Rheumatoid Arthritis
advertisement

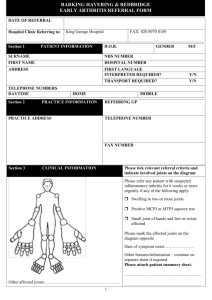
Rheumatoid Arthritis Presentation Sir, this patient has Rheumatoid arthritis affecting the hands as evidenced by Presence of symmetrical deforming polyarthropathy PIPJ/MCPJ Swan neck, Boutonniere’s, Z-thumb, ulna deviation Subluxation (MCPJ, dorsal subluxation of the ulna at the carpal joint) Active arthritis/quiescent Intrinsic muscle wasting CTS Dropped fingers from tendon rupture Synovial thickening Vasculitic lesions, nail-fold infarcts Palmar erythema No nail changes and skin lesions of Psoriasis SLE skin changes Elbows for Rh nodules Function Preserved vs impaired Coarse and fine functions Treatment Steroid – atrophied skin, bruisability Surgical intervention – CTS decompression, tendon release Requests Other joint involvement (MTPJ, knees) Extra articular features of RA Questions What are the extra-articular features of RA? Eye o Conjunctiva – Keratoconjunctivitis sicca, pallor o Sclera – episcleritis, scleritis, scleromalacia perforans o Lens – Cataracts from chronic steroid usage o Retina – vasculitis, drug induced (Gold, Hydroxychloroquine) o Extra-ocular muscles – mononeuritis multiplex, myasthenia sec to penicillamine Respiratory o Upper airways – Cricoarytenoid o Pleura – pleurisy, effusions o Airway – BOOP o Parenchyma – Pulmonary fibrosis, pneumonitis, PHT ( RA or MTX) o Caplan’s, Nodules Neurological o Peripheral neuropathy o Mononeuritis multiplex o Nerve entrapment o Cx atlanto-axial subluxation +/- Cx myelopathy o Muscle atrophy, proximal myopathy sec to steroids, penicillamine induced myasthenia Abdomen o Splenomegaly in Felty’s syndrome What are the causes of anaemia in RA? Fe deficiency – GI bleed from NSAIDS Megaloblastic anaemia – Pernicious anaemia Anaemia of Chronic disease Hypersplenism from Felty’s Syndrome Aplasia – Gold, Penicillamine What are the poor prognostic indicators? Insidious onset and high activity at onset Rh nodules or early erosions within 1 year Extra-articular features Persistent activity after 1 year – Active arthritis, ESR High levels of Rh factor and Anti CCP Ab (anti cyclic citrullinated peptide Ab) What are the criteria for Dx RA (American college of Rheumatology)? Any 4 of the following: Morning Stiffness for >1 hr duration for > 6 weeks Arthritis of 3 or more joints for > 6 weeks Arthritis of wrists, MTCP, PIPJ Symmetric Rh nodules Rh factor Radiographic changes typical changes including erosions or unequivocal decalcification How would you investigate this patient? Blood Ix – Rh factor, anti-CCP, ESR, CRP X-rays of the joints – erosions and periarticular osteopenia How would you manage this patient? Education and counselling Non-pharmacological o OT, PT Pharmacological which will depend on the severity o Analgesia – NASIDS o DMARDS Methotrexate (Check FBC and LFT) Sulphasalazine Hydroxychloroquine Low dose prednisolone Newer agents Leflunomide Tacrolimus Cyclosporine A Rapamune (sirolimus) o Immunomodulators (biologics) Anti TNF – Etarnacept (FDA approved), infliximab, humira Beware of TB and atypical pneumonia resulting from their use Anti CD20 – Rituximab Surgical What is Z thumb deformity? Deformity that occurs in RA hands With hyperextension of the first IPJ and fixed flexion and subluxation of the first MCPJ Resulting squaring appearance of the hands What is Boutonnière’s deformity? Hyperflexion of the PIPJ and hyperextension of the DIPJ Due to rupture of the central slip of the extensor tendon over the PIPJ with imbalance of the flexion and extension forces of the finger What is swan neck deformity of the fingers? Hyperextension of the PIPJ and hyperflexion of the DIPJ Due to synovitis of the flexor tendons leading to flexion at the MCPJ with constant effort to extend the finger; leading to stretching of the collateral ligaments and the volar plate of the PIPJ; intrinsic muscle balance leads to swan neck deformity What are the differential diagnoses for deforming polyarthropathy of the hands? Rheumatoid arthritis Psoriatic arthritis of the RA type Jaccoud’s arthropathy which is ulna deviation with subluxation of the 2nd to 5th fingers at the MCPJ which is voluntarily correctable; initially described in patient’s with Rh fever but now used synonymously with SLE deforming arthropathy