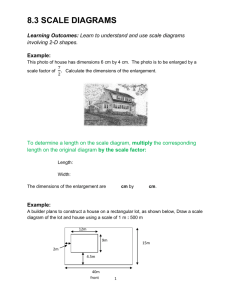
polb23705-sup-0001-suppinfo
advertisement

Supporting Information Light modulation and coupling and rugby-shaped resonators based on polymer fiber waveguide junctions Huaqing Yu*, Liangbin Xiong, Qingdong Zeng, Yaoming Ding School of Physics and Electronic-information Engineering, Hubei Engineering University, Xiaogan 432000, China *Address correspondence to yuhuaqing@126.com Sheng Wen, Feng Wang, Genwen Zheng College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Hubei Engineering University, Xiaogan 432000, China By changing the total power and power ratio of the input RGB lights, the color coordinates and CCT can be tuned. As an example, first, the RGB lights (total power of 52.5 μW) with a power ratio of 100 : 16 : 11 were launched into the PNFs 1, 2, and 3, respectively, a warm-white spot was observed at the crossed junction with a radius of 857 nm (inset of Figure S1a). The corresponding color coordinates is (0.45, 0.37), correlated color temperature (CCT) is 2487 K. And then the power ratio was changed to 50 : 9 : 8 (total power of 64.3 μW) and 100 : 18 : 21 (total power of 70.6 μW), white spots were formed at the junction with a radius of 893 and 871 nm, respectively. The corresponding color coordinates and CCT are (0.41, 0.36) and (0.38, 0.34), 3134 and 3771 K, respectively (inset of Figure S1b-c). Finally, when the power ratio was changed to 50 : 11 : 20 (total power of 82.8 μW), a cool-white spot was observed. The radius of the cool-white spot is 898 nm (inset of Figure S1d). Its color coordinate is (0.32, 0.30) and CCT is 6316 K. Figure S2a shows an optical microscope of incorporation rhodamine B (RhB) into a rugby-shaped polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, n = 1.48) microresonator (65.6 μm in length, 26.4 μm in equator diameter) supported by the crossed PTT fibers 1 (1.64 μm in diameter) and 2 (1.82 μm in equator diameter) excited by blue light with a power of 0.2 μW. As evident from the plot, a yellow rugby was observed at the crossed junction, suggesting the RhB molecular in resonator was efficiently excited. Figure S2b shows an optical microscope of incorporation CdSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots (QD) into a rugby-shaped poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA, n = 1.49) microresonator (6.9 μm in length, 5.4 μm in equator diameter) supported by the crossed PTT fibers 1 (864 nm in diameter) and 2 (731 nm in diameter) excited by blue light with a power of 0.1 μW. Similarly, a red rugby was observed at the crossed junction, confirming the QDs was efficiently excited. This demonstration indicates that the resonators based on the polymer fiber junctions can incorporate dyes or quantum dots into them, serving as active devices. Figure S1. ad. Optical microscope images of the mixed colors at the PNF junction. The inset shows a magnified (10) view of the white spot at the junction. The arrows show the propagation directions of the launched lights. Figure S2. Optical mciroscope images of rugby-shaped microresonators. (a) Incorporation RhB into a rugby-shaped PVP microresonator. (b) Incorporation CdSe/ZnS core/shell Dots into a rugby-shaped PMMA microresonator. The arrows show the propagation directions of the launched lights.