Chemistry Unit 14 Practice Test
advertisement
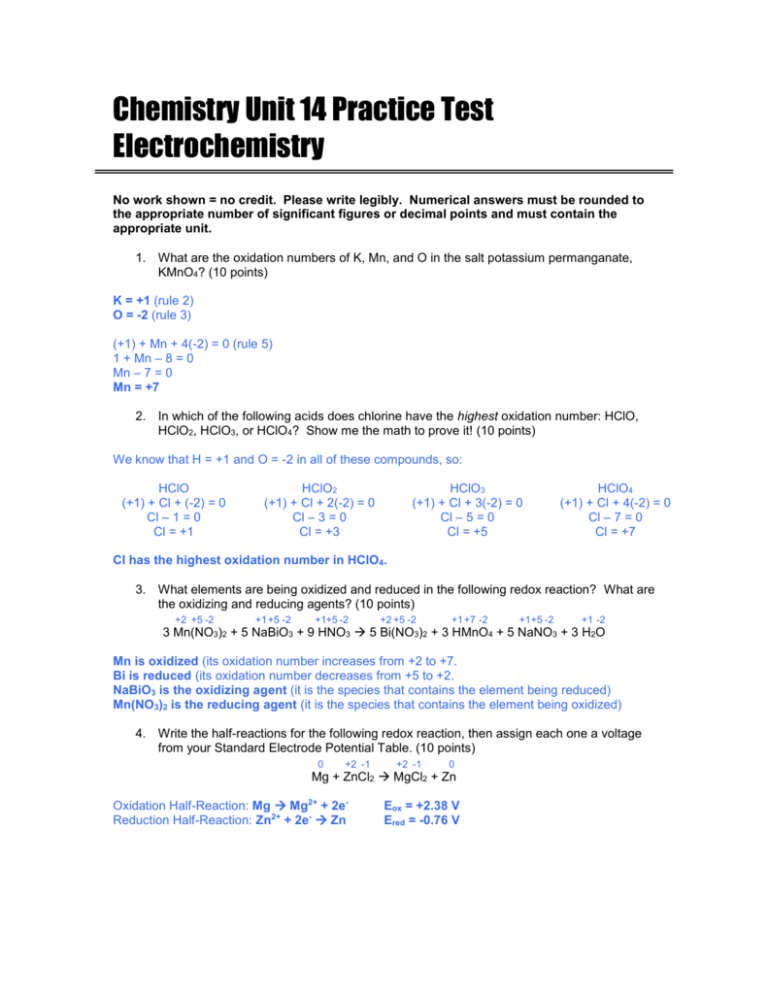
Chemistry Unit 14 Practice Test Electrochemistry No work shown = no credit. Please write legibly. Numerical answers must be rounded to the appropriate number of significant figures or decimal points and must contain the appropriate unit. 1. What are the oxidation numbers of K, Mn, and O in the salt potassium permanganate, KMnO4? (10 points) K = +1 (rule 2) O = -2 (rule 3) (+1) + Mn + 4(-2) = 0 (rule 5) 1 + Mn – 8 = 0 Mn – 7 = 0 Mn = +7 2. In which of the following acids does chlorine have the highest oxidation number: HClO, HClO2, HClO3, or HClO4? Show me the math to prove it! (10 points) We know that H = +1 and O = -2 in all of these compounds, so: HClO (+1) + Cl + (-2) = 0 Cl – 1 = 0 Cl = +1 HClO2 (+1) + Cl + 2(-2) = 0 Cl – 3 = 0 Cl = +3 HClO3 (+1) + Cl + 3(-2) = 0 Cl – 5 = 0 Cl = +5 HClO4 (+1) + Cl + 4(-2) = 0 Cl – 7 = 0 Cl = +7 Cl has the highest oxidation number in HClO4. 3. What elements are being oxidized and reduced in the following redox reaction? What are the oxidizing and reducing agents? (10 points) +2 +5 -2 +1 +5 -2 +1+5 -2 +2 +5 -2 +1 +7 -2 +1+5 -2 +1 -2 3 Mn(NO3)2 + 5 NaBiO3 + 9 HNO3 5 Bi(NO3)2 + 3 HMnO4 + 5 NaNO3 + 3 H2O Mn is oxidized (its oxidation number increases from +2 to +7. Bi is reduced (its oxidation number decreases from +5 to +2. NaBiO3 is the oxidizing agent (it is the species that contains the element being reduced) Mn(NO3)2 is the reducing agent (it is the species that contains the element being oxidized) 4. Write the half-reactions for the following redox reaction, then assign each one a voltage from your Standard Electrode Potential Table. (10 points) 0 +2 -1 +2 -1 0 Mg + ZnCl2 MgCl2 + Zn Oxidation Half-Reaction: Mg Mg2+ + 2eReduction Half-Reaction: Zn2+ + 2e- Zn Eox = +2.38 V Ered = -0.76 V 5. Calculate the standard cell potential for the redox reaction shown below, then determine if the reaction will or will not occur as written. (10 points) 0 +2 -1 +2 -1 0 Cl2 + MgF2 MgCl2 + F2 2 F- ions are oxidized to F2: -2.87 V Cl2 is reduced to 2 Cl- ions: +1.36 V Ecell = (-2.87 V) + (+1.36 V) = -1.51 V Because the potential is negative, we should not expect this reaction to occur as written. 6. Would you expect a piece of aluminum foil to react if placed in a solution of copper(II) chloride? Justify your response. (10 points) Yes. There are two ways to justify this: first, aluminum is more active than copper, meaning we should expect aluminum to displace copper from copper(II) chloride, forming aluminum chloride and copper. Second, we can calculate the electric cell potential for this reaction: Al + CuCl2 AlCl3 + Cu (unbalanced) The Ecell is +2.00 V, which indicates that there will be a chemical reaction. Either explanation is acceptable. 7. TRUE or FALSE: All single displacement reactions are also redox reactions. Justify your response. (You don’t get full credit for just saying “True” or “False”). (10 points) TRUE. All single displacement reactions involve a single element entering a compound while another element is removed. Because free elements have oxidation numbers of zero and elements in compounds have non-zero oxidation numbers, every single displacement reaction must involve a change of oxidation numbers. 8. Which electrode in an electrochemical cell tends to get heavier as the cell operates: the anode or the cathode? Explain why. (10 points) The cathode gets heavier as the cell operates. Reduction is occurring at the cathode. Ions from solution are being reduced onto the cathode, making it heavier. (The anode’s mass decreases as its atoms are oxidized into ions.) V 9. What is the cell potential of the electrochemical cell shown at right (assume that all conditions are standard)? (10 points) Al is more active and is being oxidized: +1.66 V Ni is less active so Ni2+ is being reduced: -0.23 V Ecell = (+1.66 V) + (-0.23 V) = +1.43 V Ni 10. Which of the following substances is the strongest reducing agent: Na, Mg, Al, or Zn? Justify your answer. (10 points) Ni2+ Al Al3+ The strongest reducing agent would be the metal that is most easily oxidized, or which has the most positive oxidation potential. The oxidation potentials for these metals are: Na: +2.71 V Mg: +2.38 V Al: +1.66 V Zn: +0.76 V Since sodium has the most positive oxidation potential, sodium is the strongest reducing agent.