Branching Databases
advertisement

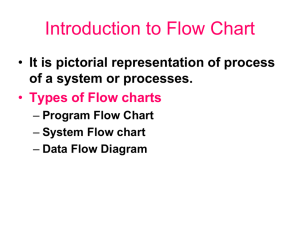
Unit: Branching Databases Year: 3 Strand: Data Handling Time: 4 - 6 hours National Curriculum Objectives – Pupils should be taught to: o Use logical reasoning to explain how a simple algorithm works and to detect errors in algorithms and programs. o Select and use a variety of software to accomplish given goals, including collecting, analysing, evaluating and presenting data and information. o Evaluate and apply information technology analytically to solve problems. You must: o Understand how branching databases can sort and identify different objects in a group. o Understand what a closed question is (e.g. 2 answers – yes/no, tall/short, etc.) o Generate appropriate closed questions to sort a group of objects. You should o Use a branching database system to create a branching database. o To understand the relationship between the answers to a closed question and a binary representation (e.g. yes/no or 1/0). o To use a branching database to solve problems. You could: o Identify and debug errors in a branching database. o Use a branching database program to create a branching database independently to solve a problem of their choosing. Key Questions: o What is a closed question? Give examples. o What is a branching database and how is it useful? o How does a branching database work? o What types of problems is a branching database useful for solving? o How does a binary system relate to a branching database? Links to more info/help videos: Resources/Programs Cleo – www.cleo.net.uk/resources/displayframe.p hp?src=841//files/Bird_Box/branchdb.html - free FlexiTree 3 ( www.flexible.co.uk/FlexiTree.html) - £216 for primary school site license.



![Branching Out: An Introduction to Family History [pptx , 2.3 MB]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005232376_1-8bb1ea3bff509441ce8b545117622545-300x300.png)