x 3MM paper on top of the membrane. Avoid trapping any air bubbles. o Place a stack of dry absorbent paper towels of at least 5 cm high. o Finally, place a glass plate and a weight (do not exceed 750 g for a 20 x 20 cm gel) on top of the paper stack. Let transfer overnight. On the next day, carefully dismantle the transfer apparatus. Before separating the gel and membrane, mark the position of the wells with soft-lead pencil on the membrane to allow identification of the tracks. Fix the nucleic acid to the membrane by leaving dry on the bench for a few hours and/or by UV crosslinking. Prehybridisation: Preheat church buffer at 65°C. Rinse the membrane briefly in 5xSSC then place it in hybridization bottle containing 15 ml (small) or 25 ml (large) of church buffer. Prehybridise for 1-2 hours at 65°C in rotating oven to block non-specific binding. Radioactive labeling of probe: This section outlines the labeling of 25-50ng cDNA probe with [-32P]dCTP by random priming using Amersham Klenow kit. This procedure must be done in the radioactive room (see Radioactivity Safe Work ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 2 of 5 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007 Practice and Risk Assessment). It is important to wear appropriate PPCE and place the perspex shielding appropriately when working with 32P. Prepare the following mixture: DNA template 25-50 ng 10x random primer solution 2.5 L Water Make up to 14 L Mix and quickly spin down in microcentrifuge. Denature the DNA sample by heating at 95-100°C for 5 minutes in water bath or heating block. Chill on ice. Spin down quickly. Add the following components in the same tube: 5x reaction buffer (containing all 5 L dNTPs except dCTP) Exonuclease-free Klenow enzyme 1 L [-32P]dCTP 5 L Flick the tube and quick spin. Incubate at 37°C for 20 minutes. Stop the reaction by adding 25 L 1xTE buffer into the tube, quick spin. Removal of unincorporated nucleotides is done by applying the 50 L of probe sample onto a Sephadex C-50 column. Purified sample is collected by placing an eppendorf tube under the column. Spin at 3500 rpm for 2 minutes. Dispose the radioactive column appropriately in a perspex waste box. Denature the probe by boiling for 5 minutes and chill on ice immediately before use. Hybridisation: Add denatured probe to prehybridisation solution in the bottle. Incubate overnight at 65°C (optimal hybridization temperature may need to be determined by individual experiment) Wash: Carefully dispose the radioactive hybridization solution into a liquid waste container that is placed in a perspex box. Wash membrane in the bottle with 0.1xSSC + 0.1%SDS (pre-warmed at 65°C), approximately 15-25 mL each time. Place the bottle back in the hybridization oven rotating for 10-15 minutes. Dispose the wash solution into the liquid radioactive waste container. Repeat washing procedure 3-4 times. Check radioactivity with Geiger-counter. Detection: Remove most of the excess wash solution by quick touch onto a 3MM paper. Wrap moist blot in plastic wrap, sealed well, before placing into a cassette. In the dark room: expose membrane to X-ray film with an intensifying screen. Store at -80°C for 1 to 6 days. Develop the film (see Using the AGFA CP1000 Film Processor SWP and Risk Assessment) List all resources required including plant, chemicals, personal protective clothing and equipment, etc Chemicals: Agarose Bromophenol Blue (Chemical hazard: Irritant) Ethidium bromide (Chemical hazard: Toxic) Hydrochloric acid (Chemical Hazard: Corrosive) Sodium hydroxide (Chemical Hazard: Corrosive) Sodium chloride Tris EDTA 20% SDS solution [-32P]dCTP (50 μCi at activity of 3000 Ci/mmol) (see ORU_NRMU_Radioactivity Safe Work Practice and Risk Assessment) Consumables: Microcentrifuge tubes Microcentrifuge (ORU_NRMU_ Centrifuge Risk Assessment) Whatmann 3MM filter paper ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 3 of 5 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007 Nitrocellulose membrane (Hybond N+) Paper towels Amersham Klenow kit (Amersham Biosciences) Amersham Sephadex G50 column (GE) Whatman 3M paper (Interpath Services) X-ray film (Level 2 Darkroom) Equipment: Pipettors (5–200uL) Gel electrophoresis tank UV transilluminator (see ORU_NRMU_UV Equipment - transilluminator Safe Work Practice and Risk Assessment) X-ray developer (see ORU_NRMU_ Using AGFA CP1000 Film Processor Safe Work Practice and Risk Assessment) Plastic tray In Radiation Lab (Wallace Wurth, level 4, Room 403): Hybridisation oven Hybridisation Bottles Water bath or heating block at 37 and 95 C Centrifuge Gilson pipettes Personal Protective Clothing and Equipment Laboratory coat/gown Gloves Safety goggles TLD badge Silicone oven mitt List potential hazards and risk controls including specific precautions required 1) Corrosive Chemicals (HCl and NaOH) Risk Controls: Wear full PPE (gloves, eye goggles, lab coat), work with only the minimum volumes and concentration required. 2) Toxic Chemicals (Ethidium bromide) Risk controls: Wear PPE (gloves, lab coat), handle in fume hood if involves aerosols, use minimum volumes. 3) Irritative Chemicals (Agarose, Tris, EDTA, 20% SDS, 20x SSC buffer, hybridization buffer) Risk Controls: Wear full PPE (gloves, eye goggles, lab coat), work with only the minimum volumes and concentration required. 4 Extreme temperature (burns risk) Hot bottles and solutions. Cassette stored at -80°C. Risk Controls: Wear PPE (gloves and lab coat) and handle object with extra materials, such as silicone oven mitt. 5) Radiochemicals (32P) Risk Controls: Wear full PPE (double gloves, eye goggles, lab coat), wear TLD badges at all times while working with radioisotopes and work behind protective Perspex screen. Stock radiochemical stored in locked dedicated radiochemical fridge in a room dedicated to radioisotope work, work to be performed in a UNSW accredited radioactive work area, keep exposure to stock concentrated radioisotopes to a minimum, all waste to be disposed of in SOMS radiochemical waste store. Constantly check for contamination with Geiger counter before, during and after work. List emergency shutdown instructions List clean up and waste disposal requirements ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 4 of 5 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007 All radioisotope waste of 32P to be disposed in appropriate Perspex container in the SOMS radiochemical waste store List legislation, standards and codes of practice used in the development of the SWP NSW OHS Act 2000 NSW OHS Regulation 2001 The NSW Radiation Control Act (1990) and Regulation (2003) Australia Dangerous Goods Code. AS/NZS 2243.2:2006. Safety in laboratories. Part 2: Chemical aspects Australian Standard AS2243.3-2002. Safety in laboratories. Part 3: Microbiological aspects and containment facilities. AS/NZS 2243.4:1998. Safety in laboratories. Part 4: Ionizing radiation AS/NZS 2243.7-1991. Safety in laboratories. Part 7: Electrical Aspects. AS/NZS 2161.1:2000 Occupational Protective Gloves – Selection, Use and Maintenance AS/NZS 1336:1997 Recommended Practices for Occupational Eye Protection MSDS for All chemicals involved Supervisory approval, training, and review Supervisor: Edna Hardeman Signature: Plant custodian: Signature List competency required – qualifications, certificates, licencing, training - eg course or instruction: Training as per Training Needs Analysis, Induction into the Lab, Training on the SWP ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________ Page 5 of 5 Safe Work Procedure Date Effective: 01/01/2007 Uncontrolled document when printed Current Version: 1.2, 15/08/2007