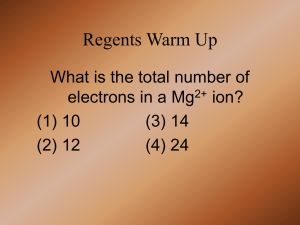Oxidation & Reduction
advertisement

Test Objectives: Redox define oxidation o know that oxidation is losing electrons define reduction o know that reduction is gaining electrons know the memory aid OILRIG and how to use it assign oxidation numbers to each element in a compound or a polyatomic ion o know the 8 rules for assigning oxidation numbers be able to identify if a reaction is a redox reaction o be able to determine; what is being oxidized what is being reduced what is the oxidizing agent what is the reducing agent be able to correctly write & balance equations for the oxidation half reaction and the reduction half reaction in a redox reaction o know that electrical charge & mass must be conserved o be able to recognize an improperly balanced half cell reaction be able to balance a redox equation by: o balancing electrons lost and electrons gained o balancing the atoms in the equation be able to identify single replacement reactions be able to use table J to predict whether a given reaction will or will not occur know that there are two types of electrochemical cells: Voltaic (or Galvanic) and electrolytic o voltaic cells are batteries/electrolytic cells are plating cells o know that NYS Regents only refers to voltaic cells as “electrochemical” cells know that voltaic cells are spontaneous and electrolytic cells are non-spontaneous o voltaic cells are exothermic; electrolytic cells are endothermic o voltaic cells produce electricity; electrolytic cells require an external source of electricity to work o be able to describe the differences between a voltaic cell & an electrolytic cell given two metals & using table J be able to draw and label all the components for a given voltaic cell including: o both half cells o salt bridge (including direction of positive ion flow) o wire (including direction of electron flow) o cathode, anode (including which electrode is positive & which electrode is negative) know which electrode increases in mass & which electrode decreases in mass know at which electrode oxidation occurs and at which electrode reduction occurs (use table J ) know that in a voltaic cell as the redox reaction occurs: o the cathode (+) loses mass while the cathode solution concentration increases o the anode (-) gains mass while the anode solution concentration decreases be able to explain the purpose of a salt bridge know that in an electrolytic cell electricity is used to force a non-spontaneous reaction to occur o know that there are two types: fused salt cell & an electroplating cell be able to draw and label all the components of an electrolytic cell: o the anode (+) & the cathode (-) o direction of electron flow o chemical components o be able to write the oxidation half reaction & the reduction half reaction o know that reduction still occurs at the cathode & oxidation still occurs at the anode know that the “polarity” of the anode & cathode in an electrolytic cell is opposite that of a voltaic cell know these differences between voltaic & electrolytic cells o voltaic: redox reaction is spontaneous & exothermic anode is negative , cathode is positive o electrolytic: redox reaction is non-spontaneous & endothermic anode is positive, cathode is negative know these similarities between voltaic & electrolytic cells o both use redox reactions o anode is site of oxidation o cathode is site of reduction o electrons flow through the wire from the anode to the cathode